First Five Presidents Review Sheet (1789-1825)
advertisement

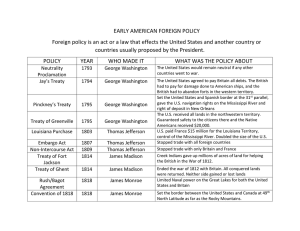
The First Five Presidents 1789—1825 Review Sheet Adams-Onis Treaty – (1819) An agreement in which Spain gave over control of the territory of Florida to the United States (p. 221 in text) Alien and Sedition Acts – (1798) The President could imprison or deport aliens (citizens of other countries). People who wrote anything of “a scandalous and malicious nature” against the government could be imprisoned. It was used to silence critics of the Federalist party (p. 195 in text) American System – a pre-Civil War set of measures designed to unify the nation and strengthen its economy by means of protective tariffs, a national back, and such internal improvements as the development of a transportation system (p. 216 in text) Bank of the US – Either of the two national banks, funded by the federal government and private investors, established by Congress, the first in 1791 and the second in 1816 (pp. 185, 232 in text) Battle of New Orleans – The final major battle of the War of 1812; the Americans were victorious, but, unbeknownst to Andrew Jackson and the Americans, the Treaty of Ghent had already been signed so, technically, neither side won the war; Jackson still emerged a hero Battle of Tippecanoe – Angry with General William Henry Harrison for persuading Native American chiefs to sign away their land, Tecumseh’s brother led a Shawnee attack against General William Henry Harrison and his men. Harrison was victorious, but suffered heavy losses. It was discovered that the Native American confederacy was using weapons supplied by the British in Canada, leading the “war hawks” to pressure Congress to enter war with Britain, eventually contributing to the War of 1812 (p. 203) Burning of Washington – (1814) During the War of 1812, in response to the Americans burning York, the capitol of Upper Canada, the British burned the Capitol, the White House, and other public buildings in Washington “Era of Good Feelings” – James Monroe was elected president and the people were pleased with the development of the country Election of 1800 – Adams and the Federalists against Jefferson and the Democratic-Republicans; Jefferson won. The election of 1800 was the first American presidential election in which power was peacefully transferred from one party to another. Embargo Act of 1807 – Britain and France were impressing soldiers; Jefferson passed the Embargo Act which barred trade with any foreign port; New England threatened to secede from the US; Put sailors out of work and hurt the US economy; Failed because Britain and France found other sources Eli Whitney – inventory; demonstrated the first musket made of interchangeable parts, parts that are exactly alike; this led to better tools which sped up the manufacture of goods and improved reliability (p. 212 in text) First Cabinet – The group or department heads who serve as the president’s chief advisers. For the first cabinet, Washington chose Thomas Jefferson as secretary of state, Alexander Hamilton as secretary of the treasury, Henry Knox as secretary of war, and Edmund Randolph as attorney general. George Washington – The first president of the U.S. Washington appointed the first cabinet. George Washington’s Horse – Washington was a skilled horse rider and his favorite horse, Nelson – whom Washington rode during many significant battles, became a famous icon for many years Hartford Convention – Federalist party met in Hartford, Connecticut to discuss grievances with the War of 1812 and concerns of the federal government’s increasing power Henry Clay – House speaker who promoted the American System (p. 216) Impressment – the forcible seizure of men for military service (p. 202). The British impressment of Americans at sea was one cause of the War of 1812. James Madison – (1809-1817) Passed the Non-Intercourse Act; President when the War of 1812 begins; Burning of Washington Capitol by the British; Treaty of Ghent ends War of 1812; 1816-Charter begins the Second Bank of the United States James Monroe – (1817-1825) President during the “Era of Good Feelings”; Adams-Onis Treaty acquires Spanish territory south of the nation for debt nullification; Monroe Doctrine states that European nations no longer had jurisdiction in colonization, interference