Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes
advertisement

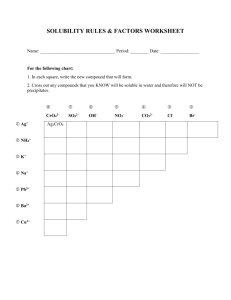
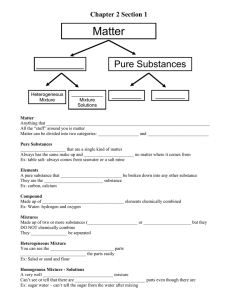
Topic: Chemistry Aim: Describe the properties and different types of mixtures. Do Now: 1. Take out Density ISA 2. CONTRAST elements and compounds. HW: Mass, Temperature and Density Exam Review Sheet 1. Identify the structure with the greatest density. Support your answer. Bolt because it sank all the way to the bottom. 2. Identify the structure with the smallest density. Support your answer. Ping pong ball because it is floating at the top. 3. Identify the liquid that is the least dense. Support your answer. Lamp oil because it is at the top. 4. Identify the liquid that has the greatest density. Support your answer. Honey because it is at the bottom. 5. Which is least dense: the milk or the rubbing alcohol? Support your answer. Rubbing alcohol because it is above milk. Which scenario represents a chemical change? Support your answer. Mixtures Mix of dissolved substances such as salt, fluoride, calcium carbonate, magnesium, iron, etc… Pure substance – made up of just water molecules • 2 or more substances PHYSICALLY MIXED together but NOT CHEMICALLY COMBINED • Ex: – Soil – cake batter – cereal with milk – Vinegar – Concrete For example powdered iron and powdered sulfur mixed together makes a mixture of iron and sulfur. They can be separated from each other without a chemical reaction, in the way that different colored sweets can be picked out from a mixed packet and put into separate piles. So… what is the main difference between a compound and a mixture? In a compound, substances are CHEMICALLY COMBINE. In a mixture, substances are NOT CHEMICALLY COMBINED. They are PHYSICALLY COMBINED! A B C Distinguish the element, mixture and compound. Support your answer. Milk is a combination of water, sugars, proteins, and fats making it a mixture. Sugar solution A sugar solution is a combination of sugar and water. Jello consists of gelatin and water. Vinegar is a combination of acetic acid and water. Solutions • Mixture that contains small and dissolved particles Parts of a solution • Solute: substance dissolved • Solvent: substance that does the dissolving Identify substances A and B. A B A soft drink is a solution that contains several dissolved substances in water. Solubility • How well a solute dissolves Soluble substance • Dissolves in another substance – Ex: Salt and sugar dissolve in water Sugar water solution Salt water solution Insoluble substance Sugarsubstance • CANNOT dissolve in another water solution Ex: oil Obviously NOT soluble in water!!!! A lava lamp depends on the globs not being soluble. It also depends on the globs being about the same density as water. It took years to develop the right ingredients to make a lava lamp work. Factors that affect solubility 1. Temperature: As temp of solvent increases, solubility of the solute increases 2. Particle size: the smaller the size, the greater the solubility powdered sugar sugar granules 3. Stirring: increases solubility Let’s summarize… 1. Explain what makes up a mixture. 2. Describe the difference between a compound and a mixture. 3. Explain what a solution consists of. 4. Identify the factors that affect solubility. Review: Which of the following is an example of a mixture of gases? 1. soft drink 2. air 3. oxygen 4. water In sweetened tea, the sugar is called the 1. solute. 2. solvent. 3. colloid. 4. solution. Which of the following would help sugar dissolve faster in water? 1. stirring the water 2. decreasing the solubility of sugar 3. using larger particles of sugar 4. decreasing the water temperature Which statement is true regarding insoluble substances? 1. They can be easily dissolved in a solvent. 2. An example of an insoluble substance is ice tea dissolving in water. 3. Insoluble substances cannot dissolve in a solvent. 4. They can easily dissolve in a solute. Chemical change Physical change Chemical change Chemical change Tarnishing of silver Chemical change Tarnish is silver sulfides that form from sulfur compounds in the air. Element or compound? 1. NaCl Compound 2. O Element 3. C6H12O6 Compound 4. CO2 Compound 5. O2 Molecule