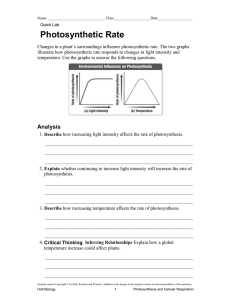
Yakima WATERS Mini Lesson Photosynthesis Learning Activity
advertisement
Yakima WATERS Mini Lesson Photosynthesis Learning Activity Targets and Assessment WA Science Standards Addressed: Grades 6-8 LS2C: The major source of energy for ecosystems on Earth’s surface is sunlight. Producers transform the energy of sunlight into chemical energy of food through photosynthesis. Grades 6-8 LISD: Both plants and animal cells must carry on life functions, so they have parts in common. But plants have specialized cell parts such as chloroplasts and cell walls. Lesson Parameters Content Area: Life Science/Botany Overview: We will learn about photosynthesis. We will learn what the photosynthetic reaction is, what the inputs and outputs are. Students will be able to demonstrate understanding of the photosynthetic equation. We will learn about parts of the plant cell that allow photosynthesis to happen. We will also explore how plants adapt to their environments by looking at the three types of photosynthesis. Grade Level: 7th grade Suggested Time: 90 minutes Assessments: Students are able to put the inputs and outputs of the photosynthetic reaction in the correct order. Special Materials: Index cards Learning Outcomes: Knowledge: Students wil be able to describe what photosynthesis is and where it happens in the plant cell. Students will be able to compare and contrast the three types of photosynthesis and describe how the plants adapt to their environment by utilizing one of the three types. Skill: Students will be able to identify a chloroplast in a plant cell. They will be able to write out the photosynthetic reaction equation. Science Concept Background: Plants are producers in the ecosystem and as such they create their own food through the process of photosynthesis. They take in water, carbon dioxide and sunlight to produce glucose through a chemical reaction and give off oxygen as a byproduct. Most of the plant’s mass comes from carbon sequestered from the air in the form of carbon dioxide. There are three types of photosynthesis, C3, C4 and CAM. Each plant has evolved to do one of the three types depending on its interaction with its environment. Most grassland plants will do C3, most succulents do CAM and plants in very humid areas do C4. The main differences between them is in how they take in carbon dioxide. CAM plants close their stomata during the day to conserve water lose but open them at night and fill their vacuoles with carbon dioxide that they use for photosynthesis during the day. Others are more efficient with certain intensities of light and rely on different photosystems. Materials: Index cards with the following words written on them: Water Carbon dioxide Oxygen Glucose Ultraviolet Rays Procedure: I talked photosynthesis while the students took notes. Then I had them break into groups of five. I taped a note card (which has one of the compounds found in the photosynthetic reaction written on it) to their back. Without seeing what is written on their back they have to talk to students in their group to figure out what they have. The other students have to be creative in their descriptions and cannot just say what it is. Once everyone has figured out what compound they have, I gave them another note card with an equals sign on it and they had to arrange themselves in the correct order for the photosynthetic reaction, ensuring that the inputs are on one side and outputs on the other. Extension: Once the kids have learned about photosynthesis, we went on to talk about the different types and why there are different types. This topic can be extended to lessons about adaptations and evolution. Teaching Tips: To make it a little harder and have the students be exposed to some chemistry, write out the chemical compounds on the cards instead of the words. Supplementary Materials: N/A Author: Holly Eagleston, Yakima WATERS Project, CWU, 2009-2010