Chapter 15.2: West African Empires and Civilizations

Chapter 15.2: West African Empires and
Civilizations
I.
Ghana: Land of Gold
Trans-Saharan trade was firmly established by
AD 200, but infrequent due to harsh desert conditions
3 rd century AD, Berber nomads began using camels
Camels could travel upwards of 60 miles a day…up to 10 days without water…trade increased
Soninke Peoples…called their ruler Ghana, war chief…Muslim traders used word Ghana to refer to the Soninke region
Ghana was rich from taxing the goods that traders carried through their territory
A.
Gold-Salt Trade
Two most important trade items were gold and salt
Gold from forest region south of Niger and
Senegal rivers…both mined and alluvial o Until 1350, about 2/3 of world’s supply of gold came from West Africa o King of Ghana passed a law that all gold nuggets went to him…amassing great wealth
Arab and Berber traders crossed the desert with camel caravans loaded down with salt, cloth, weapons, and manufactured goods from
Mediterranean ports
Merchants met in trading cities, overseen by king’s tax collector
B.
Empire of Ghana
King stored gold nuggets and slabs of salt in his royal palace
Only the king had the right to own gold nuggets
Ghana’s African ruler was also a religious leader, a chief judge, and a military commander
Headed a large bureaucracy and could call up a huge army
1067- Muslim geographer and scholar al-Bakri observed the opulence of Ghana’s royal court
By 800, Ghana had become an empire
Chief demanded tribute from surrounded areas
C.
Islamic Influences
Islam spread through North Africa by conquest, south of the Sahara, Islam spread through trade o Muslim merchants and teachers settled in the states south of the Sahara and introduced their faith there
Eventually, Ghana’s rulers converted to Islam o By 11 th century- Muslim advisors were helping Ghana run his kingdom
Ghana’s African rulers and many members of court accepted Islam, many people clung to their animistic beliefs and practices…much of population never converted…those who did
usually practiced syncretism (blending of old and new ideas)
Among the upper class, Islam’s growth encouraged the spread of literacy
To study Qu’ran, converts to Islam had to learn to read and write Arabic
1076 Muslim Almoravids of North Africa conquered Ghana…jihadist movement to purify
Islam…Almoravids eventually withdrew, but
Ghana never recovered its power
II.
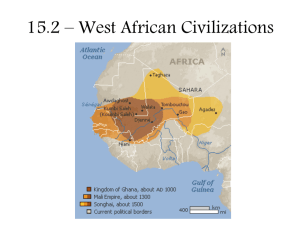
Empire of Mali
Kingdom of Mali emerged by 1235
Founders were Mande-speaking peoples from south of Ghana
Mali’s wealth was built on gold
Miners found new gold deposits further east, power shifted to Mali
A.
Sundiata Conquers an Empire
Founder of Mali= Sundiata
Crushed a cruel, unpopular leader
Became Mali’s, mansa, “emperor”
Famous epic of Sundiata, preserved by griots, recorded as Sundiata: The Lion Prince of Mali
Sundiata conquered kingdom of Ghana and trading cities of Kumbi and Walata…period of peace and prosperity followed
Sundiata set up a bureaucracy with capable administrators in charge of Mali’s finances, defense, and foreign affairs
New capital at Niani…promoted agriculture and re-established the gold-salt trade…important center of commerce and trade
Mali means “where the king lives”
B.
Mansa Musa Expands Mali
Sundiata died in 1255
Conversion of subsequent rulers to Islam, influenced by Arab traders
Most famous was Mansa Musa o Skilled military leader o Royal control over the gold-salt trade
o 100,000 man army- kept order and protected Mali from attack o Empire extended to twice the size of Ghana o Divided into provinces and appointed governors
Mansa Musa- devout Muslim- went on a hajj in
1324-1325 o Gave away so much gold he devalued its worth in Egypt for 12 years, also gained attention in Europe…featured on maps o Mansa Musa order the building of mosques at the trading cities of Timbuktu and Gao
Timbuktu was one of the most important cities of the empire o Attracted Muslim judges, doctors, religious leaders, and scholars from far and wide to mosques and universities
C.
Travels of Ibn Battuta
1352- Ibn Battuta, native of Tangier in North
Africa, traveled to Mali
Ibn Battuta traveled for 27 years through much of the Dar-al-Islam
Ibn Battuta visited Timbuktu and was impressed at the safety of the roads
Devout Muslim- Ibn Battuta praised the study of the Qur’an in Mali, but criticized them for not strictly practicing Islam’s moral code…also shocked that women were more visible in Mali
Mali declined around 1383 o Gold trade shifted eastward again o Subsequent leaders not as effective
III.
Empire of Songhai
Songhai broke away from Mali in the 1400’s
Built up an army, extended their territory to the large bend in the Niger River near Gao and gained control of the trade routes
Capital of Songhai Empire was Gao
A.
Sunni Ali, a Conquering Hero
Sunni Ali: build a vast empire by military conquest
o 1464 to about 1494
Sunni Ali built a professional army o Riverboat fleet of war canoes o Mobile fighting force on horseback
1468: Sunni Ali captured city of Timbuktu
Besieged city of Djenne for 7 years, fell in 1472, married its queen
B.
Askia Muhammad Governs Well
Sunni Ali died in 1492, his son took over, but was not a devout Muslim
Revolt led by devout Muslim named Askia
Muhammad…drove Sunni Ali’s son from power and replaced him
Askia Muhammad ruled for 35 years o Efficient tax system o Chose able officials o …ministers of treasury, army, navy, agriculture o But Songhai Empire lacked modern weapons
1591- Moroccan fighting force equipped with gunpowder and cannons, crossed the Sahara
Desert and invaded Songhai…collapse of
Songhai Empire
Name:
_____________________________
Date: _____________
Period: _________
Chapter 15.2: West African Empires and
Civilizations
1.
Who was Sundiata? (Time Period, Location,
Key Achievements)
13 th century- Mali
Sundiata was the founder of the Mali Empire…he set up able administrators in charge of Mali’s finances, defense, and foreign affairs…nicknamed the “Lion King”
2.
Who was Mansa Musa? (Time Period,
Location, Key Achievements)
14 th century- Mali
Mansa Musa was a skilled military leader and practicing Muslim who embarked on a famous hajj to Mecca from 1324-1325…Timbuktu became a center for learning
3.
Who was Ibn Battuta? (Time Period, Location,
Key Achievements)
14 th century- originally from Tangier…Ibn
Battuta travelled through much of the Dar al-
Islam, and left behind a priceless account of his travels…27 years