What is Your Profitability? - Using Financial Records to Improve Business Performance
advertisement

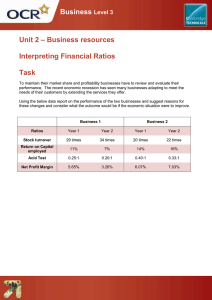
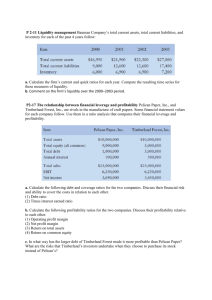
What is Your Profitability? - Using Financial Records to Improve Business Performance Dr. Wen-fei Uva Senior Extension Associate Department of Applied Economics and Management Cornell University Ithaca, NY 14853 Modified by Georgia Agricultural Education Curriculum Office July, 2002 Modified by Leanne Brown March 2007 What We Are Going to Do Today? What Is in Financial Analysis? Calculating Your Costs. Evaluating Your Profitability What Is in Business Management? The ability to use resources in an efficient manner so as to maximize returns to meet: Business goals Personal goals Achieving your goals requires Financial Management What Is Financial Management? The ability to allocate financial resources in the areas which generate the greatest returns. Financial Management Decisions You Need to Make: Making Business Decisions Are your sales covering your costs? Which product lines generate the most income? Should you operate year-round or shut down in the winter? Contributions Optimum Goal to fixed costs mix of product lines setting and increased efficiency Are Your Financially Healthy and Wise? Do You Perform Financial Analysis? Cost analysis - costs to operate the business and profitability Ratio analysis - Gross Margin Return On Investment, Return on Asset, Inventory Turns Enterprise analysis - What is your most profitability product line? Are Your Financially Healthy and Wise? Do you know how your business compare with industry benchmarks How do you compare to other firms in the industry? - Gross Margin, Inventory Turns, Profit Margin Set performance goals Track your performance over time (trend analysis) Repeat process annually Calculating Production Costs A Record Keeping System for You Pricing for Profit Expenses Records Variable costs: cost items that vary with production volume (Direct and Indirect). Costs of plant materials, pots, soil, hourly labor, advertising. Fixed costs: cost items that do not vary with production volume (Overhead costs). Costs of rent, property taxes, management salary and family living expenses. Allocate these costs to each product could be tricky (by floor space, time in store, etc.) 25 to 50% of total costs. Expenses Records - cont. Marketing costs: Advertising, packaging, shipping, billing, and special promotion, display, etc. It could also be assigned to variable and fixed costs, but why look at it separately? Production efficiency vs. marketing efficiency 5 to 15% of total costs Financial Statements and Performance Measures Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow budget Liquidity, solvency, profitability, financial efficiency, repayment capacity measures Ownership Records Asset Inventory Business assets, ownership type, control arrangement, opportunity costs Ownership Arrangement Resource sharing, owner compensation, responsibilities Estate Plan Exit/entry and retirement plans (will, trust, insurance, buy-sell agreements) Pricing for Profit Price (Revenue) Contribution Variable Costs Break-even Fixed Costs Profit Calculate Costs - Direct Variable Costs Direct Variable Costs Seeds or plants Potted soil Fertilizer and Chemicals Packaging material Direct labor TOTAL FOR THIS PRODUCT LINE $ Amount $ 750 100 50 150 2,000 $ 3,050 Calculate Costs - Indirect Variable Costs Indirect Variable Costs $ 8,000 2,075,000 $/Sq. Ft. Week $ 0.00386 Trucking 2,400 2,075,000 0.00116 Telephone 1,000 2,075,000 0.00048 500 2,075,000 0.00024 Fuel 1,000 2,075,000 0.00048 Heating for Greenhouse 2,000 450,000 0.00444 65,000 2,075,000 0.03133 2,000 Annually or special event? 0.0096 Electricity Water Hourly Labor Advertising $ Amount Total Sq. Ft. Week 2,075,000 TOTAL 0.05159 Calculate Costs - Fixed Costs Fixed Costs $ Amount Total Sq. Ft. Week $/Sq. Ft. Week Management Salary 50,000 2,075,000 0.02410 Interest 15,616 2,075,000 0.00753 Depreciation 5,497 2,075,000 0.00265 Insurance 5,102 2,075,000 0.00246 Building and Equipment M/R 2,779 2,075,000 0.00134 Property Taxes 8,025 2,075,000 0.00387 10,879 2,075,000 0.00524 Office Supplies 2,991 2,075,000 0.00144 Professional Fee 2,123 2,075,000 0.00102 Misc. 4,000 2,075,000 0.00193 Leases and Rental Family Expenses & Bank Principal Payments 20,000 TOTAL 0.05157 Calculate Enterprise Profitability Revenue Price per Unit $ 3.25 Units Sold (Take into consideration shrinkage) 4,800 TOTAL REVENUE $ 15.600 Expenses Direct Variable Costs (COGS) $ 3,050 Indirect Variable Costs (100,000 SFW * $0.05159/SFW) = $ 5,159 Fixed (Overhead) Costs (100,000 SFW * $0.05157/SFW) = $ 5,157 TOTAL EXPENSES ENTERPRISE PROFIT $ 13,366 2,134 Breakeven Analysis Variable Costs per Unit Sold ($3,050 + $5,159) / 4,800 Consider discontinue = $1.71 if below this number Overhead Costs per Unit Sold $5,157 / 4,800 = $1.07 Need to cover this number Total Cost per Unit $1.71 + $1.07 = $2.78 Breakeven price Profit per Unit Sold (4,800 pots) $1.01 Profit per Unit Grown (5,000 pots) $0.97 Profit Equation VOLUME (PRICE-COST) = PROFIT 4,800 pots* ($3.25/unit - $2.78/unit) = $2,256 4,800 pots* ($3.00/unit - $2.78/unit) = $1,056 10,254 pots* ($3.00/unit - $2.78/unit) = $2,256 For $250,000 in sales, a 4% price increase (4 cent increase for every dollar) give you $10,000 more profit. Evaluating Business Profitability Financial Ratios Efficiency Measures Financial Ratios Profitability Ratios Gross Margin: (Revenue - Variable Costs) Revenue -- (around 50%) Profit Margin: (Revenue - Total Costs) Revenue -- (around 10-15%) Return on Assets Net Business Income Average Total Assets How efficient are you using your resources to produce income. Financial Ratios Inventory Ratio (3.5) Cost of Good Sold Average Inventory How fast are you turnover your inventory Liquidity Current Ratio: Current Liability Current Assets Your ability to cover current debt (liability) Solvency Debt-to Asset Ratio: Total Liability Total Assets The percentage of the business’s assets to which creditors have claim. Efficiency Measures Operating Efficiency Sales per Full Time Worker Equivalent Net Income pre FT Worker Equivalent Sales per Square Foot Cost Efficiency Labor as percent of sales Operating expenses as percent of sales Costs per square foot (or square foot week) Profitability Net Income per Owner Net Income per Owner Hour Net Income per Square Foot