Effects of exercising on cellular respiration
advertisement

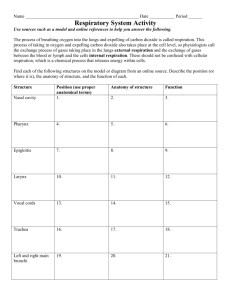
Effects of exercising on cellular respiration activity video The Respiratory System Lesson 1: Functions and Anatomy of the Respiratory System Lesson 2: Respiration: Mechanics and Control Lesson 3: Respiratory Disorders and Diseases Chapter 9: The Respiratory System Lesson 1 Functions and Anatomy of the Respiratory System Anatomy of the Respiratory System ● the nose ● the nasal cavity ● the pharynx ● the larynx ● the trachea ● the bronchi ● the lungs Anatomy of the Respiratory System Anatomy of the Respiratory System ● the nose ● ● nares the nasal cavity ● conchae ● the palate ● the sinuses Anatomy of the Respiratory System ● the pharynx ● ● the larynx ● ● tonsils epiglottis the trachea ● C rings Anatomy of the Respiratory System ● the bronchi ● primary bronchi ● bronchioles ● the alveoli ● ● surfactant ● pores of Kohn the alveolar capillary membrane Anatomy of the Respiratory System ● the lungs ● mediastinum ● apex ● pleural sac ● parietal pleura ● visceral pleura The Upper Respiratory Tract Review and Assessment Match these words with 1–4 below: surfactant, apex, epiglottis, conchae. 1. lungs 2. larynx 3. nasal cavity 4. alveoli ● https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yWnlhcqJlRk Lung Dissection ● Video Review ● Take out a piece of paper and answer these questions ● 1.How is breathing related to cellular respiration? ● 2. How did exercise affect the rate of cellular respiration? ● How can bromothymol blue pH help you measure the rate of cellular respiration? A closer look at the mechanics ● video Respiration investigation ● In this activity you will measure and monitor breathing rates to better understand respiration, inspiration, and lung capacity ● Grab a worksheet from the front: 1 per table ● Use cellphone as timer ● Work with people from your table ● Answer questions on worksheet and put everyone's name onit Chapter 9: The Respiratory System Lesson 2 Respiration: Mechanics and Control Respiration: Mechanics and Control ● respiration ● nonrespiratory air maneuvers ● control of breathing ● lung volume Respiration ● also known as breathing ● air always moves from a higher pressure area to a lower pressure area ● four key tasks involved in respiration ● pulmonary ventilation ● external respiration ● respiratory gas transport ● internal respiration Respiration ● Boyle’s law ● as the volume of a gas increases, the pressure of the gas decreases Respiration ● ● inspiration (inhalation) ● diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract ● thoracic cavity expands expiration (exhalation) ● diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax ● thoracic cavity shrinks Respiration Nonrespiratory Air Maneuvers Control of Breathing ● neural factors ● ● pons and medulla oblongata chemical factors ● central chemoreceptors ● peripheral chemoreceptors ● mechanoreceptors Control of Breathing Lung Volume ● static ● ● air volume in lungs dynamic ● air volume in lungs based on time Static Lung Volume ● tidal volume ● vital capacity ● residual volume ● functional residual capacity ● inspiratory reserve volume ● expiratory reserve volume ● total lung capacity Dynamic Lung Volume ● forced expiratory volume in one second ● forced expiratory volume in one second/forced vital capacity Review and Assessment True or False? 1. The pons and medulla control breathing. 2. Static lung volume involves time. 3. Muscles contract in inspiration. 4. Larger gas volume, higher pressure. 5. Gas moves from low to high pressure. Plan ● Quiz ● read about respiratory organ ● write a paragraph about organ (everyone must turn in) ● discuss important points with table ● write down what to say and turn in a copy ● 7.3 notes ● 7.3 key terms and study questions Review 3-2-1 ● Video ● Three things that I know about the respiratory system ● Two things I still don’t understand ● One thing that would really help me to prepare for the test Overall function ● Functions of the respiratory system ● - gas exchange ● - filter and remove foreign particles from inspired air ● - humidify and control the temperature of the inspired air ● - produce sound (voice) ● - provide sense of smell ● - aid in immune defense ● - conduct air to the lower respiratory tract Major respiratory organs ● Nose ● Pharynx ● Larynx ● Trachea ● Bronchi and Alveoli ● Lungs ● Thorax Lungs 3B ● Cone shaped organs ● Elastic sacs with branching passages ● Oxygen into the blood ● Carbon dioxide is removed ● Lungs are in vertebrates, except fish ● The lobes can be divided into more functional lobes called bronchopulmonary segments ● 3 sections in the right lung, 2 in the left ● 2 spongy air filled organs ● Contains bronchi and alveoli ● Right lung has superior, middle, and inferior ● The right lung is more indented then the left Chapter 9: The Respiratory System video 3 Respiratory Disorders and Diseases TEKS ● TEKS Covered in This Lesson: ● (2F) collect and organize qualitative and quantitative data and make measurements with accuracy and precision using tools ● (5D) analyze and describe the effects of pressure, movement, torque, tension, and elasticity on the human body ● (8A) analyze the physical, chemical, and biological properties of transport systems ● (8B) determine the factors that alter the normal functions of transport systems ● (8C) contrast the interactions among the transport systems ● (9A) identify the effects of environmental factors such as climate, pollution, radioactivity, chemicals, electromagnetic fields, pathogens, carcinogens, and drugs on body systems ● (10C) research technological advances and limitations in the treatment of system disorders OBJECTIVES ● 1. I will identify common illnesses of the upper respiratory tract. ● 2. I will explain how proper respiratory etiquette and hand hygiene can help prevent transmission of the common cold. ● 3. I will identify the most common form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and describe strategies for symptom management. ● 4. I will understand the causes and symptoms of lung cancer and available treatment options for this disease. ● 5. I will write a paragraph about a respiratory organ Respiratory Disorders and Diseases ● upper respiratory tract illnesses ● lower respiratory tract illnesses ● chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases ● asthma ● lung cancer Upper Respiratory Tract Illnesses Upper Respiratory Tract Illnesses ● avoiding URIs ● cover when sneezing and coughing ● wash hands ● don’t touch hands to eyes, nose, mouth ● influenza ● vaccine icyimage/Shutterstock.com Lower Respiratory Tract Illnesses ●acute bronchitis ●inflammation ●pneumonia ●infection ●tuberculosis ●infection Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases ●causes ●smoking ●living with COPD ●stop smoking ●purse-lipped breathing Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases ●emphysema ●decreased lung surface area ●pink puffers ●chronic bronchitis ●inflammation obstructs airways ●blue bloaters Asthma ● asthma attack ● inflamed and narrowed airways ● bronchospasms ● caused by allergens or irritants ● treatment relaxes muscles to expand airways xavier gallego morel/Shutterstock.com Lung Cancer ●more deaths from lung cancer than other cancers ●non-small cell lung cancer ●more common lung cancer ●small cell lung cancer ●less common lung cancer Review and Assessment Fill in the blanks with: non-small cell, bronchospasms, decreased lung surface area, or infection. 1. An asthma attack includes _______________. 2. A symptom of emphysema is _______________. 3. The more common lung cancer is _______________. 4. Tuberculosis is caused by _______________. Review