Water & It’s Properties
advertisement

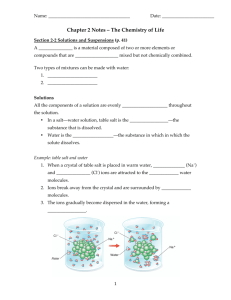
Water & It’s Properties The Molecule Water is a polar molecule because it has a “positive” and a “negative” side Oxygen is greedy and hogs the electrons, leaving the hydrogens to be a little positive Slightly Negative Slightly Positive Hydrogen Bonds The positive and negative ends of the molecule attract each other (up to 4 bonds – 2 to H’s 2 to O’s) Not as strong as ionic or covalent Causes cohesion Cohesion - attraction between molecules of the same substance Reason why water forms beads on flat surfaces Adhesion - attraction between molecules of different substances Reason why water forms a meniscus in a graduated cylinder Surface Tension: combined effect of adhesion and cohesion (ex. Insect floating on water) Hydrophilic – liking water; will dissolve in water Ex. Sugar, salt Hydrophobic – fearing water; won’t dissolve in water Ex. oil Mixtures Mixture – composed of 2 or more elements or compounds that are physically combined but NOT chemically combined. They can be separated Ex. Salt with pepper, sand with iron fillings 2 types of mixtures are solutions & suspensions 1. Solution – when particles are evenly distributed throughout the mixture Has 2 parts: Solute – substance that is being dissolved Solvent – substance doing the dissolving Ex: Kool-aid, Chocolate Milk, Tea, Salt water 2 types of mixtures are solutions & suspensions 2. Suspension – has water and undissolved materials Ex. Blood, Italian Dressing, Muddy water