Gospel of Luke Acts of the Apostles: Jesus the Savior
advertisement

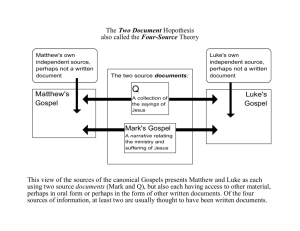
Gospel of Luke Acts of the Apostles: Jesus the Savior Background - Luke was a Gentile-Christian - Responsible for writing the gospel with the most words and its sequel (Acts of the Apostles) • Together make up more than a quarter of the New Testament -Style, language, and organization of the Gospel and Acts are very similar • Both works addressed to Theophilus Background Do we really know the author? - Identified as St. Paul’s coworker from Antioch • Remained Paul’s friend • Probably used a travel diary to construct some of the history of Acts • The prologue mentions Luke was from Antioch in Syria and died in Greece -Certain that he did not know the historical Jesus in person and did not come from the Holy Land Background - Author of Luke was a brilliant artist with words • Wrote beautiful polished Greek - Wrote for Gentile Christian churches - Major Theme • Universality of Jesus’ offer of salvation - Gospel intended for everyone • Gentiles do not have to convert to Judaism to accept Jesus Background Three main sources for writing: 1.) Mark’s Gospel 2.) Q: common source 3.) L: unique source MARK M MATTHEW LUKE Q L Background The prologue provides solid information on: • Why the gospel was written • What it is about • How the author went about writing it Background -Special Lucan material included: • Early hymns • Finding of Jesus at the Temple • Genealogy • Collection of parables • Group of miracle stories Background - Luke dedicated his gospel to Theophilus Name means “lover of God” Name helps prove the unity of Luke’s two-volume work Background - In his opening gospel address to Theophilus, Luke states his reasons for writing: • He wants to show Theophilus and all readers that the instruction in the Christian faith was sound. • His purpose in writing the Gospel was the strengthen their faith Common Themes Common themes in Luke and Acts: 1.) Jesus as a prophet 2.) The Church continues Jesus’ prophetic ministry 3.) The role of the Holy Spirit in salvation history 4.) Prayer, joy, peace 5.) The special role of Mary and women Common Themes 1.) Jesus the Prophet - Lk 4:14-44 - Jesus reveals that through him, the prophesy about the Messiah is taking place • God’s kingdom is present • What Isaiah prophesized is happening right now Common Themes 1.) Jesus the Prophet - Lk 4:14-44 Jesus outlines his ministry: • Preach the gospel • Help people live freely • Perform acts of mercy • Work for justice • Celebrate God’s presence in the world Common Themes 1.) Jesus the Prophet - Lk 4:14-44 -The scene at Nazareth foreshadows Jesus’ public life • Met with initial acceptance, however, people change their opinion and reject and kill the innocent prophet in Jerusalem Common Themes 1.) Jesus the Prophet - Lk 4:14-44 - The synagogue scene underscores two other themes that appear in Luke and Acts: • The role of the Holy Spirit • The importance of prayer in the life of Jesus and of the early Church Common Themes 2.) Church Continues Jesus’ Prophetic Mission: Acts 1-2 -Luke depicts the characteristics of an ideal Christian community • Christian fellowship or communion • Praying for each other • Gospel truth as handed on by the apostolic eyewitnesses Common Themes 3.) Role of the Holy Spirit - Stresses the vital role of the Holy Spirit in salvation history - Luke viewed history in three dramatic stages: • Stage 1 - Age of Promise • Stage 2 - The Times of Jesus • Stage 3 - The Age of the Church -Holy Spirit appears frequently in Luke and Acts Common Themes 4.) Prayer - A pervasive theme in Luke and Acts - Jesus prayed: At His Baptism In the Synagogue In lonely places At His Transfiguration Hanging on the Cross The night before choosing the Apostles Common Themes 4.) Prayer -Message to be learned is that we should pray as often as the Master did -Acts of the Apostles shows how the early Church heeded this advice well Common Themes 4.) Joy and Peace -Themes are evident from the opening verses of the gospel • Often connected with prayer -Message of several of his parables also highlighted the theme of great joy over the return of lost sinners -Key event in Jesus’ life that results in joy: • Entry into Jerusalem during Holy Week -Most joyous occasion is his resurrection Common Themes 5.) Special Role of Mary and Women - Women were considered inferior to men - Jesus’ attitude toward women was positive and revolutionary • He included women as the central characters in two of His parables (the Lost Coin and the Unjust Judge) - Most significant was the women who witnessed his death and resurrection - Mary illustrated a major Lucan theme God’s preferential love for the poor Messiah & Savior - In Luke’s gospel, Jesus is a compassionate Messiah who has come to prove God’s great love - Makes Jesus the friend of the friendless • Shepherds, usually considered outcasts, were the first to visit Jesus’ birth • Offering of the poor • Presentation in the Temple Messiah & Savior - More than the other three gospels Luke reassures the poor and warns the rich - God blesses the poor - not only those socially disadvantaged but also those that recognize they are nothing without God - Challenges the rich to repent before it is too late Messiah & Savior -Luke’s is the only Gospel that records the story of Lazarus and the rich man -Lazarus means: “May God help” or “The one whom God helps” -Jesus is warning that those who have plenty in this life must share with those who have less Messiah & Savior - Luke reports Jesus reached out to Zacchaeus, a tax collector • Jesus was enacting a living parable of God’s love for sinners • Jesus’ compassion also extended to outcasts Love of Enemies - God’s love and compassion knew no bounds - nor should ours • Parable of the Good Samaritan • Our neighbor is everyone Messiah & Savior - Luke’s Chapter 15 is the very heart of the gospel - Contains three memorable parables that deal with God’s great compassion and his joy over repentant sinners: 1.) The parable of the lost sheep 2.) The parable of the lost coin 3.) The parable of the lost or prodigal son Messiah & Savior -Most common title of Luke for Jesus is “Lord” -Luke presented Jesus as a martyr: “witness” • Jesus’ death is a witness, and example for all for how consistent, loving, faithful, and compassionate he is -Concludes his gospel with the resurrection appearances - Emmaus story summarized entire gospel Overview of Acts - Chapter 2 of Acts reports: • The coming of the Holy Spirit • Outpouring of gifts • Peter’s kerygmatic sermon • Pentecost Sunday • Ideal characteristics of the earliest church Overview of Acts -Second major section shows how Philip preached the good news to the Samaritans -Shifts to Peter who preached in Joppa and Lydda, performed miracles, and had important visions -King Herod began persecuting Christians -Paul and Barnabus began their first missionary journey