By Diana Blum RN MSN Metropolitan Community College
advertisement

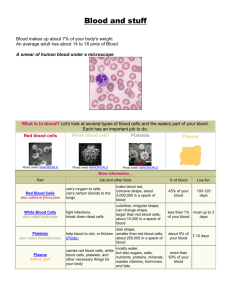
By Diana Blum RN MSN Metropolitan Community College Oxygenation Hemostasis (control of bleeding) If injury the vessel constricts Platelets adheres to injured vessel Them the coagulation cascade begins Diagnosis of problems can be difficult Bone Marrow: Liver: manufactures clotting factors Spleen: removes old RBCs from circulation Blood: transports oxygen from lungs. Maintains hemostasis About 6 liters in body RBC: made in bone marrow ◦ Transfers oxygen to from lungs to tissues ◦ Hemoglobin makes the transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide possible ◦ 120 day life span ◦ Iron and heme are recycled ◦ Have proteins called antigens 2 major parts are A and B and O Rh + and Rh- PLATELETS: made in bone marrow Numbered I to XIII Form stable fiber matrix over wound Plasma: clear straw colored fluid that carries red blood cells, platelets, and clotting factors ◦ Primarily water ◦ Other components are plasma proteins, albumin, and globulins The bone marrow becomes less productive Hemotologic function is not affected unless trauma, a chronic illness, or treatment for cancer Health Hx: Chief complaint, Hx of present illness Past Medical Hx: Ca, HIV, liver dx, kidney dx, malabsorption dx, transfusions, clots Family Hx: hemophilia, sickle cell dx Review System: ask about change in color, skin dryness, pruritus(itching), vertigo, confusion, pain, headaches (duration, location, intensity), mental status changes, bleeding, heart palpitations Functional assessment: occupation, hobbies, self concept, activity, exercise, sleep and rest, nutrition, relationships, stress, health perception See page 607 Vs Ht Wt Look for cracking of mouth Monitor for SOB Look for tachycardia, tachypnea, hypotension Look for orthostatic changes, dehydration Look for pale skin or jaundice Look for bruising (ecchymosis) Look for purpura: larger than petechiae Look for petechiae ◦ Can be from low platelet count ◦ From large blood vessels breaking ◦ (confused with a rash) ◦ Reddish purple in nature ◦ Severe coughing can cause Blood cell count Hemoglobin Hematocrit-approximately 3 times the hemoglobin Normal platelet ct is PT and PTT measure bleeding time Blood typing To prepare the client tell them that they will feel a small prick Bone marrow Bx: measures how it is making blood ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Explain the purpose and procedure Obtain consent No fasting is necessary Procedure takes about 30 minutes Transfusions see page 612-615 Minimize the # of invasive procedure Avoid prolonged tourniquet use Avoid IM injections Instruct the client to use soft bristled tooth brush No strait edge razor shaving only use electric razor Avoid NSAIDS PRBCs: 250-300ml/unit infuse over 2-4 hours Platelets: 80-60ml/pack: usually 4-6 packs are pooled for transfusion infuse as quickly as the pt tolerates FFP: 180-270ml/unit infuse in less than 4 hours Cryoprecipitate:10-15ml/bag; usually 10 bags are pooled for transfusion infuse in less than 4 hours (contains factor 1 and 8) Universal donor= ◦ Does not contain A, B, or Rh antigens Universal recipients= ◦ Blood contains A, B, and RH antigens Usually blood banks exactly match the pt blood Pt needs 18 or 20 gauge IV needle so cells are not lysed (destroyed) Prior to administration, blood needs to be checked by 2 licensed nurses. Check the expiration date, name, medical record number, type of blood, blood band id, pt birthday ◦ Check vitals prior to administration **blood must be initiated with in 30 minutes of arrival from lab to floor Use blood tubing for administration Monitor for blood reactions Monitor vitals continuously during administration Hemolytic: fever, chills, nausea, dyspnea, chest pain, back pain, hypotension ◦ Antigen/antibody rx to transfusion ◦ Happens shortly after initiation ◦ Tx: stop the transfusion, call md, supportive