Cell Reproduction • Check this out!! • Breast cancer cells dividing: •
advertisement

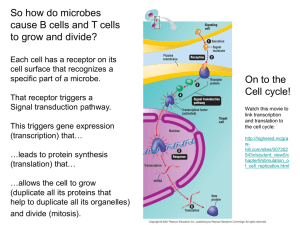
Cell Reproduction • Check this out!! • Breast cancer cells dividing: • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hm03 rCUODqg&NR=1&feature=fvwp The Cell Cycle – Eukaryotic cells that grow and divide undergo an orderly sequence of events called the cell cycle. – The cell cycle consists of two distinct phases: • Interphase – Cell growth – Sub-phases: » G1 » S phase » G2 • Mitotic phase – Cell division From One gene to 25,000 genes – OK, we’ve talked about how to transcribe and translate one gene found on the DNA in our nuclei into a functioning protein. But we have more than just one gene…. – Almost all of the genes of a eukaryotic cell • Are located on chromosomes in the cell nucleus. Transcription and Translation occur all throughout Interphase: when the cell is growing and duplicating all of its cell structures and organelles!! Eukaryotic Chromosomes – Each eukaryotic chromosome contains one very long DNA molecule, • Typically bearing thousands of genes. – The number of chromosomes in a eukaryotic cell • Depends on the species. – Detailed representations of DNA • Notice that the bases pair in a complementary fashion. DNA Replication – When a cell or whole organism reproduces, a complete set of genetic instructions must pass from one generation to the next. – This happens during S phase Figure 10.8 The Cell Cycle – Eukaryotic cells that grow and divide undergo an orderly sequence of events called the cell cycle. – The cell cycle consists of two distinct phases: • Interphase – Cell growth – Sub-phases: » G1 » S phase » G2 • Mitotic phase – Cell division Mitosis and Cytokinesis – Mitosis • Is the division of the chromosomes. • Is preceded by interphase. From movie folder play: - AnimalMitosis_SV.mpg – Chromosomes • Are made of chromatin, a combination of DNA and protein molecules. • Are not visible in a cell until cell division occurs. – The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding. – Before a cell divides, it duplicates all of its chromosomes, resulting in two copies called sister chromatids. – When the cell divides, the sister chromatids separate from each other. G1 phase S phase G2 phase M phase Figure 8.8.1 – Mitosis consists of four distinct phases: • • • • Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Figure 8.8.2 Figure 8.8.3 – Cytokinesis • Typically occurs during telophase. • Is the division of the cytoplasm. • Is different in plant and animal cells. Figure 8.9b http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SlgV_zoHQxE&p=AC919FD768804 41F&playnext=1&index=39 Cancer Cells: Growing Out of Control – Normal plant and animal cells have a cell cycle control system. – Cancer is a disease of the cell cycle. – Cancer cells do not respond normally to the cell cycle control system. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hm03rCUO Dqg&NR=1&feature=fvwp – Cancer cells can form tumors, • Abnormally growing masses of body cells. – If a tumor is malignant, • It can spread to other parts of the body. Cancer Treatment – Cancer treatment can involve • Radiation therapy, which damages DNA and disrupts cell division. • Chemotherapy, which uses drugs that disrupt cell division. • Turn and talk: How would damaging the DNA of a cell disrupt cell division? – Cancer cells are often grown in culture for study. Cancer Prevention and Survival – Cancer prevention includes changes in lifestyle: • • • • • • Not smoking Exercising adequately Avoiding exposure to the sun Eating a high-fiber, low-fat diet Visiting the doctor regularly Performing regular self-examinations