Interest on Reserves: A Review of the Federal Reserve’s New Zamira Simkins
advertisement

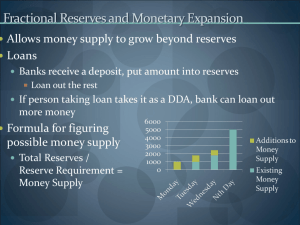
Interest on Reserves: A Review of the Federal Reserve’s New Monetary Policy Tool Zamira Simkins University of Wisconsin-Superior Wisconsin Economics Association Annual Conference November 9-10, 2012 Traditional Central Bank Key objectives: 1. Low inflation 2. Sustainable economic growth 3. Financial system stability 4. Stable interest rates 5. Stable exchange rates Monetary policy tools: 1. Open Market Operations 2. Discount rate 3. Reserve requirement Interest on Reserves • Friedman (1960) ▫ Opportunity cost of holding RR ▫ IOR = market interest rate • Goodfriend (2002) ▫ IOR as a monetary policy tool Interest Rate Policy Regimes A. Open Market Operations i Disc. rate i Supply Supply Disc. rate FFR1 FFR2 B. Interest on Reserves FFR1 Demand Q1 Q2 Reserves Demand IOR Q1 Q2IOR Reserves Benefits of IOR Regime • Enables the Fed to conduct monetary policy even when interest rates are near zero • Enables the Fed to pursue additional monetary policy objectives • Allows the Fed to inject liquidity (i.e. reserves) in financial markets Fed and IOR • Fed had no legal authority to pay IOR prior to 2008 • Financial Services Regulatory Relief Act (2006): IOR effective October 1, 2011 • Emergency Economic Stabilization Act (2008): IOR effective October 1, 2008 Key Interest Rates in 2008 2.50 Interest rate, % 2.00 1.50 1.00 0.50 0.00 Effective Federal Funds Rate Discount Rate Interest on Excess Reserves Interest on Required Reserves Key Interest Rates after 2008 0.80 0.70 Interest rate, % 0.60 Effective Federal Funds Rate 0.50 0.40 Discount Rate 0.30 0.20 0.10 0.00 IOR (Excess & Req) Liquidity Crisis • Liquidity crisis is a state in which financing economic activities, either via borrowing or selling of financial instruments, becomes difficult • Liquidity crisis indicators: ▫ Declining prices of financial assets ▫ Downgrading of securities ratings ▫ Increasing TED spread T-Bill - Eurodollar (TED) Spread 7.00 6.00 5.00 4.00 3.00 2.00 1.00 0.00 3M T-Bill Rate 3M LIBOR TED Spread IOR and Liquidity Bill $ 3,000 Monetary Base M1 Stock 2,500 2,000 Dec 2008 1,500 1,000 500 0 IOR and Liquidity Bill. $ 1,800 1,600 1,400 1,200 1,000 800 600 400 200 0 Excess Reserves Interest on Excess Reserves % 1.00 0.90 0.80 0.70 0.60 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 0.10 0.00 Conclusion • US liquidity conditions are still tight • Between January 2007 and December 2011, excess reserves grew from $1.5 billion to $1.5 trillion • Interest on excess reserves is reducing the opportunity cost of not lending