with settlements in the Western Hemisphere John Adams – Federalist; 2nd president of the U.S.; president during the XYZ Affair. Judicial Review – Supreme Court’s power to declare an act of Congress unconstitutional (p. 199 in text) Judiciary Act of 1789 – created the Supreme Court and other Federal courts; provided for the appeal of certain state court decisions to the federal courts (p. 183) Kentucky and Virginia Resolves – Virginia and Kentucky declare the Alien and Sedition Acts “null” because they violated the Bill of Rights. Asserted the principle of nullification. Lewis & Clark – Commissioned by President Jefferson to explore the Louisiana Purchase and look for a water route to the Pacific; (1804) travelled from St. Louis, Missouri to the Pacific Ocean (p. 197 in text) Louisiana Purchase – (1803) United States purchased France’s Louisiana Territory – from the Mississippi River to the Rocky Mountains – for $15 million (p. 201) Marbury v. Madison – (1803) a case in which the Supreme Court ruled that it had the power to abolish legislative acts by declaring them unconstitutional; this power became known as judicial review (p. 199) Missouri Compromise – a series of agreements passed by Congress in 1820-1821 to maintain the balance of power between slave states and free states (p.222 in text) Monroe Doctrine – (1823) a policy of U.S. opposition to any European interference in the affairs of the Western Hemisphere, announced by President Monroe (p. 221 in text) Nationalism – belief that national interests should be placed ahead of regional concerns or the interests of other countries (p. 220 in text) Neutrality Act of 1793 – said that the United States would not get involved in a war between the French and the British Non-Intercourse Act – (1809) Lifted all embargoes on American shipping except with Britain and France; this act contributed to the War of 1812 Nullification Crisis – South Carolina declared that federal tariffs of 1828 and 1832 were null and void due to being unconstitutional Sacagawea – a young American Indian woman, served as a guide and translator for the Lewis and Clark expedition Tariff of 1816 – a protective tariff designed to aid American industries (p. 218 in text) Tecumseh – Native American Shawnee chief; believed that Native Americans should unite and form a confederacy in order to protect their homeland against intruding white settlers (p. 203) Thomas Jefferson – Democratic-Republican; writer of the Declaration of Independence; served as secretary of state from 1790-1793; 3rd president of the U.S. Treaty of Ghent – (1814) Treaty that ended the War of 1812 when the war failed to produce a victory for either side (p. 205 in text) War Hawks – members of Congress who favored war with Britain in the early years of the 19 th century (p. 203 in text) War of 1812 – Both France and Britain “impressed” American sailors; “War Hawks” pressured US Congress to enter war with Britain; Westerners thought the British were supplying weapons to Native Americans; War ended with Treaty of Ghent in 1814 when both sides failed to produce a victory Washington’s Farewell Address – Washington’s final advice to the United States was that the US should be neutral, remain united, avoid permanent alliances, and not have political parties. Whiskey Rebellion – Farmers in western Pennsylvania refused to pay the federal excise tax on whiskey and attacked tax collectors. Washington made 15,000 militia men into federal troops and put down the rebellion. As a result, the Federal government showed its new power XYZ Affair – (1797) During John Adams’ presidency; incident in which French officials insulted U.S. by demanding a bribe from U.S. diplomats; Adams was eventually able to negotiate and demand that the US be treated with respect Three achievements for each of the first five presidents: Washington – 1. Appointed First Cabinet 2. Whiskey Rebellion 3. Created the First National Bank Adams – 1. Alien and Sedition Acts 2. XYZ Affair 3. Virginia and Kentucky Resolves Jefferson – 1. Louisiana Purchase; Lewis and Clark 2. Election of 1800 3. Embargo Act Madison – 1. Passed the Non-Intercourse Act 2. War of 1812 3. Burning of Washington Capitol Monroe – 1. “Era of Good Feelings” 2. Adams-Onis Treaty 3. Monroe Doctrine *There are more achievements for each president, there are just a few for each.