End of the Cold War Ch.35, pg. 839-847
advertisement

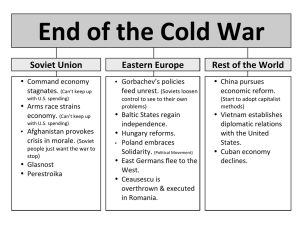
End of the Cold War Ch.35, pg. 839-847 End of the Cold War & Explosion of the 1980s & 1990s Causes of change in Russia’s pattern of expansion 1. Internal decline: • Leadership • Environmental degradation • Declining industrial production amidst rising military costs 2. External pressure: • Islamic fundamentalism • Western consumerism • China’s shift away from USSR toward capitalism • U.S. diplomacy & defense spending stretched USSR thin Age of Reform • Gorbachev ushered in atmosphere of change, openness, & innovation • Economically, perestroika allowed for some private ownership & decentralization • Politically, created new parliament & allowed opposition groups • Yet, results were slow from efforts to balance reform & stability Dismantling the Soviet Empire • Soviet decline prompted successive, usually peaceful political changes throughout Eastern Europe • Symbolized by fall of Berlin Wall in 1989 ↳ New flexible communist leadership or democratic republics installed ↳ Market reforms caused rapid inflation ↳ Old nationalist tensions boiled Renewed Turmoil of the 1990s • Gorbachev’s authority declined & Soviet Union broke into independent republics in 1991 • Boris Yeltsin takes leadership of Russia • Economic & political uncertainty reigns supreme Global Connections • End of Cold War promised a new age of peace yet regional conflicts remained • Democracy spread • U.S. as sole superpower •Global influence •Harsh reactions to this dominance now centered on single nation