Lab 19 Cranial Nerves & Brain dissection
advertisement

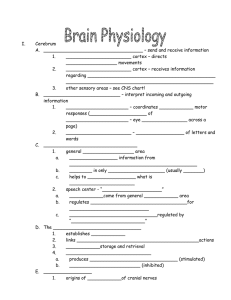
Lab 19 Cranial Nerves & Brain dissection Today • • • • • Intro to the brain The cranial nerves Human and sheep brain anatomy Get to work CLEAN UP Practical 4 • Thurs 12/6 • 50 points: about half brain models and half book figures (with a few fresh brains too) • Know: – List of brain parts on objectives (names and locations only; you will need to know functions on the exam though) – The 12 cranial nerves: names, locations, & functions (shown in blue in this lecture) Brief intro to the brain External structures • cerebral hemispheres • cerebrum • midbrain • cerebellum • pons • medulla • central sulcus • precentral gyrus • postcentral gyrus • lateral sulcus • longitudinal fissure • frontal lobe • parietal lobe • occipital lobe • temporal lobe Internal structures: • corpus callosum • basal ganglia (nucleus) – – • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Caudate Putamen internal capsule thalamus hypothalamus hippocampus amygdala pineal gland pituitary gland reticular formation fornix substantia nigra cingulate gyrus optic chiasm lateral ventricles mammilary bodies corpora quadrigemina – – inferior colliculus superior colliculus Major Regions and Landmarks Figure 14–1 Regions of the Adult Brain • Telencephalon (cerebrum) – cortex, white matter, and basal nuclei • Diencephalon – thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus • Mesencephalon –midbrain (brain stem) • Metencephalon – pons (brain stem), cerebellum • Myelencephalon – medulla oblongata (brain stem) Some terms • nucleus: collection of neuron cell bodies in the CNS • tract: collection of axons in the CNS • ganglia: collection of neuron cell bodies in the PNS • nerve: collection of axons in the PNS – Cranial nerves – Spinal nerves Tour through the brain • From caudal/inferior to rostral/superior The Brain Stem • Includes: – mesencephalon (midbrain) – pons – medulla oblongata – Note: some consider the diencephalon part of the brain stem as well Anatomy: Brain stem Most cranial nerves are located in the brain stem Posterior view Medulla Oblongata Cerebellum Cerebellum – side view Mesencephalon Mesencephalon The Diencephalon • • • • Thalamus Hypothalamus Pineal gland Pituitary gland Figure 14–5a Telencephalon • Cerebrum – Largest part of brain, includes huge wrinkly cerebral hemispheres • Basal nuclei The Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Figure 14–14b, c Lateral Ventricles The Limbic System Figure 14–11a The Cerebral Cortex 4 Lobes: frontal parietal temporal occipital Figure 14–12b Cerebral Cortex landmarks • • • • • • Lateral sulcus Longitudinal fissure Central sulcus Precentral gyrus (primary motor) Postcentral gyrus (primary sensory) Association areas are for integrating information Motor and Sensory Areas of the Cortex • Central sulcus separates motor and sensory areas Figure 14–15a Cranial Nerves Cranial Nerves • 12 pairs connected to brain Figure 14–18 Cranial Nerves Figure 13.5a Cranial Nerves • Twelve pairs of cranial nerves arise from the brain • They have sensory, motor, or both sensory and motor functions (mixed) • Each nerve is identified by a number (I through XII) and a name • Four cranial nerves carry parasympathetic fibers that serve muscles and glands 3 main types of Cranial Nerves Sensory nerves: – carry somatic (touch) or special sensory information Motor nerves: – axons of somatic motor neurons Mixed nerves: – mixture of motor and sensory fibers Cranial Nerves • • • • • • I – Olfactory II – Optic III – Occulomotor IV – Trochlear V – Trigeminal VI – Abducens • • • • • • VII – Facial VIII – Vestibulococlear IX – Glossopharyngeal X – Vagus XI – Accessory XII – Hypoglossal On Occasion, Our Trusty Truck Acts Funny; Very Good Vehicle Anyhow Summary of Function of Cranial Nerves Figure 13.5b You need to learn: • • • • Names Numbers Locations Main functions (in blue) Lateral view Anterior View The Olfactory Nerves (I) Figure 14–19 Olfactory Nerves (I) • Don’t originate or enter brainstem • Primary function: – special sensory (smell) • Arises from the olfactory epithelium • Passes through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone • Fibers run through the olfactory bulb and terminate in the primary olfactory