Vocabulary Matching for Geological Features and Layers of the Earth Mountains Ridges
advertisement
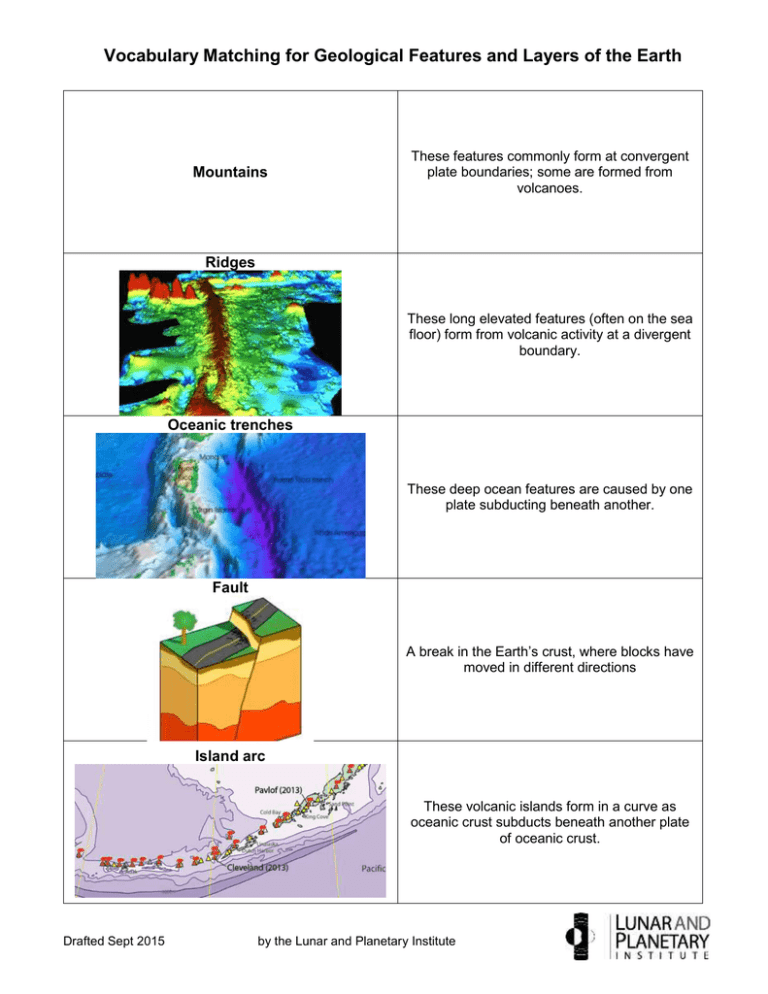
Vocabulary Matching for Geological Features and Layers of the Earth Mountains These features commonly form at convergent plate boundaries; some are formed from volcanoes. Ridges These long elevated features (often on the sea floor) form from volcanic activity at a divergent boundary. Oceanic trenches These deep ocean features are caused by one plate subducting beneath another. Fault A break in the Earth’s crust, where blocks have moved in different directions Island arc These volcanic islands form in a curve as oceanic crust subducts beneath another plate of oceanic crust. Drafted Sept 2015 by the Lunar and Planetary Institute Vocabulary Matching for Geological Features and Layers of the Earth Volcano These explosive features form at plate boundaries, especially at subduction zones. Continents The main landmasses of the Earth Crust The top or outer layer of the Earth (part of the lithosphere) Lithosphere This solid layer of the Earth makes up the tectonic plates. (It includes the crust and top part of the mantle.) Asthenosphere The layer of the Earth that flows slowly beneath the lithosphere Drafted Sept 2015 by the Lunar and Planetary Institute Vocabulary Matching for Geological Features and Layers of the Earth Rift valley A low area between mountain ranges at a divergent plate boundary Mantle This part of the Earth’s interior flows slowly but is made of solid rock. Core This part of the Earth’s interior has a liquid metal outer part and a solid metal inner part. Ring of Fire The zone of earthquakes and volcanoes surrounding the Pacific Ocean Drafted Sept 2015 by the Lunar and Planetary Institute










