Financing of hospital care in Finland Unto Häkkinen 25.05.2010
advertisement

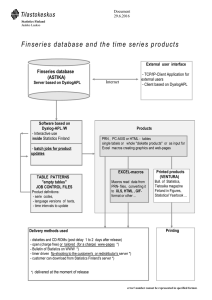
Financing of hospital care in Finland Unto Häkkinen Centre for Health and Social Economics 25.05.2010 Finland Health care system in Finland • Universal and equal availability • Public financing – 8.2% of GDP (2007) – 75% public funding – also some 40% of private services are reimbursed Government – soft regulation / information guidance Finland 25.05.2010 • Municipalities – responsible for providing health services, social services and basic education – 342 with population range from 580 000 to just 150 – 20 + 1 Central Hospital Districts (owned federations of municipalities) 25.05.2010 Finland State Tax Subsidy Municipality Tax Hospital District NHI Copayment Population/ Employer Patient 4 Hospital districts (HD) • • • • • • Responsible for most of hospital care Managed and funded by municipalities Each municipality obligated to be a member of a HD Different contractual or negations mechanism between municipalities and HDs. The budget of each HD is based on the negotiations and is formally decided by a Council, whose members are appointed by each municipality The HD council approves the financial statements (such as payment methods and levels of payments (prices)) and makes decisions about major investments 25.05.2010 Finland Financing of hospital districts • The payments for municipalities are based on the total budget and the predicted use of services • If the budget is exceeded, the municipalities must cover the deficit from their own revenues, usually by paying higher prices for services. In the case of budgetary surplus, the prices paid by municipalities can be lowered. Major purpose of hospital pricing systems has been to cover the costs of production and to allocate hospital costs fairly between the municipalities financing the provision of services within a HD. 25.05.2010 Finland Payment methods • Each HD determines activity based payment methods used to reimburse its hospitals and they vary from district to district. • The trend been consistently moving away from the bed-per-day price towards case-based prices. • Presently 13 out of 21 HDs use DRG-based pricing. The principles and rules for DRG usage vary greatly between hospital districts because there are no national guidelines how to use it. 25.05.2010 Finland International comparison • Finnish hospitals are more efficient than hospitals in other Nordic countries. • One possible explanation: the cost control by municipalities (financed by mainly by local taxes) is more effective that that of counties or governments 25.05.2010 Finland Confidence limits for efficiency scores for non university hospitals in Nordic countries. Based on pooled DEA (CRS) 1999-2004 1 0,9 0,8 0,7 0,6 0,5 0,4 0,3 Danish hospitals 2002 2000 25.05.2010 2002 2003 2004 Swedish hospitals 1999 2000 2001 2002 Finland Finnish hospitals 2003 2004 1999 2000 2001 2002 Norwegian hospitals 2003 2004 Current Issues: A somewhat greater state involvement and monitoring Earlier Softer regulation/information guidance, which relies on the assumption that the provision of information to municipalities, producers and professionals (doctors) will drive constructive behavioural or system change. Since 2005 • Introduction of clinical guidelines for a wide range of treatments, aimed partly at bringing some convergence across Finland in rates of elective surgical procedures and in the setting of thresholds for admission to waiting lists for procedures. • Introduction of a set of maximum waiting-time targets for non-urgent examinations and treatments at hospitals. Defined hospital treatments, including elective surgery, should be offered within 3-6 months • Collection a fine if a hospital district does not meet the waiting-time targets 25.05.2010 Finland Vertical integration Since mid 1990s several local reforms have been conducted to ingrate the service production into single organization in 2008 about 10 % of population lived in areas where most of the primary and secondary care is provided by the same organisation. Current initiative from the Ministry: greater integration of care between health centers and non university hospital districts (government bill 2010, implementation 2011). 25.05.2010 Finland Scope and scale Clear trend towards increasing size both producers (hospitals) and purchasers municipalities on voluntary basis: – – Three hospitals into a one in capital area in 2007 In 2009: number of municipalities from 415 to 348 and now 342 Current initiative from the Ministry: The care of diseases requiring highly demanding treatment will be centralized more to 5 special responsibility hospital districts (government bill 2010, implementation 2011). 