Genetic Engineering
advertisement

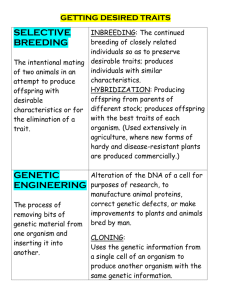
Topic: Applied Genetics Aim: Describe some methods that can be used to develop organisms with desirable traits. Do Now: Take out your genetic engineering reading notes. Tape Pedigree Chart ISA into your notebook. HW: Pedigree Chart ISA Castle Learning Genetics – Due Tuesday, May 10th 1. Define • Biological and chemical genetic methods to change the engineering. arrangement of a gene’s DNA. What is happening to the DNA in the picture? 2. Identify • Genetic material from what two different organisms. recombinant DNA consists of. • The human gene for insulin can 3. How can be INSERTED into a recombinant DNA be used bacterium. to produce • The bacterium will begin producing insulin insulin? http://www.goldiesroom.org/Shockwave_Pages/REG-20-recombination.htm https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FAMRQz7fOaE 4. Identify • Human growth hormone other • Chemicals to treat chemicals cancer that can be produced using recombinant DNA. 2000: Alba, a genetically-engineered bunny possessed "green fluorescent protein" genes from a jellyfish that made it glow in the dark. French genetic researchers created Alba. The albino rabbit glows green when placed under special lighting. In regular light, Alba appears like any other furry white rabbit. But place her under a black light, and her eyes, whiskers and fur glow a otherworldly green. "Glow in the dark" fish: These genetically modified fish were developed by a Taiwanese aquatic firm. They are planning to reproduce these fish in numbers and sell them for pets. In 2007, South Korean scientists altered a cat’s DNA to make it glow in the dark and then took that DNA and cloned other cats from it — creating a set of fluffy, fluorescent felines. 5. Describe a • The long-term effects of consuming genetically modified possible disadvantage plants are unknown. of eating genetically modified plants. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aCWH7PlBKBw This 1986 picture of a glowing tobacco plant bearing the “light” gene of fireflies demonstrates the power and potential of genetic engineering. Scientists at the University of Washington are engineering poplar trees that can clean up contamination sites by absorbing groundwater pollutants through their roots. The plants then break the pollutants down into harmless byproducts that are incorporated into their roots, stems and leaves or released into the air. Corn plants: On the left we see corn a plant that was not genetically engineered. On the right we see a pest-free genetically engineered corn plant. They were planted side by side. Scientists have recently taken the gene that programs poison in scorpion tails and looked for ways to combine it with cabbage. Why would they want to create venomous cabbage? To limit pesticide use while still preventing caterpillars from damaging cabbage crops. These GM cabbages would produce scorpion poison that kills caterpillars when they bite leaves — but the toxin is modified so it is not harmful to humans. Genetically modified pigs are created that produce higher levels of growth hormone to produce a meatier pork chop. The Enviropig, or “Frankenswine,” as critics call it, is a pig that’s been genetically altered to better digest and process phosphorus. Pig manure is high in phytate, a form of phosphorus, so when farmers use the manure as fertilizer, the chemical enters the watershed and causes algae blooms that deplete oxygen in the water and kill marine life. Bt Corn produces a chemical that makes them pest resistant and results in a 5-10% increase yield. Public opposition due to fears of human health and environmental risks associated with the production and consumption of Bt corn. Golden Rice contains higher quantities of Vitamin A and Iron. Genetically modified tomatoes reach full flavor and color on vine without rotting. The Flavr Savr tomato was the first commercially grown genetically engineered food to be granted a license for human consumption. By adding an antisense gene, the California-based company Calgene hoped to slow the ripening process of the tomato to prevent softening and rotting, while allowing the tomato to retain its natural flavor and color. Cows produce significant amounts of methane as a result of a bacterium in their intestines. Methane is a major contributor to the greenhouse effect, so scientists have been working to genetically engineer a cow that produces less methane. Scientists at the University of Alberta have identified the bacterium responsible for producing methane and designed a line of cattle that creates 25 percent less methane than the average cow. Scientists in the agriculture department of a Hebrew University have genetically engineered a chicken that has no feathers. 6. Describe • Adding or deleting gene segments of genes to therapy. correct or get rid of genetic disorders. 7. Identify • Cystic fibrosis one disease • Sickle cell anemia that can be • Muscular dystrophy treated https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bLI1Gfb0ynw using gene https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SwmK5ARnFLE therapy. Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys and intestine. It causes mucus to become thick and sticky, which can block the normal function of these organs. Sickle cell anemia is an inherited disease in which hemoglobin is abnormal. These cells can block small blood vessels and flow of blood. This reduces the oxygen supply to tissues, may damage many organs and cause severe pain. These pain attacks can occur without warning, and a person often needs to go to the hospital for effective treatment. While normal red blood cells live for about 120 days, the abnormal sickle cells die after only 10 to 20 days, resulting in chronic anemia. Other complications include organ damage, lung and breathing difficulties, chronic leg ulcers and an increased susceptibility to infections, stroke is also common in little children. Topic: Applied Genetics Aim: Describe some methods that can be used to develop organisms with desirable traits. Do Now: Take out your genetic engineering reading notes and the Pedigree Charts. HW: Castle Learning Genetics – Due Tuesday, May 10th 1. Identify the # of people in generation 1 that have dimples. 2 2. Identify the # of people generation 2 that have dimples. 2 3. Identify the # of offspring from individuals 1 and 2 in generation 1. Which offspring have dimples? 3, 1 4. Identify the # of offspring from individuals 3 and 4 in the generation 1. Which offspring have dimples? 2, 1 The diagram represents a technique used to produce insulin. 1. Identify structure A. Human insulin gene 2. Identify structure B. Bacterial DNA 3. Where is structure B inserted? Into the bacterial cell 4. What will the bacterial produce? Insulin 5. How will the bacteria reproduce? Binary fission Mitosis Asexual reproduction 6. Identify the name of this process. Genetic engineering 7. Identify another substance that can be produced using this technique. Growth hormone Chemicals to treat cancer 8. Describe • When a new organism is the process made that has the same of cloning. exact genes as the organism from which it was produced. • GENETICALLY IDENTICAL • A somatic cell of the organism 9. Identify you want to replicate the two cells used to • An empty egg cell (enucleated ) produce Dolly. 10. What was • Nuclear transplant done to the – The nucleus from the two cells to somatic cell is placed into produce the empty egg cell Dolly? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hepoJgGJtNc 11. Where was • Inside the uterus of a the new cell surrogate mother. placed? The adult sheep is Dolly, the first mammal cloned from an adult cell. The lamb is Dolly’s offspring, called Bonnie. Idaho Gem = 1st cloned mule (MAY 2003) Cloned from a champion racing mule CopyCat = 1st cloned cat (2002) 12. Describe • To bring back extinct what cloning species using the DNA can be used found in fossils for. • Save endangered species • Clone a dead pet https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e1VL4XiC9nM https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7tbxN5uwaqA Misconception #1: Instant Clones! A common misconception is that a clone, if created, would magically appear at the same age as the original. This simply isn't true. You remember that cloning is an alternative way to create an embryo, not a full-grown individual. Therefore, that embryo, once created, must develop exactly the same way as would an embryo created by fertilizing an egg cell with a sperm cell. This will require a surrogate mother and ample time for the cloned embryo to grow and fully develop into an individual. Misconception #2: Carbon Copies! Your beloved cat Frank has been a loyal companion for years. But Frank is showing signs of old age, and you realize that your friend's days are numbered. You can't bear the thought of living without her, so you contact a biotechnology company that advertises pet cloning services. Where they will clone Frank using DNA from a sample of her somatic cells. You're thrilled: you'll soon have a carbon copy of Frank - we'll call her Frank #2 - and you'll never have to live without your pal! Right? Not exactly. Are you familiar with the phrase "nature versus nurture?" Basically, this means that while genetics can help determine traits, the environment has a big impact on shaping an individual's physical appearance and personality. For example, do you know any identical twins? They are genetically the same, but do they really look and act exactly alike? So, even though Frank #2 is genetically identical to the original Frank, she will grow and develop in a completely different environment than the original Frank or will have a different mother, and she will be exposed to different experiences throughout her development and life. Therefore, there is only a slim chance that Frank #2 will closely resemble the Frank you know and love. 13. Describe • When we select two the process organisms with desired of selective traits to serve as parents breeding. of the next generation. Horses can also be produced through selective breeding. This is an Appaloosa. This horse is bred for its distinctive coat pattern. Race horses are often selectively bred. 14. Identify • Hybridization the two forms of • Inbreeding selective breeding. 15. Identify • Hybridization the type of selective breeding that creates offspring that are very different from either parent genetically. 