Review Third Midterm Investments chapter 11;13;17
advertisement

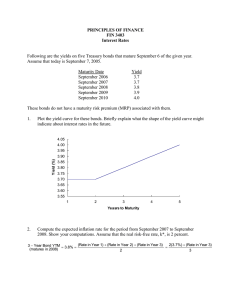
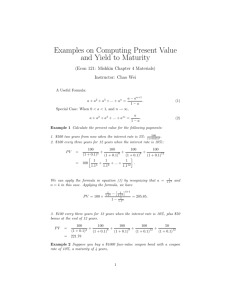
Review Third Midterm Investments chapter 11;13;17 Bond Yields and Prices Interest Rates (Fisher Effect) Bond Prices (Yield Curve) Current Yield Yield to Maturity Yield to Call Reinvestment Risk Realized Yield Yield Curve, Duration and Convexity Measuring Bond Price Volatility: A measure that accounts for both size and timing of cash flows PV(CFt ) D t t 1Market Price n Duration depends on three factors Maturity of the bond Coupon payments Yield to maturity Duration Relationships Duration increases with time to maturity, but at a decreasing rate For coupon paying bonds, duration is always less than maturity For zero coupon-bonds, duration equals time to maturity Duration increases with lower coupons Duration increases with lower yield to maturity Estimating Price Changes Using Duration Modified Duration = D* = D/(1+r) D* can be used to calculate the bond’s percentage price change for a given change in interest rates It works well for “small” changes in interest rates and parallel shifts in the term structure of interest rates. -D % in bond price r (1 r) Common Stock Valuation Fundamental Analysis Present value approach Cash Flows (1 k) t t 1 n Value of security Multiple of earnings approach P/E multiplier remains popular for its ease of use and the objections to the dividend discount model P/E Ratio Approach The higher the payout ratio, the higher the justified P/E Payout ratio is the proportion of earnings that are paid out as dividends The higher the expected growth rate, g, the higher the justified P/E The higher the required rate of return, k, the lower the justified P/E Which Approach Is Best? Complementary approaches? P/E ratio can be derived from the constantgrowth version of the dividend discount model Dividends are paid out of earnings Using both increases the likelihood of obtaining reasonable results Dealing with uncertain future is always subject to error Other Valuation Techniques Market-to-book ratio (M/B) Ratio of share price to per share shareholder’s equity as measured on the balance sheet Price paid for each $1 of equity Price-to-sales ratio (P/S) Ratio of company’s market value (price times number of shares) divided by sales Market valuation of a firm’s revenues Company Analysis Basic Financial Statements Balance Sheet Items listed in order of liquidity (assets) or in order of payment (liabilities) Income Statement DuPont Analysis NI EBT EBIT Sales TA EBT EBIT Sales TA Eqty Tax Burden Interest Burden EBIT Efficiency TA Turnover Leverage Ratio NI / Sales = Net Income Margin NI / TA = ROA TA ROA Equity Leverage Ratio = TA / Equity NI NI Sales TA Equity SALES TA EQUITY Net Profit Margin Asset Turnover Leverage Ratio TA ROE ROA EQUITY