Cell Division and Mitosis
advertisement

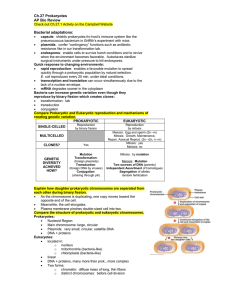
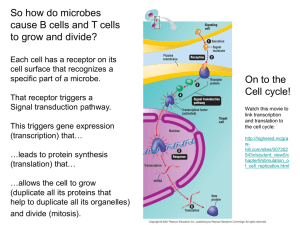
Cell Division & Mitosis Cell division varies between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells are single celled organisms. Before the bacterium can divide there must be two copies of its DNA. This occurs by the DNA molecule unzipping itself into two different strands, which will form two separate interdependent strands. Once the DNA has replicated itself and the cell has grown to an appropriate size, the bacterium splits into two equal halves through a process called binary fission. Draw a picture of Binary Fission Asexual Reproduction Eukaryotic cells undergo nuclear division ( asexual reproduction). The life of a eukaryotic cell is traditionally diagrammed as a cell cycle. 1. G1 Phase: rapid growth and metabolic activity, protein synthesis, cell spends most time in this phase. S phase: DNA synthesis and replication (copies), chromosomes duplicate and other cellular organelles. G2 Phase: centrioles replicate; cell prepares for division M phase: MITOSIS-period of nuclear division in which two daughter nuclei are formed, each containing a complete set of chromosomes. C Phase: Cytokinesis-process following mitosis or meiosis in which the cells cytoplasm divides and separates into new cells. Division of the Cytoplasm Cells Alive Cell Cycle