REVIEW SHEET – Unit 7 – Growth of the...
advertisement

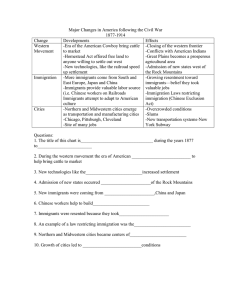
REVIEW SHEET – Unit 7 – Growth of the Nation 1865-1916 Westward movement: Reasons why settlers moved West (know exodusters, Homestead Act of 1862) Life on the Great Plains (soddies, weather hardships) Cowboys and cattle drives Impact of new technologies (railroads, mechanical reaper, steel plow) Impact on Native Americans Immigrants flock to America: Old immigrants (before 1871): from northern and western Europe: Germany, Great Britain, Ireland, Norway, and Sweden) New immigrants (1871 until 1921): from southern and eastern Europe (Italy, Greece, Poland, Russia, and presentday Hungary and Yugoslavia), and Asia (China and Japan). Immigration push factors (why did they leave their homes?) and pull factors (what pulled them to America?) Contributions of immigrants – what industries did they work in? (e.g., Chinese workers on Transcontinental Railroad); (textile and steel mills in the Northeast, the clothing industry, coalmines) Problems of immigrants (working conditions, fear they would take jobs, prejudice, Chinese Exclusion Act) Ellis Island, Angel Island, Assimilation/Americanization Growth of Cities: Industrialization growth of cities for manufacturing/transportation (Chicago, Detroit, Cleveland, New York) Problems of cities: living conditions, rapid growth, housing shortages (tenements/slums), need for sewer /water systems and public transportation Inventions/Innovations and Leaders of Industry (Robber Barons): Corporation (limited liability) Bessemer steel process Light bulb (Thomas Edison) and electricity as a source of power and light Telephone (Alexander Graham Bell) Airplane (Wright Brothers) Assembly line manufacturing (Henry Ford) Andrew Carnegie (steel) J.P. Morgan (finance) John D. Rockefeller (oil) Cornelius Vanderbilt (railroads) Business and Labor Laissez-faire capitalism – monopolies, trusts, social Darwinism, government support of business Labor supply (from immigration and migration from farms) Dangerous working conditions, child labor, long hours, low wages, no job security, Company towns (workers had to live there and pay high rent) Labor unions (8 hr day, better pay, better conditions) Knights of Labor, American Federation of Labor (Samuel Gompers), American Railway Union (Eugene V. Debs), Ladies’ Garment Workers Union (Triangle Fire) Strikes (Haymarket Square Riot, Homestead Strike, Pullman Strike) Goals of Progressive Movement – know examples of each type of reform Political: Government control to the people (initiative, referendum, recall; city managers; election reform) Economic: Economic fairness through government regulation (Sherman & Clayton Anti-Trust Acts) Social: Elimination of social injustices, response to problems of industrialization and immigration Muckrakers – who were they? Progressive Presidents: Theodore Roosevelt and Woodrow Wilson 17th Amendment (senators), 18th Amendment (Prohibition), 19th Amendment (woman suffrage) African Americans struggle for equality: Jim Crow laws, lynching Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) -- “separate but equal” “Great Migration” to Northern cities Know these people and their beliefs: Ida B. Wells; Booker T. Washington; W E.B. Du Bois (NAACP)