Supply & Demand
advertisement

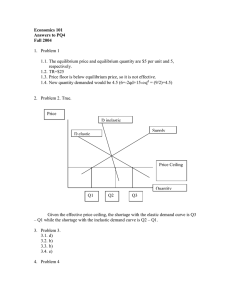
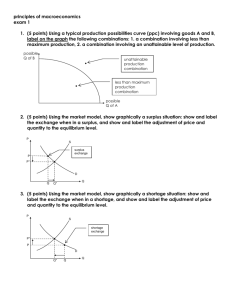
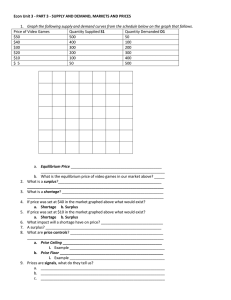
Unit 2 Notes Voluntary Exchange A market is created wherever a buyer and seller meet Both buyer and seller decide they are better off after the transaction free to choose every time you buy something you are telling the store you are okay with the price – dollar vote & consumer sovereignty Demand willingness and ability of consumers to purchase a good or service; about buying Law of Demand as price rises, quantity demand decreases P QD as price falls, quantity demand increases P QD INVERSE relationship quantity demanded: number you buy at a particular price (1 product) Demand Curve Why the law of demand is true Real income effect: as prices change your ability to buy will change; for example if the price of gas increases you cannot buy as much with the same amount of money Substitution effect: if there is a cheap alternative people buy that instead Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility: the more you have of something the less you are willing to pay for each additional one; things get old a. utility means satisfaction b. marginal means additional or extra Determinants of Demand: cause change in what we demand Population Change Income Change Taste or preference change Substitute goods: something can replace another Complementary goods: items that go together PRICE IS NEVER THE REASON!!! Types of Products in relation to Income Normal Good: the more money you make the more you buy of these; Ex: clothes Inferior Goods: the more money you make the less of these you buy; Ex: Raman noodles Neutral Goods: buy the same amount; Ex: toilet paper Elasticity of Demand Elastic Goods Inelastic Goods price change has a large effect on the little change in amount bought for any kind of number bought; wants, items with many substitutes, in long term; price change necessities, items with no substitutes, in short term; Ex: soda, new shoes, IPOD Ex: electricity, insulin Elasticity of Demand 2 Types: Elastic Follow law of demand – P Revenue & Inelastic Breaks the law of demand - P Revenue Supply Willingness & ability of producers to make and sell a product About selling Law of Supply P QS P QS DIRECT relationship Stores want profit Supply Curve Price Quantity Determinants of Supply # of businesses Taxes and subsidies = $ taken & given by gov’t Technology Price of inputs and resources PRICE IS NEVER THE REASON!!! Equilibrium Where QD = QS Perfect point of profit and efficiency Hard to reach Prices move to force markets to equilibrium Disequilibrium: Surplus: too much; QD < QS; P Shortage: run out; QD > QS; P Equilibrium P D surplus EP S E shortage EQ Q Gov’t Price Controls Price Floors Price Ceilings Lowest price that can be Highest price that can be charged for item Cause surplus b/c ppl cannot reach equilibrium; P to high Bad idea/Just say no Ex: minimum wage charged for item Cause shortage b/c ppl cannot reach equilibrium; P to low Bad idea/Just say no Ex: rent control in NYC Rationing Device Determines who gets the goods in a FES Ex: Price, 1st Come, 1st Serve Price considered most fair The prices are determined by the interaction of supply and demand