Diction-a writer’s word choice. (formal vs. informal)
advertisement

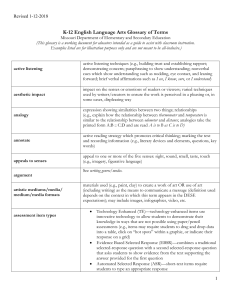
Diction-a writer’s word choice. (formal vs. informal) Connotation-attitude or a feeling associated with a word. Denotation-dictionary meaning of a word. Tone-author’s attitude; feelings of the writer. Mood-feeling the writer creates for the reader. (How the reader feels while reading the literary work). Alliteration-repetition of consonant sounds at the beginning of words. Allusion-reference to a famous person, place, event, or literary work. Hyperbole-the truth is exaggerated for emphasis or humorous effect. Imagery-descriptive words that re-create sensory experiences for the reader. Metaphor-direct comparison between two unlike things. Satire-making fun of a serious issue for the purpose of improving society. Simile-comparison between two unlike things using like or as Tragic Hero-main character who has a tragic flaw, a weakness that brings about his or her downfall. Conflict-struggle between opposing forces (problem). Characterization-the way a writer creates and develops characters’ personalities. Setting-time and place of the action of the literary work. Plot-the sequence of events in a story. Theme-underlying message about life or human nature that the writer wants the reader to understand. Allegory-a story with multiple levels of meaning.