CH3MgBr - s3.amazonaws.com
advertisement

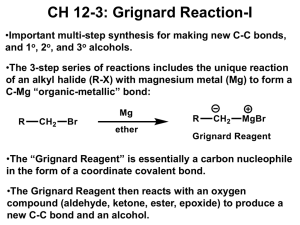
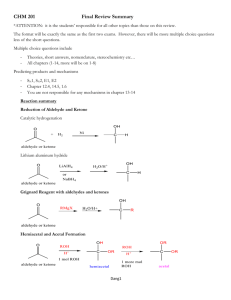
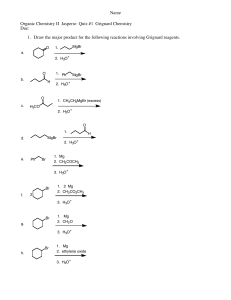
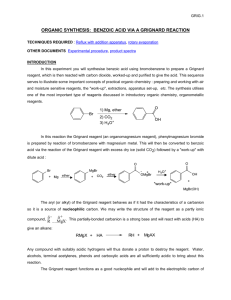
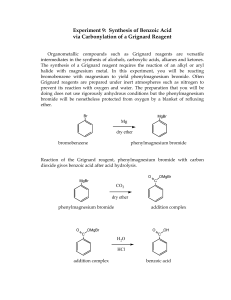
14. Answer is E R-MgBr will reduce secondary ketone into OH with an addition of R group onto the C-O carbon Drawing all the products out will help you see the structure more clearly and understand why all three reactions give the same product. 15. Answer is A (CH3)2CHCH2CH2Br + Mg/ether - (CH3)2CHCH2CH2(MgBr) (MgBr will be a good leaving group) (CH3)2CHCH2CH2(MgBr) + CO2 in H3O+ - (CH3)2CHCH2CH2-CO2H (which is a carboxylic acid) 16. Answer is D sources of a nucleophile that can attack the + end of the C=O double bond in aldehydes and ketones. The methyl group of CH3MgBr will be added into the carbon (with oxygen) also. CH3MgBr is a Grignard reagent and is a 17. Answer is E This one is a Grignard reagent reactions again as above. Reactions B & C can be explained as above. Reaction A is reaction between Grignard reagent and ester with general understanding can be shown below. Note that the circled part of ester was eliminated during the reaction and the 2 carbon groups of Grignard were added instead. 18. The answer is C (3-pentanol) Methyl formate is Grignard reagent is CH3-MgBr The reaction is Grignard with ester as shown above. 19. Answer 1. PBr3 (SN2 reaction / substitute 1 bromine in place of OH) 2. Mg/ether to give CH3MgBr (See Question 15) 3. HCHO/H3O+ (CH3MgBr react with HCHO (formaldehyde) see question 16) 20. 1. Grignard: Phenyl-MgBr + Butanal 2. Switch places between Grignard and Aldehyde on the picture to have Grignard: Propyl-MgBr + benzaldehyde