Encoding
advertisement

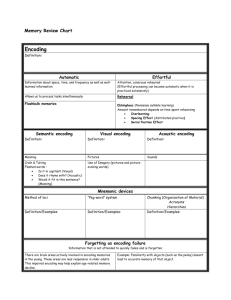
Memory Encoding The persistence of learning over time through the storage and retrieval of information The process of putting information into the memory system Storage The retention of encoded info over time. Can either be sensory, short term or long term Retrieval The process of getting info out of the memory system Sensory Memory The immediate and very brief recording of sensory information Short Term Memory Activated memory that holds a few ideas briefly.7=+/- 2 Long Term Memory The relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system Automatic Processing Unconscious encoding of incidental info, such as time and space. Effortful Processing Encoding that requires attention and conscious effort Rehearsal The conscious repetition of info. Can either be maintenance or rehearsal Spacing Effect The tendency for distributed study or practice to yield better long term retention than is achieved through massed study Serial Position Effect Visual Encoding Our tendency to recall best the last and first items in a list The encoding of picture images Acoustic Encoding The encoding of sound, especially the sound of words Semantic encoding The encoding of meaning , including the meaning of words Imagery Mental pictures Mnemonics Memory aids. Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally Chunking Organizing items into familiar, manageable units Iconic Memory A momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli Echoic Memory A momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli Long Term Potentiation Flashbulb Memory Amnesia Implicit Memory An increase in a synapse’s firing potential after brief , rapid stimulation. Neural basis for learning and memory. A clear memory of an emotionally significant event The loss of memory Skill memory. Occurs automatically Also called procedural memory Explicit Memory Hippocampus Memory of facts. Also called declarative memory Located in the limbic system. Helps process explicit memories. Recall Example- fill in the blank tests. Recognition Example- multiple choice tests. Priming Mood Congruent Memory The activation, often unconsciously, of a particular association in memory The tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one’s current good or bad mood Proactive Interference The disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of new info Retroactive Interference The disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old info Misinformation Effect Source Amnesia Karl Lashley Incorporating misleading info into one’s memory of an event Right info, but wrong source Did the experiment that showed that learning/memory is not localized to one part of the brain , instead all parts of the brain work together State Dependent Memory Transience Blocking Misattribution Absent Mindedness Repression Cerebellum Info is most easily recalled when in the same “state” of consciousness it was learned in. When unused info just fades away if your don’t use it. One of the 7 sins When info has been encoded, but you can’t retrieve it. One of the 7 sins Confusing the source of the info. One of the 7 sins Inattention to details produces encoding failures. One of the 7 Sins Freud’s idea that anxiety arousing thoughts can be banished from consciousness Where classical conditioning /associative memories are storied Cognition The mental activities associates with thinking, knowing, remembering and communicating. Concept A mental grouping or similar objects, events or people Prototype A mental image or best example Algorithm A methodical, logical procedure that guarantees that you will solve a problem Heuristic A simple, common sense, thinking strategy that allows us to make judgments. It can lead to errors Insight Confirmation Bias A sudden and often novel realization of the solution to a problem A tendency to search for info that supports our preconceptions and to ignore contradictory evidence Fixation The inability to see a problem from a new perspective Mental Set A tendency to approach a problem in one particular way Functional Fixedness The tendency to think of things only in terms of their usual function Representativeness Heuristic Judging the likelihood of things in terms of how well they seem to represent or match our prototype Availability Heuristic Over confidence Belief Perseverance Estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in our memory system. The tendency to be more confident than correct. Clinging to one’s initial conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited Framing The way an issue is posed can dramatically affect decisions and judgments Phoneme In language, the smallest distinctive sound unit Morpheme In language, the smallest unit that carries meaning Grammar The system of rules in language Semantics The study of the meaning Syntax Babbling Stage The rules for combining words into grammatically sensible sentences Starts at 4 months- infant will spontaneously utter various sounds at first unrelated to the household language One- word stage Age 1 to 2- language development Two- word stage Starts at age 2- language development Telegraphic Speech ”go car”, “ cat bad” Linguistic Determinism Whorf’s hypothesis that language determines the way we think Language Acquisition Device LAD Theory proposed by Chomsky, humans are born with innate abilities to acquire language.