Russia I Hokkaigakuen Summer Exchange Map test Questions
advertisement

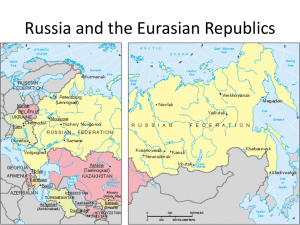
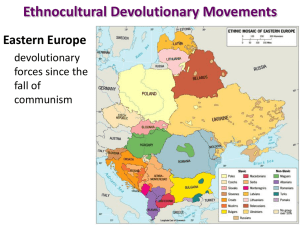
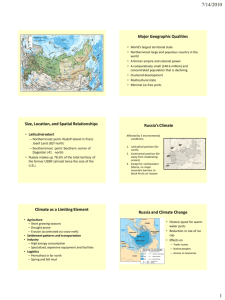
Russia I Hokkaigakuen Map test Questions Review Russia – Qualities – Evolution – Devolution – Physiography Summer Exchange HOKKAI GAKUEN SUMMER EXCHANGE (IDST 2850 & 3850) IDST 2850: Study Tour of Japan IDST 3850: Field Research in Japan (optional with additional tuition fees) Admission by application and interview Instructors: Ian MacLachlan and Diane Clark Approximate Dates: Summer Session I Pre-Departure class schedule: May 1-May 28 TBA Travel Dates: May 28 – June 26 (to be confirmed) Travel Plan Lethbridge-Kitami - fly – Kitami 11 days Kitami-Sapporo - coach – Sapporo 11 days Sapporo-Osaka - fly – Kyoto, Hiroshima 4 days Osaka-Lethbridge - fly To learn more: Information Sessions Monday, 24 January 4:30-5:30 – U-Hall D631 Tuesday, 25 January 4:30-5:30 – U-Hall B660 Wednesday, 26 January 12:00-13:00 – U-Hall C640 Details of Exchange Approximate Cost: $2,500 (includes course tuition, airfare, accommodation & meals), – plus spending money $500-1,000. Further Information: Tracy Warwick: 329 2041 (away 17-21 Jan) Glen Allen: 329 2768 (Mgr Intl Student Centre) Ian MacLachlan: 329 2076 (Geography) Russia I (reprise) Hokkaigakuen Summer Exchange Map test reminder Questions Review Russia – – – – Qualities Evolution Devolution Physiography Map test, Feb 1 Russian Realm Transcaucasian Republics Kazakhstan (Transition zone) Major Geographic Qualities Immense territorial state (11 time zones!) Northernmost large and populous country Former world colonial power A comparatively small (<145 million) and concentrated population Concentrated in the west Multicultural: 21 internal republics (ethnic) Landlocked: Few ports Russia’s Dimensions Gulf of Finland to Bering Sea 75°N to 45°N (Salt Lake City) Russia is 76.6% of total territory of the former USSR (17,075,400 km ~twice the size of Canada). Massive land area in Siberia and the far east is sparsely settled …but not unspoiled 80º 60º 40º 20º Russia and North America: Size and latitude comparison Climatology Climate – Average weather conditions for a given area over an extended period of time Weather – Refers to the atmospheric conditions at a specific time and location Russia’s Climate – High latitude – Continentality – Physiography shuts out warm subtropical air masses Russian Climate 3 natural features: Latitude Continentality Location of major mountains Russia-Canada Climate Similarities Canadian Continental Climate Climate as a Restrictive Element in Russia Agriculture – Short growing seasons – Drought prone – Erosion (accelerated by snow melt) Settlement patterns & transportation Industry – High energy consumption – Specialized equipment and facilities – Extractive Permafrost Spring and fall mud Investment in special equipment and facilities Grand Duchy of Muscovy (Czar Ivan the Terrible - 1547-1584) (Czar Peter the Great- 1682-1725) Western Orientation - St Petersburg Czarina Catherine the Great (1760-1796) Expands south and east Growth of the Russian Empire Growth Of the Russian Empire Forward Capital Capital city positioned in potentially contested territory, usually near an international border, confirming the state’s presence in the region Union of Soviet Socialist Republics Union of Soviet Socialist Republics: Devolution RSFSR Baltic Republics: – Estonia – Latvia – Lithuania European Republics: – Belorussia (White Russia) - now Belarus – Ukraine – Moldova (Moldavia) Transcaucasus: – Georgia – Armenia – Azerbaijan (with Armenian exclave) Central Asian Republics: – – – – – Kazakhstan (huge) Uzbekistan Turkmenistan Kirghizistan Tajikistan Union of Soviet Socialist Republics Russia’s physiographic regions RUSSIAN PLAIN Ural Mountains • Traditional eastern boundary of Europe • Novaya Zemlya • North-south length covers 2500 kms • Central Urals are lowest: several key crossing places • Forest and mineral resources were basis for Soviet industrialization and war machine