WOODLAND HILLS SECONDARY LESSON PLANS
advertisement

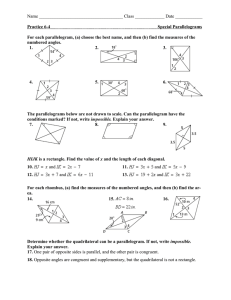
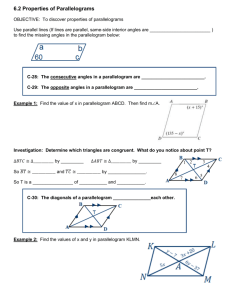
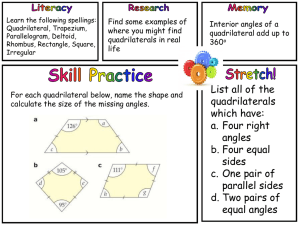
Name: Andrea Sisk Date: May 18, 2015 WOODLAND HILLS SECONDARY LESSON PLANS Content Area: Geometry Length of Lesson: 10 days STAGE I – DESIRED RESULTS Lesson Topic (Modules, if applicable): Quadrilaterals Big Ideas: Mathematical statements can be justified through deductive and inductive reasoning and proof. Numbers, measures, expressions, equations, and inequalities cab represent mathematical situations and structures in many equivalent forms. Patterns exhibit relationships that can be extended, described, and generalized. Geometric relationships can be described, analyzed, and classified based on spatial reasoning and/or visualization. Understanding Goals (Concepts): Exploring quadrilaterals including interior and exterior angles of polygons and properties of quads and special quads. Recognize and apply properties of parallelograms – extending that to rectangles, rhombi, and squares, trapezoids and coordinate proof of quads using properties Student Objectives (Competencies/Outcomes): 1. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon. Find the sum of the measures of the exterior angles of a polygon. 2. Recognize and apply properties of the sides, angles, and diagonals of a parallelogram. 3. Recognize the conditions that ensure a quadrilateral is a parallelogram. Prove that a set of points forms a parallelogram in the coordinate plane. 4. Recognize and apply properties of rectangles. Determine whether parallelograms are rectangles. 5. Recognize and apply the properties of rhombi. 6. Recognize and apply the properties of squares. 7. Recognize and apply the properties of trapezoids. 8. Solve problems involving the medians of trapezoids. 9. Position and label quadrilaterals for use in coordinate proofs. 10. Prove theorems using coordinate proofs. Essential Questions: How can you use coordinates and algebraic techniques to represent, interpret, and verify geometric relationships? How do you use the ideas of direct and indirect proof, and counter-examples to verify valid conjectures and refute invalid conjectures? How can patterns be used to describe relationships in mathematical situations? How can recognizing repetition or regularity assist in solving problems more efficiently? How are spatial relationships, including shape and dimension, used to draw, construct, model, and represent real situations or solve problems? How can the application of the attributes of geometric shapes support mathematical reasoning and problem solving? How can geometric properties and theorems be used to describe, model, and analyze situations? Vocabulary: Quadrilateral, parallelogram, rectangle, rhombus, square, trapezoid, isosceles trapezoid STAGE II – ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE Performance Task: Formative Assessments: Students will actively participate in mini-lessons, guided and independent Pre-assessments, open-ended higher-order-thinking questions, think-pairpractice, activities (including authentic problem-solving tasks and vocabulary), share, graphic organizers, do nows, observation of guided and independent and group work. Also, students will demonstrate adequate understanding via practice, brief in-class writing prompts an end-of-chapter test and project. STAGE III – LEARNING PLAN Interventions: Flexible grouping, students will be encouraged to attend Math Lab and College and Career Access Center tutoring. Materials and Resources: Textbook and notes Tuesday Date: 5/19 Day: A Review for Final Exam Wednesday Date: 5/20 Day: B Review for Final Exam Thursday Date: 5/21 Day: A Review for Final Exam Friday Date: 5/22 Day: B Review for Final Exam Review for Final Review for Final Review for Final Review for Final Assignments Procedures Instructional Procedures*: Monday Date: 5/18 Day: B Review for Final Exam Review for Final *Include Do Now, Mini Lesson, Guided Practice, Independent Practice, Summations/Formative Assessments, Reflections