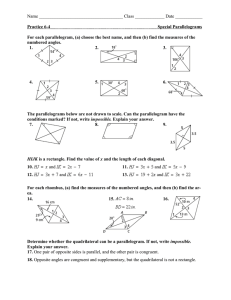
Parallelogram Properties Worksheet: Geometry Practice
advertisement

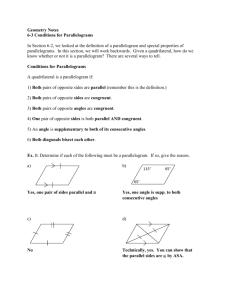
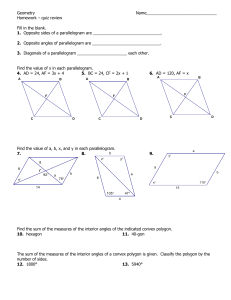
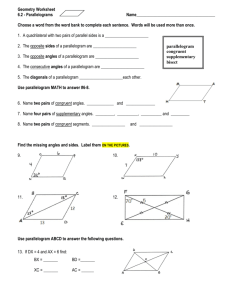
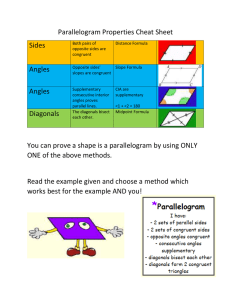
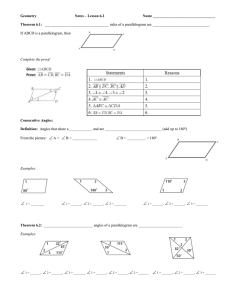
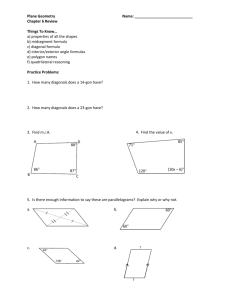
6.2 Properties of Parallelograms OBJECTIVE: To discover properties of parallelograms Use parallel lines (If lines are parallel, same-side interior angles are ________________________ ) to find the missing angles in the parallelogram below: C-28: The consecutive angles in a parallelogram are _________________________. C-29: The opposite angles in a parallelogram are _________________________. Example 1: Find the value of x in parallelogram ABCD. Then find mA. Investigation: Determine which triangles are congruent. What do you notice about point T? ∆𝐵𝑇𝐶 ≅ ∆____________ by _________ ∆𝐴𝐵𝑇 ≅ ∆____________ by _________ ̅̅̅̅ ≅ ______________ by _______________. ̅̅̅̅ ≅ ______________ and 𝑇𝐶 So 𝐵𝑇 8 So T is a ________________ of ___________ and ___________. C-30: The diagonals of a parallelogram _______________each other. Example 2: Find the values of x and y in parallelogram KLMN. 3 1 2 7 4 6 5 Check for Understanding: Summary Properties of Parallelograms Opposite sides are ________________________. (Definition) Opposite sides are ________________________. Opposite angles are ________________________. Consecutive angles are ________________________. Diagonals ________________________ each other. Check for Understanding: Properties of Special Types of Quadrilaterals C-31: If three (or more) parallel lines cut off congruent segments on one transversal, then they cut off ___________ segments on every transversal. ⃡ ∥ 𝐶𝐷 ⃡ ∥ 𝐸𝐹 ̅̅̅̅ ≅ 𝐶𝐸 ̅̅̅̅ ⃡ and 𝐴𝐶 If: 𝐴𝐵 Then: ________________________ Example 4: In the figure, ⃡𝐷𝐻 ∥ ⃡𝐶𝐺 ∥ ⃡𝐵𝐹 ∥ ⃡𝐴𝐸 . Find EH.