Adequacy of Linear Regression Models Transforming Numerical Methods Education for STEM
advertisement
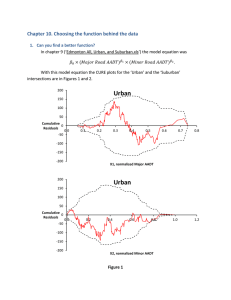
Adequacy of Linear Regression Models http://numericalmethods.eng.usf.edu Transforming Numerical Methods Education for STEM Undergraduates 7/12/2016 http://numericalmethods.eng.usf.edu 1 Data y vs x 6.5 6 5.5 5 y 4.5 4 3.5 3 2.5 2 -350 -300 -250 -200 -150 -100 x -50 0 50 100 Is this adequate? y vs x 7 6.5 6 5.5 y 5 4.5 4 3.5 3 2.5 2 -350 -300 -250 -200 -150 -100 -50 0 50 100 x Straight Line Model Quality of Fitted Data • Does the model describe the data adequately? • How well does the model predict the response variable predictably? Linear Regression Models • Limit our discussion to adequacy of straight-line regression models Four checks 1. Plot the data and the model. 2. Find standard error of estimate. 3. Calculate the coefficient of determination. 4. Check if the model meets the assumption of random errors. Example: Check the adequacy of the straight line model for given data a0 a1T T (F) α (μin/in/F) -340 2.45 -260 3.58 -180 4.52 -100 5.28 -20 5.86 60 6.36 END 1. Plot the data and the model Data and model (T ) 6.0325 0.0096964T α T (F) (μin/in/F) 2.45 -260 3.58 -180 4.52 -100 5.28 -20 5.86 6.5 6 5.5 5 -340 7 4.5 4 3.5 3 2.5 60 6.36 2 -350 -300 -250 -200 -150 -100 T -50 0 50 100 END 2. Find the standard error of estimate Standard error of estimate s / T Sr n2 n S r ( i a0 a1Ti ) i 1 2 Standard Error of Estimate (T ) 6.0325 0.0096964T Ti i a0 a1Ti i a0 a1Ti -340 -260 -180 -100 -20 60 2.45 3.58 4.52 5.28 5.86 6.36 2.7357 3.5114 4.2871 5.0629 5.8386 6.6143 -0.28571 0.068571 0.23286 0.21714 0.021429 -0.25429 Standard Error of Estimate Sr 0.25283 s / T Sr n2 0.25283 62 0.25141 Standard Error of Estimate 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 -350 -300 -250 -200 -150 -100 T Scaled Residual -50 0 50 100 i a0 a1Ti s / T Scaled Residuals Residual Scaled Residual Standard Error of Estimate Scaled Residual i a0 a1Ti s / T 95% of the scaled residuals need to be in [-2,2] Scaled Residuals s / T 0.25141 Ti αi Residual -340 -260 -180 -100 -20 60 2.45 3.58 4.52 5.28 5.86 6.36 -0.28571 0.068571 0.23286 0.21714 0.021429 -0.25429 Scaled Residual -1.1364 0.27275 0.92622 0.86369 0.085235 -1.0115 END 3. Find the coefficient of determination Coefficient of determination n S t i 2 i 1 n S r i a 0 a1Ti 2 i 1 St S r r St 2 Sum of square of residuals between data and mean n S t yi y 2 i 1 ( xn , y n ) xi , y i y _ yy x2 , y 2 x1 , y1 _ yy x3 , y 3 x Sum of square of residuals between observed and predicted n S r yi a0 a1 xi 2 i 1 xi , y i y ( xn , y n ) Ei yi a0 a1 xi x2 , y 2 x3 , y 3 x1 , y1 x Limits of Coefficient of Determination St S r r St 2 0 r 1 2 Calculation of St Ti -340 -260 -180 -100 -20 60 i i 2.45 3.58 4.52 5.28 5.86 6.36 -2.2250 -1.0950 0.15500 0.60500 1.1850 1.6850 4.6750 St 10.783 Calculation of Sr Ti i a0 a1Ti i a0 a1Ti -340 -260 -180 -100 -20 60 2.45 3.58 4.52 5.28 5.86 6.36 2.7357 3.5114 4.2871 5.0629 5.8386 6.6143 -0.28571 0.068571 0.23286 0.21714 0.021429 -0.25429 Sr 0.25283 Coefficient of determination St S r r St 2 10.783 0.25283 10.783 