Document 17602656
advertisement

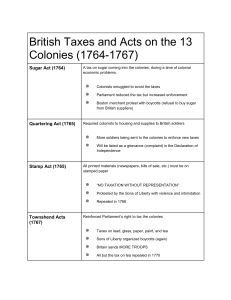
Study Guide for: Revolutionary War Study Guide Part 1 Assessment Date:_______ The colonists went to war with Great Britain because the colonists disagreed with the British Parliament on how the colonies should be governed. See the table below for the key differences in what the colonists believed versus what the British Parliament. What Colonists Believed That local assemblies had legal authority. What British Parliament Believed They had legal authority in the colonies. That they should not be taxed since they had not representation in Parliament. They had the right to tax the colonies. Declaration of Independence: A document written by Thomas Jefferson. It states that authority to govern belongs to the people rather than to kings, and that all people are created equal and have rights to life, liberty and pursuit of happiness. A divided Virginia: Some Virginians were neutral to the war (meaning that they did not choose a side). There were also some Virginians who remained loyal to Great Britain. They were called loyalists. However, most Virginians considered themselves to be Patriots. Independence: Freedom from control by another person or country. Protest: To stand up for what you believe is unfair or wrong. Patrick Henry: Inspired patriots from other colonies when he spoke out against taxation without representation by saying, “…give me liberty or give me death.” Taxation without Representation: When a government is taxing people but the people are not given a ‘say’ or ‘voice’ over how they are governed, nor are their interests being considered. If people do not have representation, they cannot vote on laws or elect their leaders. Sugar, Stamp, and Tea Acts: These acts were taxes that were forced on the colonists so that George III could pay off debts that England owed from fighting expensive wars. Boycott: Refusing to buy something Virginia Patriots: Served in the Continental Army and fought for independence leading to the British surrender at Yorktown. Great Britain in the 1700s: Included England, Scotland and Whales. The king was George III. Examples of local assemblies in the colonies: Burgesses, Virginia Assembly Thomas Jefferson: Provided political leadership by expressing the reasons for colonial independence from Great Britain in the Declaration of Independence. Sons of Liberty: A group of colonists who began to express their ganger at the new taxes by having secret meetings, refusing to buy British goods and protesting. Boston Tea Party: An angry group of Bostonian protesters led by Samuel Adams. They dressed as Mohawk Indians. They boarded a ship that was docked in the harbor and threw crates of tea into the water. This was an act of protest against the tea act.