Ch 21 Kinetic Theory
advertisement

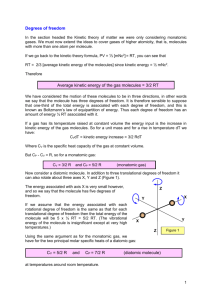
In the kinetic theory model of an ideal gas, molecules are viewed as point particles that collide elastically with the walls of the container. In this model the temperature of the gas is associated with: 1) 2) 3) 4) Total potential energy of the gas. Total kinetic energy of the gas Average potential energy of a gas molecule. Average kinetic energy of a gas molecule. A sealed box contains an ideal gas. The gas is heated until the pressure doubles. What has happened to the average speed of each molecule? That is, what is vf/vi? For which process is W the largest? For which process is W the smallest? For which process is Q the largest? For which process is Q the smallest? Molar Specific Heats 𝐶𝑝 𝛾≡ 𝐶𝑣 Two pistons initially have equal volumes of gas at room temperature. Piston A has a monatomic gas. Piston B has a diatomic gas. Both pistons are set to compress their gas to ½ the original volume adiabatically. Which compression requires more pressure? Equipartition of Energy Each degree of freedom contributes 1 𝑘 𝑇 2 𝐵 of energy per molecule. Problem A system of monatomic ideal gas experiences an adiabatic expansion that moves it from an initial state, at 400 K, to a final state at a temperature of 200 K. The process is shown on the P-V diagram below. Calculate the a) final pressure. b) final volume. c) work done on the gas.