cortex • Functions solely by carrying afferent impulses for the sense of smell The Optic Nerves (II) Figure 14–20 Optic Nerves (II) • Enter diencephalon • Primary function: – special sensory (vision) • Arises from the retina of the eye • Optic nerves pass through the optic canals and converge at the optic chiasm • They continue to the thalamus (diencephalon) where they synapse CNs III,IV,VI • All motor only • All innervate eye muscles The Oculomotor Nerves (III) Figure 14–21 Oculomotor Nerves (III) • Primary function: – motor (many eyeball movements, pupil constriction, controlling lens shape) • Origin: – mesencephalon • Destination: – somatic motor: 4 extrinsic eye muscles: – visceral motor: parasympathetic NS cell bodies in the ciliary ganglion, got to intrinsic eye muscles The Trochlear Nerves (IV) Figure 14–21 Trochlear Nerves (IV) • Smallest CN • Primary function: – motor (eye movement: looking down) • Origin: – mesencephalon • Destination: – superior oblique muscle (that’s it!) The Abducens Nerves (VI) Figure 14–21 The Abducens Nerves (VI) • Primary function: – motor (eye movement: looking to the side) • Origin: – pons • Destination: – lateral rectus muscle (just one eye muscle) The Trigeminal Nerves (V) Figure 14–22 Trigeminal Nerves (V) • Largest CN – it’s huge! • Primary function: – mixed (sensory and motor) to face All sensory from face; motor for chewing • Three branches – ophthalmic branch (sensory) – maxillary branch (sensory) – mandibular branch (sensory and motor) • Destinations – sensory: sensory nuclei in pons – motor: muscles of mastication The Facial Nerves (VII) Figure 14–23 Facial Nerves (VII) • Primary function: – mixed (sensory and motor) to face Motor to facial muscles; taste • sensory: – taste receptors on anterior 2/3 of tongue • motor: – Facial muscles, parasympathetic to lacrimal and salivary glands **Bell’s Palsy The Vestibulocochlear Nerves (VIII) Figure 14–24 Vestibulocochlear Nerves (VIII) • Primary function: special sensory – vestibular branch: • balance and equilibrium – cochlear branch: • hearing • Origin: receptors of inner ear • Destination: nuclei in both pons and medulla The Glossopharyngeal Nerves (IX) Figure 14–25 Glossopharyngeal Nerves (IX) • Primary function: – mixed (sensory and motor) to head and neck Mainly: swallowing, some salivary gland function • Origins: – sensory: • posterior 1/3 of tongue • part of pharynx and palate • carotid bodies (blood pressure/CO2 sensors) – motor: • motor nuclei of medulla The Vagus Nerves (X) Figure 14–26 Vagus Nerves (X) • Primary function: – mixed (sensory and motor) of thorax and abdomen – Only CN that extends beyond head and neck – “Mr. parasympathetic” motor to para-NS – Runs outside of spinal cord to visceral organs – Originates in medulla The Accessory Nerves (XI) Figure 14–27 Accessory Nerves (XI) • Primary function: – motor to muscles of neck and upper back • Origin: – motor nuclei of spinal cord and medulla oblongata • Two roots: – The spinal root passes upward into the cranium via the foramen magnum – The accessory nerve leaves the cranium via the jugular foramen • Destinations: – voluntary muscles of palate, pharynx, and larynx – sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles The Hypoglossal Nerves (XII) Figure 14–27 Hypoglossal Nerves (XII) • Primary function: – motor (tongue movements) • Origin: – motor nuclei of medulla • Destination: – muscles of tongue which aid in speech Gross Anatomy of the human brain Human brain Midsagittal Coronal Inferior View Sheep brain Sheep brain inferior view Midsagittal Anterior View Follow instructions in lab book • look at the meninges • start by examining the external brain – Ventral surface first, then dorsal • then look internally without cutting (fig 19.12) • cut it midsagittally to see inside • Try a coronal cut to see what you can find • Review Sheet due next Thursday To find: • Meninges • Cranial nerves I – XII (?) • fissures and sulci on surface, lobes • pineal gland • corpora quadrigemina (part of midbrain) • midbrain • pons • medulla • cerebellum • mamillary body (just one) • optic chiasm • • • • corpus callosum (central) fornix lateral ventricles choroid plexus (inside ventricles) • hypothalmus • “pituitatry gland” (hangs off hypothalamus • arbor vitae (inside cerebellum)