BE SURE TO WRITE YOUR NAME ON YOUR ANSWER SHEET!! IMPORTANT
advertisement

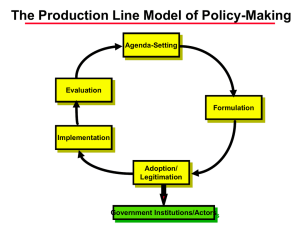
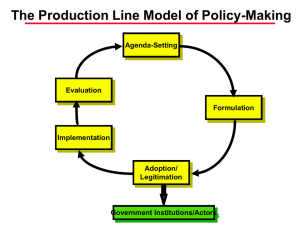
BE SURE TO WRITE YOUR NAME ON YOUR ANSWER SHEET!! IMPORTANT: MAKE ALL ERASURES COMPLETELY - IT IS YOUR RESPONSIBILITY TO CLEARLY INDICATE YOUR CHOSEN ANSWER. RESPONSES THAT ARE NOT COMPLETELY ERASED WILL BE COUNTED AS INCORRECT. THIS EXAM IS WORTH 100 POINTS. Temple College Government 2301 Fall, 1998 Exam #1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. INSTRUCTIONS: Answer each of the following multiple choice questions by marking the letter on your scan-tron form that corresponds to the BEST response. 71 questions/1.41 points each/100 points total. 1. Which of the following systems model concepts describes authoritative decisions and actions (generally thought of as benefits or deprivations)? a. environments b. input structures c. outputs d. feedback 2. According to systems model terminology, which of the following would be an example of a CONVERSION STRUCTURE? a. the Republican Party b. the National Rifle Association c. the news media d. the United States Congress 3. Which of the following systems model concepts describes social, economic, physical or other sets of variables that are external to a political system but affect its operation? a. environments b. input structures c. outputs d. feedback 4. According to systems model terminology, the “channels, linkages, and connections from the environments to government institutions” are known as a. input structures. b. feedback. c. outputs. d. conversion structures. 5. According to the authors of your AMERICAN GOVERNMENT text, GOVERNMENT refers to a. any group of people involved in politics. b. the structured arrangements which produce decisions resolving conflict. c. only a predetermined set of countries that recognize each other as having legal power. d. any person or group of persons who have power but who respect the right of all people to be free. 6. According to the authors of your AMERICAN GOVERNMENT text, one reason that citizens obey laws is that government a. has a monopoly on law-making. b. only passes laws that are acceptable to the majority. c. has legitimate authority to make the laws. d. always protects the minority viewpoint. 7. A(n) __________ government exists when citizens generally recognize the decisions it makes and the policies it carries out; a(n) _______________ government exists when it coerces or forces citizens to comply with policy mandates and/or does not take citizen preferences into account when making policy decisions. a. authoritarian; dictatorship b. authoritative; authoritarian c. authoritative; illegitimate d. legitimate; illegitimate 8. The process that determines “who gets what, when, and how” is known as a. decision-making. b. political science. c. politics. d. paternalism. 9. Harold Laswell’s definition in question #8 implies that a. people are in conflict over valued things in society. b. societies have a set of procedures to resolve the question of “who gets what, when, and how.” c. individuals are anti-social. d. both a and b. 10. Which of the following defines POLITICS? a. “who gets what, when, and how.” b. “the authoritative allocation of valued things.” c. “the competitive process engaged in a society to allocate scarce resources and determine priorities.” d. All of the above are definitions of politics. 11. According to the authors of your AMERICAN GOVERNMENT text, decisions which are AUTHORITATIVE are those a. which can be backed up by legitimate power. b. that are made with the approval of a majority of the public. c. which can be repealed in a referendum. d. that are made by a small percentage of society. 12. According to the authors of your AMERICAN GOVERNMENT text, the concept of COMPLIANCE means a. accepting and carrying out authoritative decisions. b. the ability to cause others to modify their behavior. c. the ability to get others to disobey the dictates of the ruler. d. both b and c. 13. Suppose a city council passed an ordinance in 1990 which prohibits individuals and businesses from posting signs (i.e., garage sale signs, small business advertising) on right-of-ways, intersections, street lights, telephone poles, city property, etc. Because Code Enforcement (the city department responsible for enforcement of the ordinance) does not have enough manpower, it has not issued a single citation for violation of the ordinance in seven years. Consequently, these signs are pervasive around the city. What important principle of public policy does this example illustrate? a. Public policies NEVER work. b. City governments have little authority to make public policy decisions. c. Public policies consist of decisions AND action - the action of government determines the content of public policy. d. Public policies are what government intends to do. 14. In class, we introduced a public policy classification scheme. Which of the following questions must be answered in order to classify a policy under this scheme? 