Topographic Maps TEKS 8.9 C
advertisement
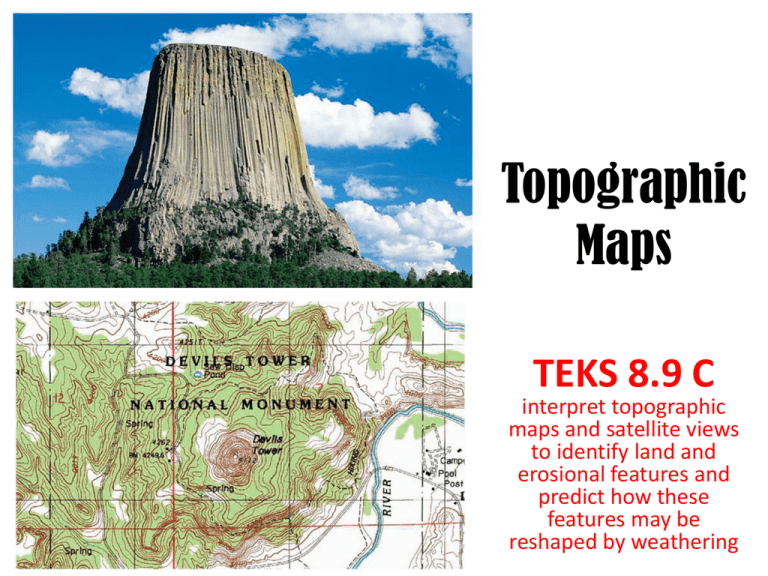
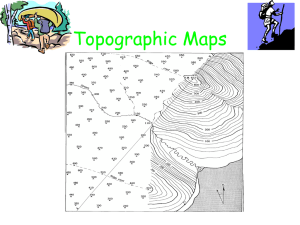
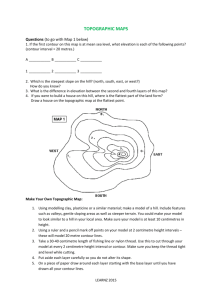
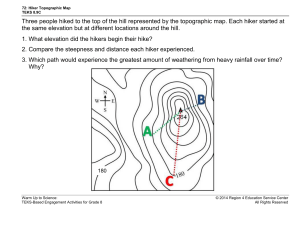
Topographic Maps TEKS 8.9 C interpret topographic maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these features may be reshaped by weathering A 2D view of a 3D surface How do topographic maps give you a picture of what the landscape looks like? By showing ELEVATION Contour lines do not cross, split or branch off Contour lines form a “v” or “u” shape in valleys or streambeds - bottom of shape points uphill/upstream What is the highest elevation? What is the lowest elevation? Which way is the stream flowing? NOTE: Contour lines form a “V” or “U” shape in valleys or stream beds with the bottom of the shape pointing uphill/upstream. This shape indicates weathering and erosion! - as the surface continues to weather and erode, the “v/u” will widen &/or become more pointed. - deposition occurs downstream U - weathering and erosion affects higher elevations first! U Where is weathering and erosion taking place? • Spacing between contour lines indicates slope = the steepness of the land - if contour lines are far apart the slope is gradual (flat) - if contour lines are close together the slope is steep Where is the slope the most gradual (or flat)? Where is the slope the steepest? Where is the slope of the land the steepest? flattest? The contour interval of a map remains consistent throughout the map What is the contour interval of this map? What is the contour interval of this map? Identify and Label the following on the topographic map above: Highest Elevation = _______ Place an “F” where the slope is the most gradual (flat) Lowest Elevation = _______ Place an “S” where the slope is the steepest Contour Interval = _______ Draw an arrow showing which way the stream is flowing What the landscape (or horizon) looks like Topographic Map & Profile Topographic Map & Profile Interpret Create a profile showing elevation from point A to B.