Minneapolis_Bridge_Collapse[1].pptx
advertisement
![Minneapolis_Bridge_Collapse[1].pptx](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/015465459_1-e16a46c2a7c1e8e900ff666d1aafbc4c-768x994.png)
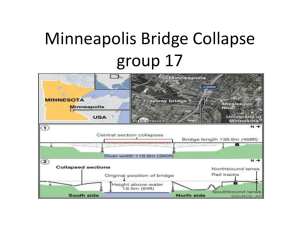
Minneapolis Bridge Collapse group 17 What Happened? • • • • • The 1nterstate 35W Minneapolis Bridge collapsed on 1st August 2007 at 6.05pm during rush hour traffic killing 13 people and injuring 145. The centre span of the bridge fell into the river almost completely intact, as the failure occurred close to the vertical supports. The bridge failed at the north end first. This left the whole centre span resting on the south end’s concrete block support as a sort of cantilever. This only lasted a moment, as the north end soon failed, sending the centre span of the bridge into the river. Why did this happen? After its collapse the gusset plates were found to be undersized and roughly half of the required thickness for the intended load of the bridge. Gusset plates are rectangles of steel that hold several girders at connecting points. This load had also increased over the life of the bridge and this contributed to failure. How did this happen? • • • • • • • • The structure of the bridge being flawed was first noted in 1990, when it was declared ‘Structurally deficient’ and was said to be in need of repair due to the severe corrosion of its bearings. Further reports discovered other structural problems with the bridge cracking in the transverse trusses, little or no movement from the severely corroded bearings and deformation in the main trusses connected to these bearings. There was little or no redundancy in the main truss system, which meant if one single truss failed the bridge as a whole would almost certainly collapse. Prior to the collapse a wide-scale steel reinforcement project was planned for the bridge but was later cancelled in favour of periodic safety inspections. The inspections never checked the thickness of the gusset plates so calculated a higher load capacity than the actual bridge could sustain. Since the bridge had opened an extra 2” of concrete had been added to the roadway (an additional 20% of the dead weight of the bridge). At the time of the collapse roughly 261,000kg of construction equipment and materials were situated on the deck. This increased the load on the bridge greatly. And so ..... Since the collapse, there have been changes..... • • • 25 similar truss bridges and their gusset plates were inspected after the collapse and more inspectors were hired to increase the frequency of inspections. Bridge inspection in the area has been adopted to better inspect the size and strain in gusset plates. There are new directives as to where construction contractors can place materials on bridges and increased loading must be checked before use.