E1 Elimination Mechanism: SN1, SN2, E1, E2 Reactions
advertisement
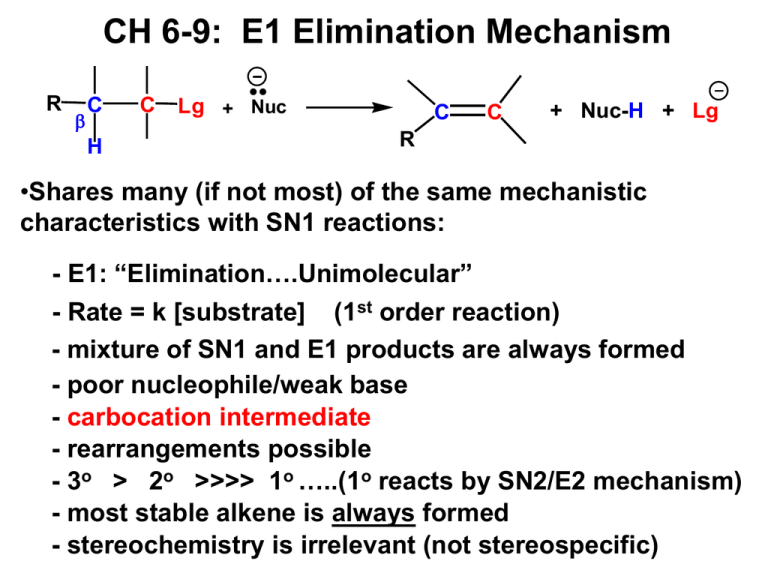
CH 6-9: E1 Elimination Mechanism R C H C Lg + Nuc C C + Nuc-H + Lg R •Shares many (if not most) of the same mechanistic characteristics with SN1 reactions: - E1: “Elimination….Unimolecular” - Rate = k [substrate] (1st order reaction) - mixture of SN1 and E1 products are always formed - poor nucleophile/weak base - carbocation intermediate - rearrangements possible - 3o > 2o >>>> 1o …..(1o reacts by SN2/E2 mechanism) - most stable alkene is always formed - stereochemistry is irrelevant (not stereospecific) SN1/E1 Substitution/Elimination Mechanisms •What type of products will the partial reaction above give us? In other words, what mechanisms are most likely? •ANSWER: Combination of SN1 & E1 mechanisms and products. The SN1 Mechanism CH3 + CH3 H3C CH3 CH3 + H3C H2O SN1 OH2 H3C CH3 OH2 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 H3C Br + H2O acid/base H3C OH CH3 + H3O The E1 Mechanism H3 C H3 C CH3 Br H2 O RLS CH3 + H3C CH3 CH3 + H3C CH2 H H2 O Br CH3 E1 + H3C CH2 H3O Distinguishing Between SN1, SN2, E1 and E2 Reactions (1) Poor nucleophiles, weak bases (H2O, ROH): •Mixture of SN1 and E1 products with 2o or 3o alkyl halides; •SN1: Racemic mixture of stereoisomers; •E1: Most stable alkene is always major product; •Carbocation intermediates: beware of rearrangements; •Nucleophile is usually the solvent (H2O, ROH; solvolysis). (2) Good nucleophile, weak base (-CN, X-, NH3, HS-, RCOO-): •SN2 products only, with methyl, 1o or 2o alkyl halides; •SN2: Inversion of configuration always; •3o alkyl halide gives SN1/E1. Distinguishing Between SN1, SN2, E1 and E2 Reactions (3) Good nucleophile, strong base: •Mixture of SN2 and E2 with 1o or 2o alkyl halides; •SN2: Inversion of configuration always; •E2/small base (HO-, RO-, NH2-) produces most stable alkene; •E2 and large, bulky base (tert-butoxide salt): SN2/E2 with methyl and 1o; E2 only with 2o and 3o; produces less stable alkene; •3o alkyl halide gives E2 products only ; •Best solvents are acetone, DMSO, DMF. Keys for Solving Substitution/Elimination Reactions For each reaction consider: • Type of alkyl halide (1o, 2o, 3o) • Classify the nucleophile (poor/good, weak base/strong base, small/bulky) • ID Mechanism(s)/Reaction(s) (SN1, SN2, E1, E2) • For substitution reactions: inversion or racemization? • For eliminations: most or least stable alkene? • Draw structure(s) of all major product(s) • I will provide a flow chart in class and on the web site.