1. Who is the primary target group? 2. Why is government implementing the policy? 3. What are the goals of the policy? 4. What is the activity of government with respect to the primary target group [what is government doing to or for the primary target group]? 5. Who are the secondary target groups? a. 1, 3, and 5 b. 1, 2, and 4 c. 2 and 4 d. 1 and 4 15. In which class of public policy does government set standards for behavior, inspect for compliance with the standards, and punish for non-compliance? a. resource extractive b. regulatory c. redistributive d. internal organization and management 16. Under the policy classification scheme introduced in class, which of the following is NOT one of the five activities that government can undertake with respect to a primary target group? a. give b. take c. symbolize d. lie 17. A city council passes and the police enforce an ordinance imposing fines on the parents of minor children who are “on the streets” past a 1:00 a.m. curfew. This is an example of which class of policy? a. resource extractive b. symbolic c. regulatory d. resource extractive 18. The United States denies the People’s Republic of China most favored nation trading status as a result of China’s alleged human rights violations. This is an example of which class of policy? a. resource extractive b. symbolic c. regulatory d. resource extractive 19. Which of the following sets of stages in the policy-making process is listed in the correct logical order? a. evaluation, adoption, implementation, formulation, designation b. formulation, adoption, designation, implementation, evaluation c. agenda-setting, adoption, designation, implementation, evaluation d. agenda-setting, formulation, adoption, implementation, evaluation 20. In which stage of the policy-making process are problem identification (perception) and priority-setting important activities? a. agenda-setting b. designation c. adoption d. formulation 21. Which of the following BEST illustrates implementation? a. The president gives a speech calling for welfare reform. b. The Supreme Court upholds a city fire department’s affirmative action program. c. The Pentagon proposes new procedures for making defense-related purchases. d. The Occupational Safety And Health Administration (OSHA) inspects a plastics factory looking for levels of vinyl chloride in excess of federal standards. 22. The stage of the policy-making process that involves “choosing an official course of action from among alternative policy strategies” is a. implementation. b. designation. c. adoption. d. formulation. 23. Which stage of the policy-making process exclusively involves governmental actors? a. agenda-setting b. designation c. adoption d. formulation 24. The United States Congress passes, and the president signs, a bill forbidding Medicaid funds from being used to finance abortions for poor women. This is an example of which stage of the policy-making process? a. evaluation b. adoption c. implementation d. designation 25. A city health director designs an educational program to inform teenagers about the dangers of “unprotected sex.” The city council must vote next week whether to fund the program. This is an example of which stage of the policymaking process? a. implementation. b. formulation. c. adoption. d. evaluation. 26. The Texas Sunset Advisory Commission reviews the performance of a state agency and recommends to the state legislature that the agency be not be funded during the next fiscal year. This is an example of which stage of the policy-making process? a. implementation. b. designation. c. adoption. d. evaluation. 27. The U.S. Supreme Court strikes down a law school’s affirmative action admissions program as unconstitutional. This is an example of which stage of the policy-making process? a. implementation. b. designation. c. agenda-setting. d. evaluation. 28. The star quarterback on the local high school football team fails a course and is ruled by school administrators to be ineligible to play football under the provisions of the “no-pass/no-play” law. This is an example of which stage of the policy-making process? a. implementation. b. designation. c. agenda-setting. d. evaluation. 29. A president gives a speech in which he claims that violent juvenile crime is out of control and the government needs to respond with decisive action. This is an example of which stage of the policy-making process? a. implementation. b. agenda-setting. c. adoption. d. evaluation. 