Early River Civilizations Unit 1: AP World History
advertisement

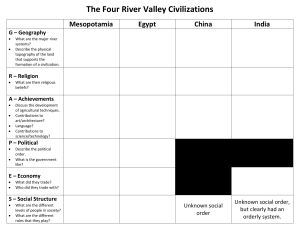
Early River Civilizations Unit 1: AP World History Agenda for Today 1. Bell Ringer: What defines a “Civilization”? 2. Lecture: Early River Civilizations 3. Indus River Crash Course. 4. Document Analysis: Hammurabi’s Code 1. Discussion of “An Eye for an Eye 5. Writing a Thesis Statement for AP 6. Comparison of Early River Civ’s 7. Bias in literature, The Lemon Tree 1. Discussion of the home in Al-Ramla. 8. HW: Jared Diamond reading The Emergence of Civilization As communities become permanent, protection and structure is needed. Civilizations develop with the onset of several basic factors. Defining a Civilization An Urban focus Political and Military Structures Social Structures built on economic power Material culture Distinct Religious Structure Development of Writing New Artistic and Intellectual Activity Causes of Civilization Several Theories exist. 1. Uniting under a common religious practice led to the formation of civilizations. 2. Specialization of labor, and more wealth allowed for government structures. 3. They had to adapt, and this meant creating a stable environment for survival. Mesopotamia The basis of Sumer were city-states. Religion was polytheistic, and the gods looked over the cities. Ziggurats constructed for worship. Origins of government may be found in religion. (Theocracy) Government and Social Life Kings were regarded as near-gods. Often lived in elaborate homes, just like Priests. Trade common with India and Eastern Med. Class System Sargon and the Akkadians. Cuneiform Egypt Extremely similar to Mesopotamia. Divided into three kingdoms, all under a dynastic rule. Pharoahs regarded as near-gods. Upper classes were merchants, artisans. Burial Methods: Mummification Pyramids The New Kingdom This is the final stable era in Ancient Egypt. The Hyksos were driven out (introduced the chariot) Akhenaten would attempt to make Egypt monotheistic, only worshipping the sun god. King Tut helps return tradition to Egypt. Persian Empire Led by Cyrus, very expansive empire. Took most of Asia and the Middle East. Set up as satrapies. Individual provinces. Major Religion Zoroastrianism Struggle between good and evil, use of a final judgement. Crash Course Studying the video on the Indus River Valley, answer the following question: How does this qualify as a Civilization? Does it meet all of the factors? Explain your reasoning. Jared Diamond Reading This reading draws connections to the formation of Civilizations and borders. On Monday, you will have to explain in a paragraph: How does a government system form? How are people kept in line? What is the purpose of a centralized authority?