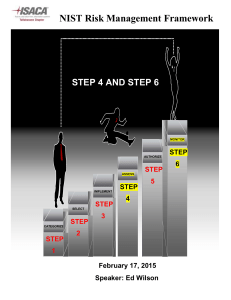
National Institute of Standards and Technology NIST Assets Include:
advertisement

1 National Institute of Standards and Technology NIST … is an agency in the Technology Administration of the US Department of Commerce. NIST Assets Include: 3,000 employees 1,600 guest researchers $760 million annual budget NIST Laboratories -- National measurement standards - $400 million budget Advanced Technology Program -- $570 million current R&D partnerships with industry Manufacturing Extension Partnership -- 400 centers nationwide to help small manufacturers Baldrige National Quality Award NIST Laboratories 2 3 CSTL/NIST Goals Measurement Standards Establish CSTL as the pinnacle of the national traceability and international comparability structure for measurements in chemistry, chemical engineering and biotechnology, and provide the fundamental basis of the nation’s measurement system Chemical and Process Information Assure that U.S. industry has access to accurate and reliable data and predictive models to determine the chemical and physical properties of materials and processes Measurement Science Anticipate and address next generation measurement needs of the nation, by performing cutting-edge research 4 • Explosive growth in the need for reliable physical, chemical, biochemical, and materials property data to support process and product optimization and discovery. Millions of Pages • combinatorial methods • high throughput experimentation • doubling of the volume of published thermodynamic data in the last 10 yrs 1.6 Growth in monthly use Chemistry WebBook 1.2 0.8 0.4 0 7/1996 1/2003 Information & Knowledge Management Knowledge Knowledge Development Information Information Synthesis Data Collection 5 6 Reliable Data Information • Reliable Data • suitably documented • established uncertainty – first step in the creation of information – core of NIST mission “...critically evaluated data on well-characterized substances...” Standard Reference Data Act • Trustworthy information “on-demand”: 7 – data collection • autonomous input at publication • federation of data archives world-wide – data management • metadata, uncertainty, provenance – data mining – data evaluation – best value, “self-improving” archives • • • • expert systems comprehensive archives non-linear, multi-variate, constrained, statistical optimization self-consistent, reflexive annotation of uncertainty – “virtual measurements” • first principles computations 8 PrIMe – Process Informatics in a Community Collaboration for the Development of Combustion Models • Needs – reliable hardware – modern data-management tools – sustained experimental data collection and evaluation – scientific tools for mechanism generation, model reduction, dataset analysis, … Challenges • 100’s gigabytes - federated world-wide – semantics & syntax – legacy • mirror archives or only query federation? – real-time access to comprehensive archive • • • • non-standard, legacy database schema non-standard or non-existent provenance quality measures and annotation metadata update upon evaluation – enable dynamic self-consistency • computation in a distributed environment • architectures for “on-demand” first principles computational estimation 9