-- 張瑞星 ____________________
advertisement

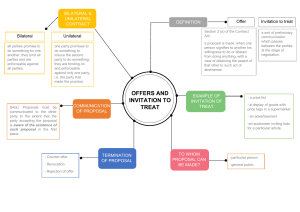
網路購物機制之微調--從購物網站標價錯誤之數件判決談起 張瑞星* 目 次 壹、 前言 貳、 網路購物交易網頁之法律定位與契約之成立 一、 認網路購物交易網頁之性質為要約者 二、 認網路購物交易網頁之性質為要約之引誘者 三、 小結 參、 自動回覆確認信函之法律效力與契約之成立 肆、 以標價錯誤為由撤銷錯誤意思表示之法效 一、業者標價錯誤的過失責任 二、消費者的信賴利益與誠實信用 伍、綜合分析與建議 ____________________ * 美國聖路易華盛頓大學法學博士,現為南台科技大學財經法律研究所助理教授。作者感謝兩位 匿名審查人所提供之寶貴意見,並特對研究助理李沛宸協助整理資料與王偉霖教授、林玫君教 授、宋金比律師所給予之修正建議致上謝忱。 1 摘 要 電子商務時代的來臨,網際網路已成為企業經營者與消費者進行 商業交易的新興管道,業者可以透過網頁購物機制提供商品與服務內 容的介紹,直接與消費者在網路平台上進行交易;然而,網路交易畢 竟與傳統實體商店陳列商品進行買賣時消費者得以實際檢視商品的 情況不同,一旦網路業者因標價錯誤衍生消費爭議,業者往往因顧慮 大額損失而不願承認契約,消費者雖有其應享之權益,但若明知標價 錯誤而仍訂購,是否值得保護?若干法律爭議涉及網路購物交易網頁 之性質究竟是要約或要約之引誘?其定性是否影響交易契約之成 立?業者在消費者下訂後的自動回覆信函是否為承諾?契約是否因 而成立?業者得否撤銷契約?應否課予網路業者標價錯誤的過失責 任?而消費者因標價錯誤的機會而購買商品,其信賴利益是否值得法 律保護?業者與消費者間之權益應如何取得衡平? 本文自我國法院已作成之逢陞科技及戴爾電腦案共七件判決,並 參考國外法院之處理方式,就前述之法律爭議加以整理分析比較,以 圖表方式表現,以收一目了然之效,並發現法院做成結論的三大決定 點,企圖以此提供業者就其購物機制作些許調整,以免除日後發生類 似的消費爭議。 關鍵詞:網路購物、標價錯誤、要約、要約之引誘、自動回覆確認信 函、意思表示錯誤、信賴利益保護 2 The Fine Tuning for Online Shopping Mechanism: Lessons from Pricing Error Cases Ruey-Hsing Chang** ABSTRACT E-commerce is a mechanism where business and consumers make transactions directly over the Internet. For forming an online contract, business provides detailed product information online, including product photos, specification and even reviews, by creating web pages to attract customers. However, electronic transactions are different from physical store transactions which customers can actively touch and examine products before they decide to place an order. When online price errors occur, most stores choose not to honor price and orders because of tremendous economic loss caused. Nevertheless, the issues of online price errors are complicated; the issues include whether valid contracts between customers and online stores have been formed when a customer places an order online? Is the detailed web page information a contract offer or just an invitation to offer? Do replies by automated system created by online stores constitute contract acceptances? Are online stores eligible to cancel the contract in case of pricing errors? All these issues need delicately considering the interest balance between business loss and consumer protection. This article focuses on solving above issues by analyzing and comparing seven related Taiwanese court decisions, including well-known Dell price error cases, and referring to international judicial opinions. The conclusion of the comments providing comparison chart of court decisions has found three decisive points by which courts accordingly exercise to make decisions. For avoiding future price error controversy, this article suggests that business should slightly adjust the content of replied mail sent by automated system to verify the validity of the contract. This article concludes that since online business is capable of designing an enforceable 3 system to control its own risk, it is not appropriate for business to shift its price error liability to consumers. KEY WORDS: Online Shopping, Price Error, Offer, Invitation to Offer, Auto-reply System, Errors on Promise, Protection of Reliance Interest 4 5