10. Proteins and Nucleic Acids PPT

Proteins & Nucleic Acids
Macromolecule #3: Proteins
C, H, O, N, sometimes S
Serve the most varied purposes, including
:
Support structural proteins (e.g. keratin, collagen)
Enzymes
Transport
Defense
Hormones
Movement speed up chemical reactions cell membranes channels, transporters in blood (e.g. hemoglobin) antibodies of the immune system cell signaling (e.g. insulin) contractile proteins (e.g. actin, myosin)
Collagen
Antibodies
Hemoglobin
Actin & myosin
Enzymes
Amino Acids
= building blocks of proteins only 20 different AA exist, these build thoudsands of different proteins
AA are held together by peptide bonds
Note:
Our bodies can make only 12 amino acids = nonessential AA
We have to get the remaining 8 from diet = essential AA
Protein Structure:
Changing just one amino acid can cause the protein to change shape, not work properly, and sometimes cause diseases
High T, pH, or salt can change the shape of protein and thus inactivate it
(denaturing)
Macromolecule #4: Nucleic Acids
C, H, O, P, N
Types of nucleic acids: DNA & RNA
Nucleotides : building blocks of nucleic acids
Each nucleotide contains:
phosphate
nitrogenous base
5-carbon sugar
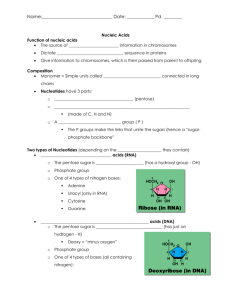
DNA vs. RNA
DNA
Deoxyribose
Double stranded
Nitrogen bases:
A, G, C, T adenine guanine cytosine thymine
Only 1 type
RNA
Ribose
Single stranded
Nitrogen bases:
A, G, C, U adenine guanine cytosine uracil
Types - mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
The DNA Song
(to the tune of Row, Row, Row your Boat)
We love DNA made of nucleotides.
Sugar, phosphate, and a base bonded down one side.
Adenine and thymine make a lovely pair, cytosine without guanine would feel very bare.
Macromolecule #5: ATP
ATP = adenosine triphosphate
Energy currency of living organisms
Can by produced by aerobic & anaerobic processes (with oxygen or without oxygen)
THE BIG PICTURE:
Chemistry is essential for life…
Be prepared to answer three of the following
You will answer one from each goal.
•
What are some healthy sources of carbohydrates? (goal 1)
•
What are some good sources of protein? (goal 1)
•
What foods do we need to eat in order to obtain essential amino acids? (goal 1)
•
Why do you think whole wheat bread is better than white bread? (goal 1)
•
What are some good sources of fats? Why are saturated and trans fats unhealthy?
How is their structure different from the structure of unsaturated fats? (goal 1)
•
Does "low fat" means always healthy? Explain your reasoning. (goal 1)
•
Can you give 3 examples of diseases that can result when there is a nutritional deficiency? (goal 2)
•
Heart disease is still #1 cause of death in the U.S. (and the world). Other than making sound nutritional choices, what else can we do to try to prevent this condition? (goal 2)
•
Data from NIH show that adhering to treatment plan of chronic diseases is difficult. Less than 50% of diabetics follow their medication plan and only 30% follow dietary guidelines. Patients with hypertension also do not frequently follow doctor advice. Why do you think it is so difficult to change behavior?
(goal 3)