25.05.2010 Finland Patient choice • Current situation: patients do not have a freedom to choose between hospitals • Current initiative from the Ministry: patient can choose (public) hospital from his own special responsibility hospital district, pop about 1 million (government bill 2010, implementation 2011). • Not decided (or even thought) how the municipalities will pay hospitals 25.05.2010 Finland Measuring productivity of hospital care: benchmarking project • Joint venture - STAKES & hospital districts 19982006, 2007- part of routine statistical system (THL) • Provides versatile data on – – – – Finland 25.05.2010 Utilisation Costs Productivity From provider and regional perspective The hospital benchmarking system • A data warehouse containing all patient contacts in hospital and inpatient primary care since 1998 • Output data is grouped using NordDRG, to cover the whole episode of care • Combines cost data with output data (allowing for productivity comparisons) • Gives a process view both from a regional and producer perspective Finland 25.05.2010 Available indicators reported in the benchmarking system • • Cost efficiency (productivity, unit costs, use of intermediate services) • Use of services (age- and sex standardized) • Rates for various types of services • • Process indicators (% of bed-days in specialized care/primary care) Finland 25.05.2010 Calculating the total episode of care A) Total episode of care District 1 District 2 Patient's use of services in 3 different hospitals visit1 visit2 DRG1 DRG3 DRG2 visit3 Patients use of services in one hospital hospital x hospital y hospital z B) Producer episode of care 25.05.2010 Finland Measurement levels - Hospital care: Producer perspective • Hospital district • Hospital • Speciality • Patient group Finland 25.05.2010 25.05.2010 SS AI R AA LA N KE AA SK LA US KA NA SA N N TA IR KE AA -H SK ÄM LA U SS EE VA AI N AS SE R KE AA AN IN SK LA Ä KE JO US KE EN SK S SK AI U KE RA SS I-S SK AL AI U O U R A M S AA SA EN LA IR KE /C AA KE SK E LA SK N U TR SS I-P AL AI O SJ R HJ AA U AN KH LA M U AA SE N T KE IV M IK SK AS KE U A SS LÄ LI N A NS KE IR I -P AA SK O LA U H PÄ SS JA IJ N A IR ÄT KE AA -H S KU LA ÄM S EE SA N IR KE AA PO SK LA LA H U JO SS PI N IS AI KE -K R AA AR SK LA JA U SS LA AI N R KE AA SK LA U SS AI R AA LA KE SK U AA LA SS AI R SS AI R KE SK U KE SK U N NA N LA AK SO SA TA KU EN KY M UN JA LA N U LI N KA R Ä- KA IN SA VO N ET EL Hospital level productivity in 2008 - central hospitals 1.40 1.20 1.00 0.80 0.60 Episodes DRGs 0.40 0.20 0.00 Finland New developments in hospital bencmarking at disease level • PERFECT = PERFormance, Effectiveness and Cost of Treatment episodes (since 2006) comparative database that allows the treatments and their costs and • Aoutcomes to be compared between hospitals , hospital districts and years 25.05.2010 Finland Description of PERFECT-Project BASIC REPORTS RESEARCH F E E D B A C K PERFECT DATA BASE THL Hospital discharge register, Hospital productivity (Benchmarking) database Finland 25.05.2010 SOCIAL INSURANCE INSTITUTION Register on Health and Social Benefits STATISTICS OF FINLAND Cause-of-Death Register OTHER REGISTERS Implant Register on Orthopaedic Endoprostheses, Hospitals patient registers Content of basic reports http://www.thl.fi/fi_FI/web/fi/tutkimus/hankkeet/perfect Levels Hospital Districts (responsible for providing specialist care in Finland) based on the municipality of the patient) Hospitals (over 50 patients), based on patients treated in a hospital Indicators Basic information on patients such as number of patients, age structure, co-morbidity (about 40 indicators) Process indicators describing length of stay, outpatient visits, use of procedures, drugs, cost of care (about 140 indicators) . Indicators describing outcomes of patients (about 60 indicators) Finland 25.05.2010 Current status of Perfect Acute myocardial infarction (regional level and hospital data available from the years 1998-2007) Bypass surgery and PTCA (regional and hospital level data under development from years 1998-2007) Hip Fracture (regional and hospital level data available from years 19992007) Hip and knee replacements (regional and hospital level data available from years 1998-2007) Very low birth weight infants (regional and hospital level data available from years 2000-2007) Schizophrenia (regional and hospital level data available from years 1995-2001 cohorts) Stroke (regional and hospital level data available from years 1999-2007) Finland 25.05.2010 One year hospital cost of AMI patients (€/patient) by hospital disrircts in 2007 . Risk adjusted figures. 18000 16000 14000 12000 10000 8000 6000 4000 2000 0 25.05.2010 Finland One year hospital mortality among AMI patients (%) by hospital districts 2007 (risk adjusted figures, 95 % confidence intervals) 30 28 26 24 22 20 18 16 14 12 10 25.05.2010 Finland One year cost (€/patient) ja one year mortality (%) by hospital districts of AMI patients (risk adjusted figures) 18000 One year cost, €/patient 17000 16000 15000 R² = 0,0574 14000 13000 12000 11000 10000 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 One year mortality % 25.05.2010 Finland 22 23 24 25 Conclusions • Internationally: Finnish decentralised hospital system rather effective producing services, but not yet information on its performance in outcomes • Great regional and hospital level differences in efficiency, cost and outcomes. • New initiatives from government (patient choice) without considering how financing will be arranged Finland • Benchmarking of hospital efficiency and outcomes well developed. Originally initiated by researchers and afterward implemented together with producers (hospitals districts) using financial support from research funds. The information has been increasingly used in local and national decision making • 25.05.2010