Jeffersonian Era: Jefferson, War of 1812, Era of Good Feelings
advertisement

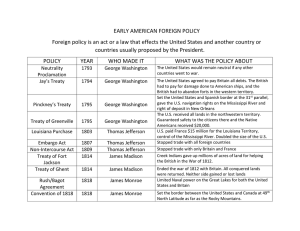
Chapter 8 A New President March 4, 1801 “pomp and circumstance” Race mixing Accusations Educated small farmers Jeffersonianism Jefferson’s Revolution Dealing with Hamilton’s economic plan The Alien and Sedition Acts Reducing Taxes and the national debt Fighting the Judicial System The Judiciary Act of 1801 Federalist Judges Marbury V Madison John Marshall Judicial Review Expansion Napoleon Bonaparte The Louisiana Territory James Monroe and Robert Livingston Napoleon’s offer The “backbone of the nation” The Election of 1804 Thomas Jefferson Aaron Burr George Clinton Charles Pinckney Reasons for Republican Victory Exploring New Land Lewis and Clark The Louisiana Purchase Results A Second Term The Napoleonic Wars Aaron Burr Quids John Randolph The Yazoo Land Scandal Economic woes Seizing US ships Impressment HMS Leonard USS Chesapeake Jefferson’s Reaction Economic Woes The Embargo Act of 1807 Impact of the Embargo James Madison The Non Intercourse Act War Hawks Foreign policy Canada The role of Native Americans Tecumseh and the Prophet William Henry Harrison Tippecanoe The War of 1812 Madison goes to War June 1, 1812 Reasons for declaring war on Britain The War of 1812 Americans try to take Canada Detroit Oliver Perry William Henry Harrison The Battle of the Thames The War of 1812 The British Offensive Burning Washington Baltimore The British break off the campaign The War of 1812 The Treaty of Ghent December 1814 The Battle of New Orleans Andrew Jackson The Era of Good Feelings The Hartford Convention James Monroe The Federalist Party The Era of Good Feelings The Supreme Court John Marshall Dartmouth College V Woodward McCulloch V Maryland Interpretations Slavery National Harmony Missouri Balancing the Senate The Missouri Compromise (1819-1820) Results of the compromise Monroe’s Foreign Policy Rush-Bagot Treaty British American Convention Florida The Adams-Onis Treaty The role of Andrew Jackson Monroe’s Foreign Policy 1823 The Monroe Doctrine European Affairs The Western Hemisphere “unfriendly acts”