Excretory System “I excrete, therefore, I am” Excreto,
advertisement

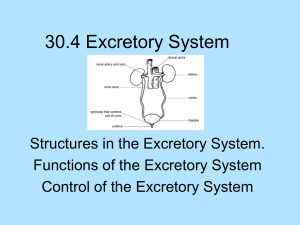
Excreto, ergo sum Excretory System “I excrete, therefore, I am” Excretion Removal of metabolic wastes Metabolism: Chemical reactions that build up, break down or change compounds Macromolecule Metabolism used Cellular Respiration Carbohydrates C H O Stored Glycogen Lipids product ATP waste CO2, H2O Macromolecule Metabolism Stored Lipids C H Fat O As lipids (hormones, cell parts, etc. ) Used Converted back to carbohydrates waste “Ketones” Macromolecule Metabolism Used Protein C H O Enzymes, Hormones, Chaperones, Cell parts, etc… N Converted to In the liver Muscle waste (ATP use) Lipids, Carbohydrates. (C – H – O) Heat, Other wastes What happened to the Nitrogen? Nitrogenous Waste • Deamination = removing amine group • Forms ammonia NH3 (Very Toxic) Nitrogen Excretion Ammonia Uric acid Urea The Liver • No wastes removed • Processes most macromolecules and ingested toxins (including medicines and alcohol) • Blood and lymph vessels from small intestine go through liver before being circulated. Excretory organs Liver doesn’t remove wastes detoxifies and deaminates Skin sweat H2O, urea, salts Lungs breath CO2, H2O Urinary system = kidneys, ureter, bladder, urethra make urineH2O, urea, salts and surplus stuff (vitamins, sugars, etc.) Note = this does not include the digestive system Feces are not really excretory (its not a metabolic waste) The Urinary System ADRENAL GLAND – not excretory KIDNEY URETER URINARY BLADDER URETHRA The Kidney The Kidney Bean URETER The Nephron How to make URINE: 1. Filtration: All dissolved material leaves blood. This occurs here 2. Reabsorption: “good” material returns to the blood This occurs here What is left over is…URINE! The microscopic, functional unit of the kidney. There are millions of these in each kidney Kidney Stones! Don’t want one of these? Don’t eat too much of Spinach. these Rhubarb. Beets. Strawberries. Nuts Chocolate. Thanks for checking in… www.mrulrichslandofbiology.com kulrich@newpaltz.k12.ny.us Yay! Science!