WWI & Great Depression Timeline: League of Nations & Global Impact
advertisement
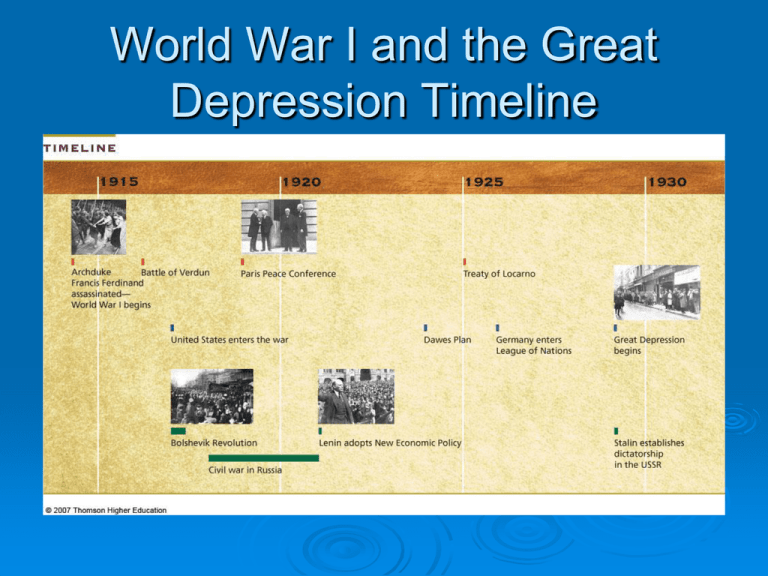
World War I and the Great Depression Timeline League of Nations What did it do? Established the mandate system Mandates – former colonies/territories of defeated Central Powers administered by mainly France and Great Britain. Iraq, Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria are examples of mandate territories Mandate System League of Nations Why did it fail? United States did not become a member – US wants to “isolate” itself from Europe (isolationism) L of N did not have the power to enforce its decisions Wanted United States isolation from the rest of the world. Dominant world economy after WWI Led to economic “boom” = immense prosperity. People borrowed money on credit for goods and stocks. Great Britain Horrors of war deeply impacted British society and economy. Lost factory jobs to USA and Japan Labour Party (worker’s party) won general elections in the 1920’s. France Devastated by WWI Economic hardship High unemployment, gov’t nearly bankrupt Political chaos No party could get a majority Horrors of War 50% of men ages 18-32 killed in war Italy Resented Treaty of Versailles Did not give enough rewards to Italy High unemployment and inflation Political and economic chaos led to the election of Mussolini and his Fascist government in 1924. Between the Wars: Global Depression & Dictatorships Fasces Benito Mussolini Germany Anger and Resentment over the Treaty of Versailles. Weimar Republic - democratic gov’t elected in 1919. Reparations caused economic hardships in Germany Loans from the US led to a period of relative prosperity in the 1920’s. But…Political unrest still occurs… Rise of Adolf Hitler Between the Wars: Global Depression & Dictatorships Adolf Hitler Hitler - Parade Russia Lenin’s NEW ECONOMIC POLICY Changes name – now U.S.S.R Lenin Dies » Stalin in power 1st FIVE YEAR PLAN Industrialization Collectivization Japan After WWI – felt West did not treat it as an equal. Industrialization – need for raw materials Wanted more control in China Increasingly nationalistic and militaristic The Stock Market Crash Causes Overproduction in USA – prices go down sharply Excessive dependence on credit to buy goods and stocks – people cannot pay debts High protective tariffs stifle world trade The Stock Market Crash OCTOBER 1929 Banks call in loans People unable to pay off their credit bills Stock prices tumble Businesses start to fail, laying off workers RESULTS IN… Run on the Bank The GREAT DEPRESSION WORLDWIDE effects Production of goods cut around the world Prices, Salaries, and Wages fell (Deflation) Many workers lost their jobs 13 million in the USA alone Franklin United States D. Roosevelt elected Pres. in 1932 NEW DEAL –Fed gov’t would spend money, put workers back to work. Regulated banks, stock market Social security and unemployment insurance France Fascists and Communists constantly battled for influence among workers 1934 – Socialist-led gov’t comes to power Passed many laws that benefited workers and farmers Germany 1929 – Hitler appeals to German workers - He can bring back economic prosperity/German national pride (nationalism). 1930’s – NAZI’s win big in elections 1933 – Hitler is appointed “Chancellor” or leader of the German gov’t Russia Results of the FIVE YEAR PLAN Rapid Industrialization Workers work for little, no pay Food is scarce Famine 1930’s - Great Purge – Stalin tries to “eliminate” his “enemies” Japan Japan dependent on US market – Great Depression in USA carried to Japan Millions unemployed, starving Military leaders promised stable leadership and national pride (nationalism) Eyed imperial expansion in Asia











