Exam 1 Study Guide Chapter 1
advertisement

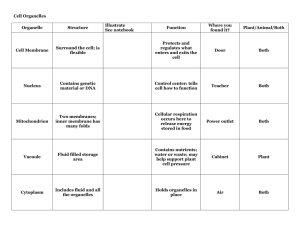
Exam 1 Study Guide Chapter 1 What is the smallest, basic unit of life? Know unicellular vs multicellular and where they are found What is an organ? What are organ systems? What are tissues? What is metabolism? What is photosynthesis? Understand homeostasis Understand reproduction Asexual vs sexual reproduction EX: sexual reproduction allows for genetic diversity…better survival and adaptation Understand evolution and the process of natural selection Know the 8 classification categories? What are the three domains? What is a biosphere? What is a population, community, and ecosystem? What is science? Name the steps of the scientific method. What is a variable? What is a test group? Control group? Give five characteristics of scientific theory. Chapter 2 What is an element? What are atoms? Understand the atomic mass and number What is a proton? What is an electron? What is a neutron? Looking at the atomic number, what can you deduce? Looking at the atomic mass, what can you deduce? Where can you find the metals and nonmetals on the periodic table? Answer: metals are generally of the left (left of the stairs) and nonmetals are on the right What are isotopes? Do they have the same atomic number? Atomic mass? What are the uses of isotopes…i.e. radioisotopes? Understand electron shells, octet rule and valence electrons Use valence electrons to understand ionic and covalent bonds Know the difference between ionic vs covalent bonds What is a compound? Answer: one that is made up of 2 or more elements Understand the properties of water Know the general trend of the pH scale (above 7 is basic and below 7 is acidic) Know the definition of a buffer Chapter 3 Know the definition of organic molecules, hydrocarbons, and isomers Know that functional groups can confer polarity Polarity contributes to how the molecule will react with other molecules or the environment Know hydrophobic vs hydrophilic What are the biological molecules? What’s a monomer? What is a hydrolysis reaction? Dehydration reaction? What are carbohydrates? Know the monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides Especially for the polysaccharides, where are they found? Animal cells, plant cells, etc Know lipids and their uses in the cell What are triglycerides? What are phospholipids? What are steroids? What are the functions of proteins? What is a peptide? Polypeptide? What are the different structures of protein? Know nucleic acids What are the differences between RNA and DNA? What are the relationship between proteins, mRNA, and DNA Chapter 4 Why are cells so small? Define prokaryotic cells What are bacteria and what do they have? Understand the components of the plasma membrane Know the functions of the plasma membrane Why are phospholipids so important for the plasma membrane? What are eukaryotic cells? Compare them to prokaryotic (make a chart if you must) What are the 4 categories of organelles? What the different organelles and their functions? Be sure to know which organelles are only found in plant cells and which are only found in animal cells (Don’t be confused. Both animal cells and plant cells are eukaryotic cells. They just have some organelles that are different from each other.) Understand the process of making proteins Know the cell junctions