Document 15464711
advertisement

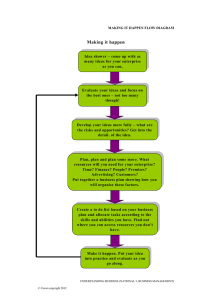
Evidence, support, proof/foundation for claim Basis for claims may be 1 of 2 types Artistic Proof-reasoning, analysis, inspiration of advocate-personal knowledge Primary Research-original, first hand findings Interviews, surveys, questionnaires, field studies Inartistic Proof-someone else’s words, ideas, numbers, examples used as proof Secondary Research Aristotle identified 3 types of artistic proof-3 ways we gain support for argument Logos Pathos Ethos Premises are often used as grounds for a claim-as proof A point accepted without the requirement of additional support-common knowledge Premises used to support a claim are based on 2 types of knowledge Personal Knowledge Cultural Knowledge Personal Knowledge Type of artistic proof What we know to be true because of first hand experience Cultural Knowledge Shared values and shared truths-common knowledge Come from stories we tell and hear Can be codified into the rules, principles, laws we follow Reinforced through rituals-repeated behavior patterns Ex. Graduation ceremony=reinforces value in discipline, education, etc. Reinforced through symbols Presumption-audience believes premises until convinced otherwise Evaluating the use of premises in support of claim requires considering 3 things 1. Is premise truly shared by audience-majority 2. Are there contradictory premises 3. Are there discrepancies between our public and private beliefs Ex. We frown upon racism in US, but that doesn’t mean racist people don’t exist in US Supporting a Premise/Claim/Proposition Hard Evidence Includes factual examples and statistics Soft Evidence Rests on opinion or inference. Hypothetical illustrations, descriptions, explanations, analogies Variety Accuracy-credibility Relevance Conveying info through giving meaning. Focuses on addressing the meaning of a new or complex concept Defining can take at least 5 forms • 1-operational definition • 2-definition by negation • 3-definition by example • 4-definition by synonym • 5-definition by etymology Examples-illustrate, describe, or represent ideas+ aid understanding -Brief example -Extended example -Hypothetical example Explanation-involves providing reasons or causes and demonstrating relationships, & offering interpretation and analysis • Testimony-first hand findings, eye-witness accounts and opinions • Expert testimony-provided by professionals trained to evaluate or report on a given topic • Credibility important-competence Ex. According to Dr. Lee Jones from Harvard Medical School, people with diabetes who exceed the consumption of 2 eggs per week increase their chances of heart disease. NOT REAL -Lay testimony-evidence provided by non- experts (eye- witness)-credibility is still important According to one student who witnessed the shootings at Virginia Tech University, the shooter was …………(description) quantified evidence-summarizes numerical data percentage, average, frequency, mean, median, mode- ex. Smoking increases one’s chances of getting lung cancer. 75% of people who get lung cancer are smokers. present ethically avoid cherry-picking Underreporting Overreporting Is statistic coming from random sample Facts-documented occurrences that include events, dates, times, etc -people usually require evidence or facts in order to accept something as true Documenting Source Material-cite sources -keep track of where you get everything (working bibliography) -cite within and at the end of work (reference page) Pg. 140 MLA and ABA samples in back of book