Review of CHEM 121
advertisement
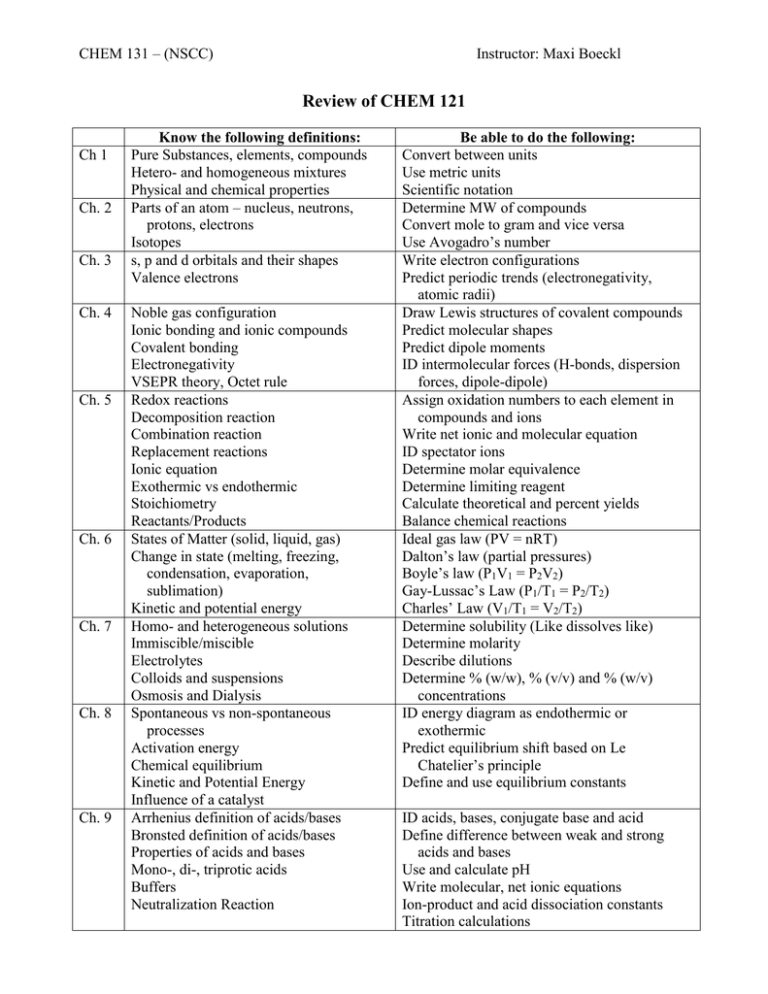
CHEM 131 – (NSCC) Instructor: Maxi Boeckl Review of CHEM 121 Ch 1 Ch. 2 Ch. 3 Ch. 4 Ch. 5 Ch. 6 Ch. 7 Ch. 8 Ch. 9 Know the following definitions: Pure Substances, elements, compounds Hetero- and homogeneous mixtures Physical and chemical properties Parts of an atom – nucleus, neutrons, protons, electrons Isotopes s, p and d orbitals and their shapes Valence electrons Noble gas configuration Ionic bonding and ionic compounds Covalent bonding Electronegativity VSEPR theory, Octet rule Redox reactions Decomposition reaction Combination reaction Replacement reactions Ionic equation Exothermic vs endothermic Stoichiometry Reactants/Products States of Matter (solid, liquid, gas) Change in state (melting, freezing, condensation, evaporation, sublimation) Kinetic and potential energy Homo- and heterogeneous solutions Immiscible/miscible Electrolytes Colloids and suspensions Osmosis and Dialysis Spontaneous vs non-spontaneous processes Activation energy Chemical equilibrium Kinetic and Potential Energy Influence of a catalyst Arrhenius definition of acids/bases Bronsted definition of acids/bases Properties of acids and bases Mono-, di-, triprotic acids Buffers Neutralization Reaction Be able to do the following: Convert between units Use metric units Scientific notation Determine MW of compounds Convert mole to gram and vice versa Use Avogadro’s number Write electron configurations Predict periodic trends (electronegativity, atomic radii) Draw Lewis structures of covalent compounds Predict molecular shapes Predict dipole moments ID intermolecular forces (H-bonds, dispersion forces, dipole-dipole) Assign oxidation numbers to each element in compounds and ions Write net ionic and molecular equation ID spectator ions Determine molar equivalence Determine limiting reagent Calculate theoretical and percent yields Balance chemical reactions Ideal gas law (PV = nRT) Dalton’s law (partial pressures) Boyle’s law (P1V1 = P2V2) Gay-Lussac’s Law (P1/T1 = P2/T2) Charles’ Law (V1/T1 = V2/T2) Determine solubility (Like dissolves like) Determine molarity Describe dilutions Determine % (w/w), % (v/v) and % (w/v) concentrations ID energy diagram as endothermic or exothermic Predict equilibrium shift based on Le Chatelier’s principle Define and use equilibrium constants ID acids, bases, conjugate base and acid Define difference between weak and strong acids and bases Use and calculate pH Write molecular, net ionic equations Ion-product and acid dissociation constants Titration calculations










