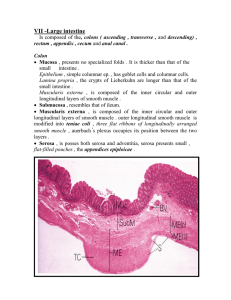
Important Differences in the Layers of the Alimentary Tract Serosa
advertisement

Important Differences in the Layers of the Alimentary Tract Area of GI Tract Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Mucosa Stratified columnar epithelium Rugae folds, gastric pits between folds, gastric glands/parietal cells below colum. epith. make HCl: chief cells make zymogen enzymes; lamina propria at base of mucosa (superficial to submucosa); goblet cells make mucus Villi, microvilli on columnar epithelium; brush border enzymes made by columnar cells; goblet cells make mucus here; deep crypts between villi; bounded on deep surface by lamina propria; Duodenum Heavy villi folds, found in retroperitoneal position Illeum Less elaborate villi Large intestine Great numbers of goblet cells, no villi but still has crypts; lamina propria at base Submucosa Muscularis mucosa most superficially, going deep to connective tissue Muscularis Some skeletal muscle with smooth muscle 3 smooth muscle layers: oblique (for mixing), circular, longitudinal for squeezing Serosa Serosa is called aventitia in thoracic cavity Serosa also called visceral periotoneum 2 smooth muscle layers: longitudinal and circular layers; no oblique layer. Serosa also called visceral periotoneum 2 major layers; longitud. layer reduced to 3 sublayers called tenae coli; circular layer also;reduced longit. muscle creating puffy haustra Serosa also called visceral periotoneum; fatty eplipoic appendages hang from visceral peritoneum Duodenal/Brunner's glands evident Peyer's patches in submucosa, increasing in number distally