30. A medical doctor writes an article calling for swifter approval of AIDS drugs by the Food and Drug Administration. This is an example of which stage of the policy-making process? a. implementation. b. designation. c. adoption. d. evaluation. 31. The board of a Texas school district votes on a proposal to include a course on moral values in the high school curriculum. This is an example of which stage of the policy-making process? a. implementation. b. designation. c. adoption. d. formulation. 32. Inmates in the Texas Department of Corrections file a class action lawsuit in state district court in an attempt to force the state to deal with the issue of prison over-crowding. This is an example of which stage of the policy-making process? a. agenda-setting b. implementation c. adoption d. formulation 33. The results of a vote by a city council require that benefits under the city’s health plan be extended to the “live-in” (unmarried) partners of city employees, irrespective of sexual orientation. This is an example of which stage of the policy-making process? a. agenda-setting b. adoption c. implementation d. designation 34. The National Endowment for the Humanities awards a research grant to a team of historians and anthropologists to study the ancestral claims of certain native American tribes to “ceremonial” lands. This is an example of which type or class of public policy? a. resource allocative b. resource extractive c. regulatory d. internal organization and management 35. The City Health Department inspects a local restaurant and finds “slime in the ice machine,” inadequate refrigeration for perishable foods, and roach and rodent droppings on cabinet shelves, the floor, and food containers. This is the third round of violations for this restaurant. The Health Department closes down the establishment until standards are met. This is an example of which type or class of public policy? a. resource allocative b. resource extractive c. regulatory d. internal organization and management 36. Once every ten years (subsequent to the decennial census), the 450 seats in the United States House of Representatives are reapportioned to reflect population shifts. Legislatures in each of the 50 states redraw congressional district lines (within their states) so that each district contains (roughly) the same number of people. As a result of the 1990 census, the number of representatives allotted to Texas increased from 28 to 30. The Texas legislature last redrew district lines in 1991 to account for this change. Redrawing congressional district lines by state legislatures is an example of which type or class of public policy? a. resource allocative b. resource extractive c. regulatory d. internal organization and management 37. The Federal Trade Commission enforces the standards of the Fair Credit Reporting Act of 1968. This legislation requires finance companies, retail stores, nonfederal credit unions, and other creditors to inform consumers on the costs of buying on credit, including total charges and the rate of interest on unpaid balances. This is an example of which type or class of public policy? a. resource allocative b. resource extractive c. regulatory d. internal organization and management 38. In 1964, Congress passed the Employment Opportunity Act that established the Job Corps. This program provides intensive vocational training and basic education to youths from 14 to 21 years of age who are poor, out of school, and out of work. This is an example of which type or class of public policy? a. resource allocative b. resource extractive c. regulatory d. internal organization and management 39. A few years ago, Congress passed a resolution declaring that surviving Japanese-Americans who had their property confiscated when they were interned in concentration camps during World War II were entitled to compensation. Checks for $20,000 were then mailed by the U.S. Treasury Department to all those eligible. This is an example of which type or class of public policy? a. resource allocative b. resource extractive c. regulatory d. internal organization and management 40. Under state law in Texas, voters may elect to establish special district governments called Crime Control and Prevention Districts to distribute sales tax revenues to municipal governments for the purposes of implementing law enforcement programs. In March 1995, voters in the City of Fort Worth established the first such district in the state. In October 1995, the Fort Worth Crime Control and Prevention District began funding anti-crime programs to be implemented by the City of Fort Worth Police Department. This is an example of which type or class of public policy? [HINT: the policy action in this case is the distribution of sales tax revenues from the Crime Control District to the Fort Worth Police Department.] a. resource allocative b. resource extractive c. regulatory d. internal organization and management 41. A condition that exists when a private market fails to capture all of the social costs associated with the production and consumption of a good or service is known as a. a negative externality. b. a positive externality. c. adverse selection. d. the free rider problem. 