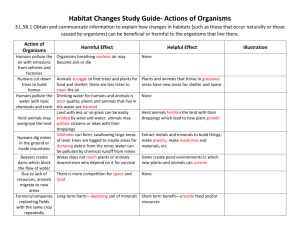
Keystone species: A species whose presence and role within an
advertisement

Clear-cutting: Method of timber harvesting in which all trees in a forested area are removed in a single cutting leaving bare soil exposed. Deforestation: Removal of trees from a forested area without adequate replanting. Endangered species: A wild species with so few individual survivors that the species could soon become extinct in all or most of its natural regions. Erosion: Process of group of processes by which loose or consolidated earth materials are dissolved, loosened, or worn away and removed from one place and deposited in another. Extinction: Complete disappearance of a species from the earth. This happens when a species cannot adapt and successfully reproduce under new environmental conditions or when it evolves into one or more new species. Greenhouse Gases: Gases in the earth’s lower atmosphere (troposphere) that cause the greenhouse effect. Examples are carbon dioxide, chlorofluorocarbons, ozone, methane, water vapor, and nitrous oxide. Habitat: Place or type of place where an organism or population of organisms lives. Keystone species: A species whose presence and role within an ecosystem has a disproportionate effect on other organisms within the system. A keystone species is often a dominant predator whose removal allows a prey population to explode and often decreases overall diversity. Other kinds of keystone species are those, such as coral or beavers that significantly alter the habitat around them and thus affect large numbers of other organisms. Logging: the process, work, or business of cutting down trees and transporting the logs to sawmills. Monoculture: cultivation of a single crop, usually on a large area of land. Pest: Unwanted organism that directly or indirectly interferes with human activities. Plantation agriculture: Growing specialized crops such as bananas, coffee, and cacao in tropical developing countries, primarily for sale to developed countries. Population: Group of individual organisms of the same species living in a particular area. Rainforest: a tropical forest, usually of tall, densely growing, broad-leaved evergreen trees in an area of high annual rainfall. Rainforest Canopy: the cover formed by the leafy upper branches of the trees in a forest. Renewable Resource: Resource that can be replenished rapidly (hours to several decades) through natural processes. Examples are treed in forests, grasses in grasslands, wild animals, fresh surface water in lakes and streams, most groundwater, fresh air, and fertile soil. If such a resource is used faster than it is replenished, it can be depleted and converted to a nonrenewable resource. Tolerance: Minimum and maximum limits for physical conditions (such as temperature) and concentrations of chemical substances beyond which no members of a population can survive.