therapy to maintain HR and BP Anaphylactic: urticartia, wheezing, dyspnea, hypotension ◦ Type 1 hypersensitivity rx to plasma proteins ◦ Occurs within 30 minutes of initiation ◦ Tx: stop transfusion, call md, be ready for epi and steroids Febrile: fever, chills ◦ Recipients antibodies rx to donor leukocyte ◦ Occurs within 30-90minutes of initiation ◦ Tx: stop infusion, call md Circulatory overload: cough, frothy sputum, cyanosis, decreased BP ◦ cardio system is unable to manage the additional fluid load ◦ Occurs anytime during transfusion and up to several hours after completion ◦ Tx: stop infusion, call for help, be prepared for code, be prepared to administer oxygen and Lasix Start IV of NS using at least 24 gauge needle ◦ Platelets are smaller so a smaller needle can be used Check just like you check blood Prior to administration check vs Continue to check vs during administration Run platelets through blood tubing with a filter Infuse as fast as the pt can tolerate Monitor for rx See page 614 Naturally occuring hormones that stimulate bone marrow to produce more blood cells Ferrous sulfate: iron replacement Iron dextran: iron replacement Vitamin B12: Vitamin B12 replacement Hydroxyurea: prevention of sickle cell crisis Epogen: stimulates the bone marrow to produce more RBCs ◦ Used frequently with hemodialysis ◦ Used for anemia secondary to HIV or cancer See page 614 Too many RBCs produced ◦ Blood more viscous s/s: headache, dizziness, ringing in the ears, blurred vision, ruddy complexion Tx: Complete failure of the bone marrow Low RBC count Low WBC Low Platelet cts S/S: pallor, fatigue, tachycardia, sob, hypotension, prolonged/spontaneous bleed, frequent infections Tx: transfusion of RBC and Platelet, antibiotics, corticosteroids, bone marrow transplant, ICU setting Enough RBCs made but they are destroyed once they are released into circulation Causes: infection, drug reaction, cancer s/s: pallor, fatigue, tachycardia, sob, hypotension, jaundice, high bilirubin levels Postive direct coombs antiglobulin test Tx: blood transfusions, corticosteroids Recovery in few days to weeks Low RBC Low HGB andHCT Low serum Iron level Low ferritin level High TIBC level Results from diet low in iron Results from body not absorbing enough iron from GI tract ◦ Not enough hemoglobin made as result s/s: fatigue, pallor, orthostatic changes (in severe cases) Tx: iron supplements, iron rich foods Pt does not absorb vitamin B12 from stomach Pt may lack intrinsic factor-essential for b12 absorption Assess hx: gastrectomy, s/s: weakness, sore tongue, numbness of hand and feet Tx: B12 injections monthly RBCs normally disc shaped In sickle cell they are sickle shaped Easily rupture Obstruct blood flow Genetic in nature Most common in African Americans Sickle cell is recessive (inherit from mom and dad) Too few platelets ◦ Causes: cancer treatment Too many platelets being destroyed ◦ Causes: idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, thrombic thrombocytopenic purpura (chptr 32) s/s: petechiae, purpura, gingival bleed, epistaxis, prolonged bleeding Genetic Lack of blood clotting factor 1-2 cases per 20,000 persons Types ◦ A: factor VIII is missing-higher incidence ◦ B: factor IX is missing Trait is carried on x chromosome Rare for women to have s/s: uncontrolled bleed especially in joints, skin, GI tract Tx: no cure. Transfusions, pain treatment (IV morphine is common)..monitor for addiction to opiods. Risk for injury r/t bleed. Goal: cessation of bleeding aeb no visual signs of bleeding and stable vs Acute pain r/t bleeding into closed spaces(creating pressure on nerves. Goal: pain relief aeb: patient states pain is relieved and appears to be in relaxed manner. Ineffective therapeutic regimen management r/t lack of knowledge about dx process and self care. Goal: effective management of condition aeb patient accurately describes condition and demonstrates self care measures. THE END