42. What policy responses might government attempt to counter the condition described in question #41? a. subsidize the good or service b. provide the good or service c. regulate the market d. all of the above 43. Which good or service is most likely to have associated with it the kind of condition described in #41? a. higher education b. childhood immunizations c. automobiles d. public libraries 44. The U.S. Department of Commerce requires that shrimpers operating in U.S. waters install “turtle-excluder devices” [TEDs] on their nets to reduce the number of sea turtles that are inadvertently killed in shrimp harvests. The Coast Guard randomly inspects shrimping boats and may impose fines on or impound the vessels of shrimpers who are not in compliance. This is an example of which type or class of public policy? a. resource allocative b. resource extractive c. regulatory d. internal organization and management 45. Assume that the inmates mentioned in question #32 win their lawsuit and the District Court orders the Department of Corrections to take action to relieve over-crowded conditions. Assume also that the Department of Corrections complies with the court mandate. This is an example of which type or class of public policy? a. resource allocative b. resource extractive c. regulatory d. internal organization and management 46. Which of the following is an example of a pure public good/service? a. airplane travel b. an interstate highway c. higher education d. all of the above 47. A city council bans smoking in all public places in the city. Fines are levied against violators. Why has the city council enacted this policy? a. This is an example of adverse selection -- non-smokers are adversely affected by second-hand smoke. b. This is an example of government providing a public good -- it is doing what is good for the public. c. This is an example of a negative externality -- the market for cigarettes fails to capture all of the social costs associated with the production and consumption of cigarettes. d. none of the above. 48. The primary target group in the policy scenario described in question #47 is a. the city council. b. non-smokers. c. tobacco companies. d. none of these. 49. The policy action described in #47 would best be classified as a. symbolic. b. regulatory. c. resource extractive. d. internal organization. 50. Which of the following is (are) a quality (qualities) of a GOOD theory? 1. explanation 2. prediction 3. parsimony 4. complexity 5. generalization a. 1, 2, and 3 b. 1 and 2 c. 1, 2, 3, and 5 d. all of these 51. Professor Womberg studies presidential elections. He has noticed that candidates of the incumbent party (the party currently occupying the office) are elected when the economy is growing and are defeated when the economy is in recession. He wants to develop a model to explain the relationship between presidential election outcomes and the performance of the economy. Which of the following might be an explanatory (independent) variable(s) that he could include in his model? a. the number of electoral votes the incumbent party’s candidate receives b. the unemployment rate c. the percentage change in gross domestic output d. b and c 52. Which of the following is [are] among the possible “epistemologies” or approaches to acquiring knowledge of political phenomena? 1. intellectualism 2. fideism 3. empiricism 4. rationalism 5. journalism a. 1, 3, and 5 b. 1 and 5 c. 1, 3, and 4 d. 2, 3, and 4 53. Which of the following are central to the EMPIRICAL approach? a. experience and faith b. experience and sensory perception c. sensory perception and faith d. faith and mental reflection 54. “Knowledge gained as a result of mental reflection” is based on which epistemology? a. intellectualism b. empiricism c. rationalism d. fideism 55. Professor Ludlow has developed a model to explain congressional election outcomes. She believes that candidates who raise more money in a campaign are more likely than their opponents to win their races. Which of the following statements is (are) NOT true? 1. Ludlow believes there is a direct relationship between the amount of money a candidate raises and his/her likelihood of winning the election. 2. She will be able to perfectly predict the outcomes of all congressional elections using her model. 