1
advertisement

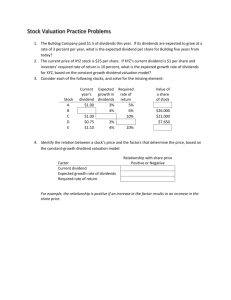
1 Learning Outcomes Chapter 7 Explain what equity is and identify some of the features and characteristics of (a) preferred stock and (b) common stock. Describe how stock prices (values) are determined when (a) dividends grow at a constant rate and (b) dividend growth is nonconstant. Describe some approaches (techniques) other than strict application of time value of money models that investors use to value stocks. Identify factors that affect stock prices. 2 Valuation of Financial Assets Equity (Stock) Preferred Stock: hybrid security • similar to bonds with fixed dividend amounts • similar to common stock as dividends are not required and have no fixed maturity date Common Stock 3 Preferred Stock Features Par Value The nominal or face value of a stock or bond Cumulative Earnings Any preferred dividends not paid in previous periods must be paid before common dividends can be distributed Maturity Generally has no specific maturity date Priority to Assets and Earnings Dividends must be paid on preferred stock before they can be paid on common stock 4 Preferred Stock Features Control of the Firm (Voting Rights) Almost all preferred stock is nonvoting stock Convertibility Most preferred stock may be converted to common stock Other Provisions Call provision - Gives the issuing corporation the right to call in the preferred stock for redemption Sinking fund - Call for the repurchase and retirement of a given percentage of the stock each year Participating - Participates with the common stock in sharing the firm’s earnings 5 Common Stock Features Par Value Legally, represents a stockholder’s minimum financial obligation in the event the corporation is liquidated Dividends The firm has no legal obligation to pay common stock dividends Maturity Generally has no specific maturity date Priority to Assets and Earnings Dividends can be paid only after the interest on debt and the preferred dividends are paid 6 Common Stock Features Control of the Firm (Voting Rights) Common stockholders have the right to elect the firm’s directors and to vote on shareholder’s proposals, mergers, and changes in the firm’s charter Preemptive Right Gives stockholders the right to purchase any additional shares of stock sold by the firm before the shares can be offered to new investors. 7 Types of Common Stock Classified Stock Common stock that is given a special designation, such as Class A, Class B, etc., to meet special needs of the company Founder’s Shares A class of stock owned by the firm’s founders who have sole voting rights 8 Equity Instruments in International Markets American Depository Receipts Certificates created by banks that represent ownership in stocks of foreign countries Foreign Equity Yankee stock Euro stock 9 Stock Valuation Models - Terms Market Price P0 = the actual market price of the stock today Pt = the expected price at the end of Year t P0 = the intrinsic value as seen by the investor P1 = the price expected at the end of Year 1 10 Stock Valuation Models - Terms Expected Dividends Dt = the dividend the investor expects to receive at the end of Year t D0 = most recent dividend already paid D1 = is the next dividend expected to be paid and it will be paid at the end of this year 11 Stock Valuation Models - Terms Growth Rate g = the expected rate of change in dividends per share 12 Stock Valuation Models - Terms Required Rate of Return rS = the minimum rate of return on a common stock that stockholders consider acceptable given its riskiness and returns available on other investments 13 Stock Valuation Models - Terms Dividend Yield The expected dividend divided by the current price of a share of stock 14 Stock Valuation Models - Terms Capital Gain Yield the change in price (capital gain) during a given year divided by its price at the beginning of the year 15 Stock Valuation Models - Terms Expected Rate of Return The rate of return on a common stock that an individual investor expects to receive 16 Stock Valuation Models - Terms Actual Rate of Return rs = the rate of return on a common stock that an individual investor actually receives, after the fact; equal to the dividend yield plus the capital gains yield. 17 Expected Dividends as the Basis for Stock Values Cash-flow Timeline s 18 Expected Dividends as the Basis for Stock Values 19 Valuing Stocks with Constant, or Normal, Growth Growth that is expected to continue into the foreseeable future at about the same rate as that of the economy as a whole. 20 Normal, or Constant, Growth (Gordon Model) 21 Present Value of Dividends of a Constant Growth Stock 22 Expected Rate of Return on a Constant Growth Stock 23 Valuing Stocks with Nonconstant Growth Nonconstant Growth: The part of the life cycle of a firm in which its growth is either much faster or much slower than that of the economy as a whole. 24 Valuing Stocks with Nonconstant Growth 1. Compute the value of the dividends that experience nonconstant growth, and then find the PV of these dividends, 2. Find the price of the stock at the end of the nonconstant growth period, at which time it has become a constant growth stock, and discount this price back to the present, and 3. Add these two components to find the intrinsic value of the stock P0. 25 Other Stock Valuation Models P/E Ratios The higher the P/E ratio the more investors are willing to pay for each dollar earned by the firm P/E ratio gives an indication of a stock’s “payback period” 26 Other Stock Valuation Models Economic Value Added Approach 27 Changes in Stock Prices Prices move opposite to changes in rates of return They move in the same direction as changes in cash flows expected from the stock in the future 28