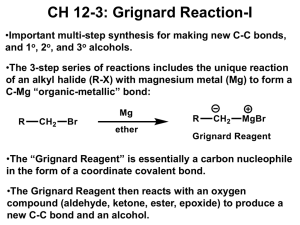
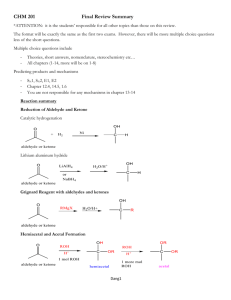
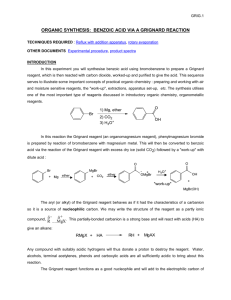
GRIGNARD REACTION POST LAB QUESTIONS 1. Why do Grignard reactions have to be dry? Water or alcohols would protonate and thus destroy the Grignard reagent, because the Grignard carbon is highly nucleophilic. The Grignard reagent is a very strong base and would deprotonate water. This would form a hydrocarbon and prevent the synthesis of triphenylmethanol. 2. Benzene is often produced as a side product during Grignard reactions using phenylmagnesium bromide. How can its formation be explained? Give a balanced equation for its formation. Benzene will be formed when water is present, which is why you must keep a Grignard dry. Rather than proceeding through attack of your carbonyl, which is the desired reaction, the benzene ring will attack any water molecules around, grabbing a proton and kicking off the MgBr. The Grignard reagent PhMgBr will react with traces of water or other protic solvents to produce benzene: C6H5MgBr + H2O --> C6H6 + MgBrOH 3. Interpret the principal peaks in the infrared spectrum of triphenylmethanol. The infrared spectrum of triphenylmethanol will have a broad peak for the OH group at 3550 - 3200 cm^-1. It will also have a C-O peak at 1300 - 1000 cm^-1. Because of the aromatic C=C groups in the three benzene rings, there will be prominent peaks around 1600 - 1585 cm ^-1 and 1500 - 1400 cm^-1. 4. List 4 functional groups that must be avoided during the formation of a Grignard reagent. Grignard and organolithium reagents are powerful bases. Because of this they cannot be used as nucleophiles on compounds which contain acidic hydrogens. If they are used they will act as a base and deprotonate the acidic hydrogen rather than act as a nucleophile and attack the carbonyl. A partial list of functional groups which cannot be used are: alcohols, amides, 1o amines, 2o amines, carboxylic acids, and terminal alkynes. 5. What conditions favor the formation of biphenyl side products? Rapid addition of bromobenzene to magnesium presents a high concentration of bromobenzene to react with previously formed Grignard reagent. 6. Why must you add benzophenone slowly to reaction mixture? The reaction between the benzophenone and the phenylmagnesium bromide is extremely exothermic. Pouring in the benzophenone too quickly can result unwanted chemical byproducts if the reaction happens too fast, not to mention hazardous possibility of explosions occurring. Anhydrous diethyl ether – solvent Magnesium metal + bromobenzene = Grignard reagent Iodine = reaction initiator Possible side reactions: Grignard reaction can react with different reactants to give many side products (Weldegirma, 2013): 1. Grignard reagent can react with water to yield benzene 2. Grignard reagent can react with bromobenzene . to yield biphenyl . 3. Grignard reagent can react with CO2 to yield benzoic acid ion 4. Grignard reagent can react with O2 to give . .