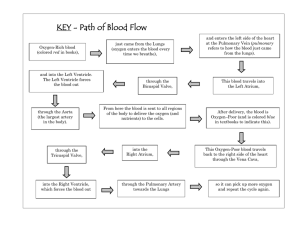
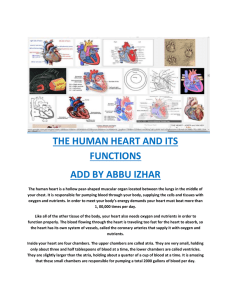
• LESSON GOALS: • TO LEARN ABOUT HEART, ITS PARTS AND THE FUNCTIONS • TO LEARN ABOUT KIDNEY, ITS PARTS AND THE FUNCTIONS • Learn the lab safety rules and follow them HEART •INTRODUCTION Heart is a muscular organ which pumps blood through the blood vessels Size: size of one’s fist Position: center of the chest, usually pointing slightly left beats about 100,000 times per day Functions • Pumps oxygenated blood all over the body • Supply nutrients and oxygen in the body • Elimination of Carbon dioxide and waste Parts of heart Chambers of heart • Four chambers: two upper chambers are atrium (singular: atrium) and the lower two are known as (singular: ventricle). • Muscular walls, septa or septum, divide the heart into two side Valves of heart • 3 types: Tricuspid: between the right atrium and ventricle. Mitral: between left atrium and ventricle Pulmonary: between right ventricle and pulmonary artery Aortic: between left ventricle and aorta Function: to prevent the backflow of the blood Major Blood vessels • Pulmonary arteries and veins • Aorta: distributes blood to the body • Superior venacava: brings blood from the body • Inferior venacava: brings blood from the body KIDNEYS • INTRODUCTION Bean shaped excretory organs Paired organs Location : below the rib cage on each side Parts of kidney : • Renal Capsule – outer membrane that surrounds the kidney • Renal Pelvis – basin-like area that collects urine from the nephrons • Cortex – the outer region of the kidney • Medulla – inner region of the kidney • Renal artery and renal vein Functions • remove wastes and extra fluid from your body • maintain a healthy balance of water, salts, and minerals—such as sodium, calcium, phosphorus, and potassium—in your blood. LAB SAFETY • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VGeUcQ5s3jw