Lecture #2 Cellular Anatomy
advertisement

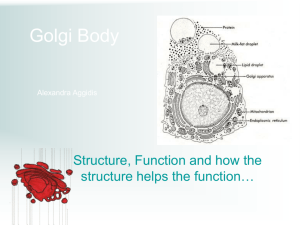
Lecture #2 Cellular Anatomy The Eukaryotic Cell ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) Rough ER Smooth ER Nuclear envelope Nucleolus NUCLEUS Chromatin Flagelium Plasma membrane Centrosome CYTOSKELETON Microfilaments Intermediate filaments Ribosomes Microtubules Microvilli Golgi apparatus Peroxisome Mitochondrion Lysosome In animal cells but not plant cells: Lysosomes Centrioles Flagella (in some plant sperm) The Nucleus Nucleus Nucleus 1 µm Nucleolus Chromatin Nuclear envelope: Inner membrane Outer membrane Nuclear pore Pore complex Rough ER Surface of nuclear envelope. TEM of a specimen prepared by a special technique known as freeze-fracture. 0.25 µm 1 µm Ribosome Close-up of nuclear envelope Pore complexes (TEM). Each pore is ringed by protein particles. Nuclear lamina (TEM). The netlike lamina lines the inner surface of the nuclear envelope. The Nuclear Envelope Ribosomes Ribosomes ER Cytosol Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Free ribosomes Bound ribosomes Large subunit 0.5 µm TEM showing ER and ribosomes Small subunit Diagram of a ribosome The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Smooth ER Rough ER Nuclear envelope ER lumen Cisternae Ribosomes Transport vesicle Smooth ER Transitional ER Rough ER 200 µm The Golgi apparatus Golgi apparatus cis face (“receiving” side of Golgi apparatus) 1 Vesicles move 2 Vesicles coalesce to 6 Vesicles also from ER to Golgi form new cis Golgi cisternae transport certain Cisternae proteins back to ER 3 Cisternal maturation: Golgi cisternae move in a cisto-trans direction 5 Vesicles transport specific proteins backward to newer Golgi cisternae 0.1 0 µm 4 Vesicles form and leave Golgi, carrying specific proteins to other locations or to the plasma membrane for secretion trans face (“shipping” side of Golgi apparatus) TEM of Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Nucleus 1 µm Lysosome containing two damaged organelles 1µm Mitochondrion fragment Peroxisome fragment Lysosome Lysosome contains Food vacuole fuses Hydrolytic active hydrolytic enzymes digest with lysosome enzymes food particles Digestive enzymes Lysosome fuses with vesicle containing damaged organelle Lysosome Plasma membrane Lysosome Lysosome Hydrolytic enzymes digest organelle components Digestion Food vacuole (a) Phagocytosis: lysosome digesting food Digestion Vesicle containing damaged mitochondrion (b) Autophagy: lysosome breaking down damaged organelle Peroxisomes Chloroplast Peroxisome Mitochondrion 1 µm Summary 1 Nuclear envelope is connected to rough ER, which is also continuous with smooth ER Nucleus Rough ER Smooth ER Nuclear envelope 3 Summary 1 Nuclear envelope is connected to rough ER, which is also continuous with smooth ER Nucleus Rough ER 2 Membranes and proteins produced by the ER flow in the form of transport vesicles to the Golgi Smooth ER cis Golgi Nuclear envelope Transport vesicle 3 Golgi pinches off transport vesicles and other vesicles that give rise to lysosomes and vacuoles trans Golgi 4 Lysosome available 5 Transport vesicle carries for fusion with another proteins to plasma vesicle for digestion membrane for secretion Summary 1 Nuclear envelope is connected to rough ER, which is also continuous with smooth ER Nucleus Rough ER 2 Membranes and proteins produced by the ER flow in the form of transport vesicles to the Golgi Smooth ER cis Golgi Nuclear envelope Transport vesicle 3 Golgi pinches off transport vesicles and other vesicles that give rise to lysosomes and vacuoles trans Golgi Plasma membrane 4 Lysosome available 5 Transport vesicle carries 6 Plasma membrane expands for fusion with another proteins to plasma by fusion of vesicles; proteins vesicle for digestion membrane for secretion are secreted from cell Mitochondria Mitochondrion Intermembrane space Outer membrane Free ribosomes in the mitochondrial matrix Inner membrane Cristae Matrix Mitochondrial DNA 100 µm Plant Cells Nuclear envelope Nucleolus Chromatin NUCLEUS Centrosome Rough endoplasmic reticulum Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes ( small brown dots ) Central vacuole Tonoplast Golgi apparatus Microfilaments Intermediate filaments Microtubules Mitochondrion Peroxisome Plasma membrane Cell wall Wall of adjacent cell Chloroplast Plasmodesmata CYTOSKELETON The Central Vacuole Central vacuole Cytosol Tonoplast Nucleus Central vacuole Cell wall Chloroplast 5 µm Chloroplasts Chloroplast Ribosomes Stroma Chloroplast DNA Inner and outer membranes Granum 1 µm Thylakoid