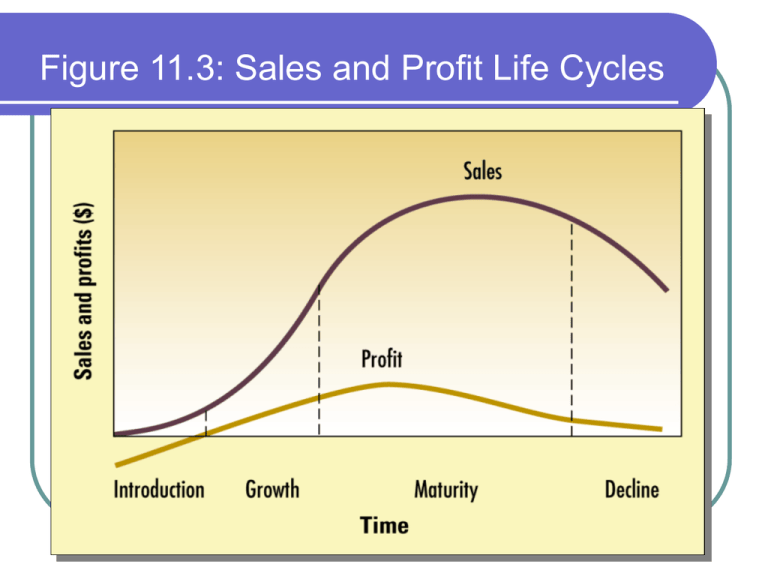
Figure 11.3: Sales and Profit Life Cycles
Product Life-Cycle Marketing Strategies
Issues in Collecting
and Using Information #6
Invasion of customer
privacy
e.g., use of medical
databases to sell healthcare
products
Information and ethics
e.g., guidelines for sharing
of confidential information
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
© 2003 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
TM 5-13
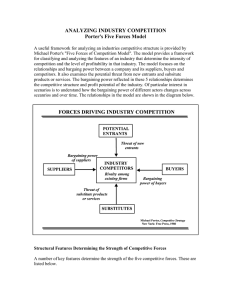
Bargaining Power of Buyers
Concentrated or large volume sales
Purchased products are a significant
fraction of buyer’s costs
Products are standard or undifferentiated
There are few switching costs
Low profits - pressure on suppliers
Buyers pose threat of backward
integration
Buyer has full information
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Concentrated suppliers, fragmented
buyers
Little substitution threat
Customer is not an important buyer
Supplier’s product is important input
High buyer switching costs
Suppliers pose threat of forward
integration
Government - defense, timber, regulation
Rivalry: Price competition, advertising,
product introductions, customer service..
Numerous Competitors: More mavericks
Slow Industry Growth
High Fixed or Storage Costs (Excess
capacity often leads to price wars)
Lack of Differentiation = commodity
Foreign Competitors
High Strategic Stakes
High Exit Costs
Likelihood of retaliation to entry
History of retaliation
Established firms with substantial
resources such as cash, borrowing
capacity, excess productive capacity,
distribution leverage
Established firms with illiquid industry
assets
Slow industry growth - can’t absorb new
competition.
Figure 9-2: Barriers and Profitability