3. The amount of campaign money raised is the independent variable; the likelihood of winning an election is the dependent variable. 4. The relationship between the independent and dependent variables is exact. 5. A graph of the relationship between these two variables would probably be a line that slopes upward to the right. a. 2 and 4 b. all of the above are true c. 3, 4, and 5 d. 1, 2, and 3 56. The relationships among variables that political scientists typically study are best characterized as a. deterministic. b. exact. c. inexact. d. perfect. 57. A statement that predicts an expected relationship between two or more variables and that can be empirically-tested is a a. scientific theory. b. scientific law. c. hypothesis. d. supposition. 58. “Knowledge gained as a result of faith” is based on which epistemology? a. intellectualism b. empiricism c. rationalism d. fideism 59. Which of the following is NOT considered an empirical science? 1. medicine 2. chemistry 3. biology 4. meteorology 5. political science a. All of the above ARE empirical sciences. b. 5 only, because it is a social science and therefore it is impossible for the scientist to manipulate variables. c. 4 and 5, because it is impossible for the scientist to manipulate variables. d. NONE of the above should be considered empirical sciences. 60. Which of the following is an hypothesis? a. “The majority party will lose seats in Congress in election years in which unemployment rates are high.” b. “The incumbent president lacks foreign policy leadership skills.” c. “Students who begin the day with a nutritious breakfast are likely to score higher on exams than students who do not eat breakfast.” d. “A daily regimen of oral hygiene which includes brushing with a fluoride toothpaste can reduce the chances of developing cavities.” 61. Pluralist and elite theories agree on which of the following propositions? a. The only real basis for political power is economic power. b. All social groups in the United States have some impact on policy-making. c. The traditional democratic ideal that all citizens are politically equal is NOT a very realistic reflection of the American system. d. Virtually anyone can step into politics and have at least some political influence. 62. The pluralist theory of democracy 1. is basically the same as traditional democratic theory in its assumptions about the role of citizens in the political process. 2. sees democracy as operating through competition among groups. 3. suggests that there are several types of political resources which may be effective in influencing public policy. 4. argues that the only meaningful political resource is money. 5. views public policy as a balance or equilibrium among competing group interests. a. 1 and 2 b. 2 and 5 c. 2, 3, and 5 d. 1 only 63. Which of the following theories argues that political power is held by a relatively small group of people whose main source of political power is economic power [wealth]? a. elitism b. pluralism c. majoritarianism d. substantive democracy 64. With regard to policy change, elite theory holds that a. changes in policy never occur. b. changes in policy will occur only when the masses force the power elite to alter the status quo. c. changes in policy occur only as a result of the elite redefining their own values and interests. d. changes in policy narrow the gap between the elite and the masses. 65. Which of the following tends to emphasize policy outcomes? a. traditional democratic theory b. pluralist theory c. procedural democracy d. elite theory 66. Which of the following tends to emphasize policy process? a. substantive democracy b. pluralist theory c. majoritarian democracy d. elite theory 67. Which of the following accurately describe American democracy? 1. procedural 2. representative 3. liberal 4. socialist 5. substantive a. 1, 2, and 3 b. 1 and 2 c. 2, 3, 4, and 5 d. 3 only 68. The process by which citizens propose legislation is called a. ratification. b. amendment. c. initiative. d. referendum. 69. James Madison indicated in the FEDERALIST PAPERS that pure (direct) democracy a. could deteriorate into mob rule. b. is a style of government for noble men and elites. c. prevents the majority from depriving the rights of the minority. d. none of these. 70. The requirement that “citizens must participate in the political process” is characteristic of which theory of democracy? a. elite theory b. traditional democratic theory c. pluralist theory d. none of these 71. Which of the following variations of democracy places an emphasis on the existence of individual (and minority) rights even at the expense of majority rule? a. liberal democracy b. traditional democracy c. procedural democracy d. egalitarian democracy