16. Identify the • Hybrids offspring of hybridization. Hybridization Braham cattle: good resistance to heat but poor beef Shorthorn cattle: good beef but poor heat resistance Santa Gertrudis cattle: formed by crossing Braham and shorthorn good heat resistance and beef Labradoodle Buggs (Boston Terrier / Pug mix) The Mule is the result of breeding a female horse (mare) to a male donkey (jack). The mule is superior to the horse in strength, endurance, intelligence and disease resistance. The Cama is the result of breeding a Llama to a Camel. Parents in background of picture. The Zebroid is the result of breeding a female Horse and a male Zebra. The Zedonk / Zonkey is the result of breeding a female Donkey and male Zebra. Hybridization Tigon = male tiger + female lion Hybridization Liger = male lion + female tiger The liger has both stripes and spots. The stripes are inherited from its tiger parent and the spots from the lion parent. On their hind legs, ligers stand approximately 12 feet tall. At most, ligers may weigh up to 1,000 pounds. • Inbreeding 17. Identify the type of selective breeding that creates offspring that will be very similar to both parents. • It increases the chance of 18. Describe recessive genetic disorders. the disadvantage of inbreeding. • Disadvantages = – Smaller and weaker offspring – More susceptible to diseases – More prone to genetic disorders The last white tiger ever seen in the wild was shot in 1958. As such, today’s white tigers are products of severe inbreeding, causing more genetic aberrations with every generation. A BBC documentary showed that some of Britain’s most popular dogs are plagued with health problems, ranging from cancer, epilepsy and heart disease, after decades of inbreeding. Let’s summarize: 1. Describe the process of genetic engineering. Humans change an organism’s DNA 2. What is recombinant DNA made up of? A combination of DNA from 2 different organisms 3. What substances can be made using recombinant DNA and bacteria? Insulin, GH, chemicals to treat cancer 4. Identify the technique of adding or deleting genes to help treat genetic disorders. Gene therapy 5. Describe cloning and the two cells used. Producing a genetically identical offspring. Somatic cell and an enucleated egg cell 6. Describe the process of selective breeding. Humans choose the organisms that will mate and produce offspring. 7. Identify the type of selective breeding in which two organisms with similar traits are crossed. Inbreeding 8. Identify the type of selective breeding in which two organisms with different traits are crossed. Hybridization Review: 1.Genetic engineering is presently used in the biotechnology industry to (1.) eliminate all infectious disease in livestock (2.) increase the frequency of fertilization (3.) synthesize insulin, interferon, and human growth hormone (4.) create populations that exhibit incomplete dominance Using special enzymes, scientists have successfully removed the gene that controls the production of clotting factors and have inserted this gene into the DNA of certain bacteria. These bacteria can now produce clotting factors. This technique is known as (1.) amniocentesis (2.) genetic engineering (3.) differentiation (4.) karyotyping Cloning an individual usually produces organisms that (1) contain dangerous mutations (2) contain identical genes (3) are identical in appearance and behavior (4) produce enzymes different from the parent Which process is most similar to the process of cloning? (1)Fertilization (2) Vegetative propagation (3) Meiosis (4) Gamete formation Which process could be used by breeders to develop tomatoes with a longer shelf life and to develop cows with increased milk production? (1) natural selection (2) genetic engineering (3) sporulation (4) chromatography 3. A man with blue eyes marries a woman who is heterozygous for brown eyes. If brown eyes are dominant, what are the chances of having a blue eyed child? Also, give the phenotypes and genotypes of all possible offspring. B = Brown bb X Bb b = blue bb X Bb b b B Bb Bb b bb b b Phenotype percentages: 50% blue 50% brown Genotype percentages: 50% heterozygous 50% homozygous recessive 4. In tomatoes, red fruit color is dominant to yellow fruit color. Predict the phenotypes and genotypes of the offspring by crossing a homozygous dominant parent with a homozygous recessive parent. Draw a Punnett Square to illustrate your prediction. R = red RR X rr r = yellow RR X rr R r Rr R Rr r Rr Rr Phenotype percentages: 100% red Genotype percentages: 100% heterozygous AA aa Aa 1. How many offspring of the 1st generation have the trait? 2. Describe individual U and W. 3. Identify the genotype of individual Y. 4. Identify the genotype X. Farmer Brown is a dairy farmer and is known for his very creamy milk. The milk produced by his cows has become so popular that he is not able to fill his orders anymore. This is because his cows don’t produce enough milk each day to meet the demand. He was looking for a cow that produced large amounts of creamy milk. His vet suggested that he could solve his problem by selective breeding. He needed to identify the Friesian cows that produce the most milk and those Jersey cows that produce the creamiest milk and breed only with them. By mating these selected few, Farmer Brown was able to produce offspring which had an enhanced version of this characteristic. Over several years he followed this program until he got the desired result, a cow that produced a large amount of creamy milk. Mr. Renaldo Jane’s mom Joe’s mom Joe’s dad George Emily Jane Smith Joe Smith Grace Clarissa Having dimples is a recessive trait. Although Jane and Joe Smith have dimples, their daughter, Clarissa, does not. Joe’s dad has dimples, but his mother, and his sister, Grace, do not. Jane’s dad, Mr. Renaldo, her brother George, and her sister, Emily, do not have dimples, but her mother does.