0.97655 Correlation coefficient r St S r St 0.98820 How do you know if r is positive or negative ? What does a particular value of |r| mean? 0.8 to 1.0 - Very strong relationship 0.6 to 0.8 - Strong relationship 0.4 to 0.6 - Moderate relationship 0.2 to 0.4 - Weak relationship 0.0 to 0.2 - Weak or no relationship Caution in use of r2 • Increase in spread of regressor variable (x) in y vs. x increases r2 • Large regression slope artificially yields high r2 • Large r2 does not measure appropriateness of the linear model • Large r2 does not imply regression model will predict accurately Final Exam Grade Final Exam Grades 100 Final Exam Grade 90 80 70 60 50 40 0 10 20 30 Student No 40 50 60 Final Exam Grade vs Pre-Req GPA y = 9.8669x + 41.75 R² = 0.2227 R=0.4719 100 FInal Exam Scores 90 80 70 60 50 40 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 Pre-Requisite GPA 3.5 4 4.5 5 END 4. Model meets assumption of random errors Model meets assumption of random errors • • • • Residuals are negative as well as positive Variation of residuals as a function of the independent variable is random Residuals follow a normal distribution There is no autocorrelation between the data points. Therm exp coeff vs temperature T 60 40 20 0 -20 -40 -60 -80 α 6.36 6.24 6.12 6.00 5.86 5.72 5.58 5.43 T -100 -120 -140 -160 -180 -200 -220 -240 α 5.28 5.09 4.91 4.72 4.52 4.30 4.08 3.83 T -280 -300 -320 -340 α 3.33 3.07 2.76 2.45 Data and model 6.0248 0.0093868T 7 6.5 6 5.5 5 4.5 4 3.5 3 2.5 2 -350 -300 -250 -200 -150 -100 T -50 0 50 100 Plot of Residuals 0.3 0.2 Residual 0.1 0 -0.1 -0.2 -0.3 -0.4 -350 -300 -250 -200 -150 -100 T -50 0 50 100 Histograms of Residuals Check for Autocorrelation • Find the number of times, q the sign of the residual changes for the n data points. • If (n-1)/2-√(n-1) ≤q≤ (n-1)/2+√(n-1), you most likely do not have an autocorrelation. ( 22 1) 22 1 22 1 q 22 1 2 2 5.9174 q 15.083 Is there autocorrelation? 0.3 0.2 Residual 0.1 0 -0.1 5.9174 q 15.083 -0.2 -0.3 -0.4 -350 -300 -250 -200 -150 -100 T -50 0 50 100 y vs x fit and residuals n=40 (n-1)/2-√(n-1) ≤p≤ (n-1)/2+√(n-1) Is 13.3≤21≤ 25.7? Yes! y vs x fit and residuals n=40 (n-1)/2-√(n-1) ≤p≤ (n-1)/2+√(n-1) Is 13.3≤2≤ 25.7? No! END What polynomial model to choose if one needs to be chosen? First Order of Polynomial -6 7 Polynomial Regression of order 1 x 10 6.5 5.5 4.5 4 0 2 5 1 m y = a +a *x+a *x 2+.....+a *x m 6 3.5 3 2.5 2 -350 -300 -250 -200 -150 -100 -50 0 50 100 Second Order Polynomial -6 7 Polynomial Regression of order 2 x 10 6.5 5.5 4.5 4 0 2 5 1 m y = a +a *x+a *x 2+.....+a *x m 6 3.5 3 2.5 2 -350 -300 -250 -200 -150 -100 x -50 0 50 100 Which model to choose? y vs x 7 6.5 6 5.5 y 5 4.5 4 3.5 3 2.5 2 -350 -300 -250 -200 -150 -100 x -50 0 50 100 Optimum Polynomial -14 Optimum Order of Polynomial x 10 5 Sr[n-(m+1)] 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 Order of Polynomial, m 5 6 THE END Effect of an Outlier Effect of Outlier 25 y = 2x R2 = 1 20 15 10 5 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Effect of Outlier 60 y = 3.2727x - 5.0909 R2 = 0.6879 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 -10 2 4 6 8 10 12